|
Enterprise Performance Management
Enterprise performance management (EPM) is a field of business performance management which considers the visibility of operations in a closed-loop model across all facets of the enterprise. Specific to financial activities in the office of the chief financial officer, EPM also supports financial planning and analysis (FP&A). Corporate performance management (CPM) is a synonym for enterprise performance management. Gartner has officially retired the concept of CPM and reclassified into "financial planning and analysis (FP&A)" and "financial close" to reflect two significant trendsincreased focus on planning, and the emergence of a new category of solutions supporting the management of the financial close. There are several domains in the EPM field which are driven by corporate initiatives, academic research, and commercial approaches. These include: * Strategy formulation * Business planning and forecasting * Financial management * Supply chain effectiveness Based on the mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Performance Management
Business performance management (BPM), also known as corporate performance management (CPM) and enterprise performance management (EPM),) is a set of performance management and analytic processes that enables the management of an organization's performance to achieve one or more pre-selected goals. Gartner retired the concept of "CPM" and reclassified it as "financial planning and analysis (FP&A)," and "financial close" to reflect two concepts: increased focus on planning and the emergence of a new category of solutions supporting the management of the financial close. Business performance management is contained within approaches to business process management. History Before the Information Age in the late 20th century, businesses sometimes laboriously collected data from non-automated sources. As they lacked computing resources to analyze the data properly, they often made commercial decisions primarily by intuition (knowledge), intuition. As businesses started automating th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Financial Officer
The chief financial officer (CFO) is an officer of a company or organization that is assigned the primary responsibility for managing the company's finances, including financial planning, management of financial risks, record-keeping, and financial reporting. In some sectors, the CFO is also responsible for analysis of data. Some CFOs have the title CFOO for chief financial and operating officer. In the majority of countries, finance directors (FD) typically report into the CFO and FD is the level before reaching CFO. The CFO typically reports to the chief executive officer (CEO) and the board of directors and may additionally have a seat on the board. The CFO supervises the finance unit and is the chief financial spokesperson for the organization. The CFO directly assists the chief operating officer (COO) on all business matters relating to budget management, cost–benefit analysis, forecasting needs, and securing of new funding. Qualification Most CFOs of large companies hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Scorecard
A balanced scorecard is a strategy performance management tool – a well structured report, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the consequences arising from these actions. The phrase 'balanced scorecard' primarily refers to a performance management report used by a management team, and typically this team is focused on managing the implementation of a strategy or operational activities – in a 2020 survey 88% of respondents reported using Balanced Scorecard for strategy implementation management, 63% for operational management. Balanced Scorecard is also used by individuals to track personal performance, but this is uncommon – only 17% of respondents in the survey using Balanced Scorecard in this way, however it is clear from the same survey that a larger proportion (about 30%) use corporate Balanced Scorecard elements to inform personal goal setting and incentive calculations. The critic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
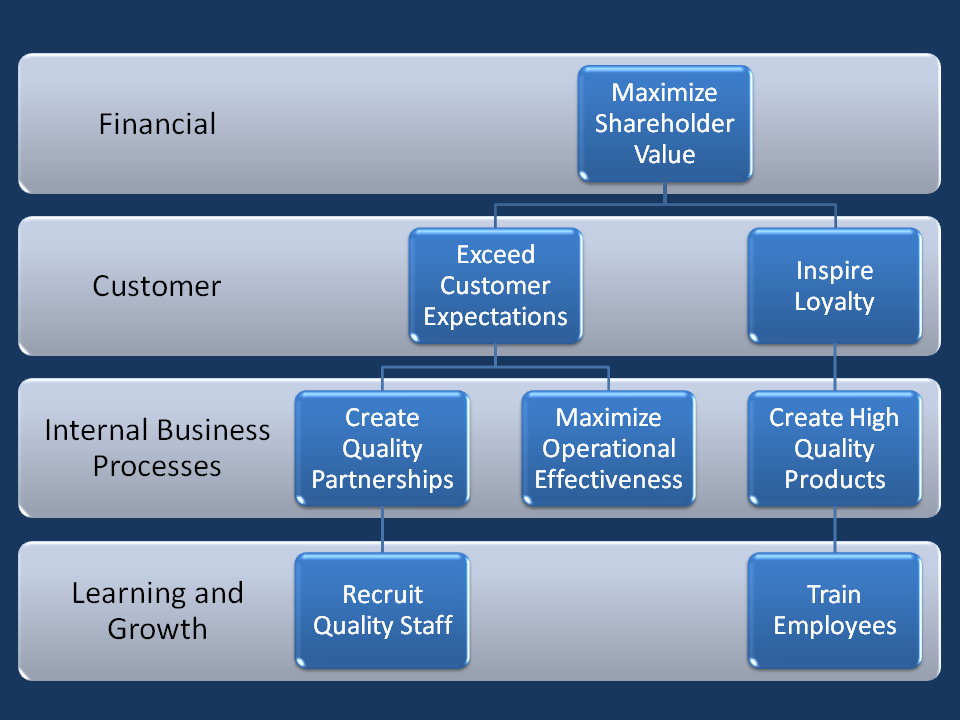
Strategy Map
A strategy map is a diagram that documents the strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team. It is an element of the documentation associated with the Balanced Scorecard, and in particular is characteristic of the second generation of Balanced Scorecard designs that first appeared during the mid-1990s. The first diagrams of this type appeared in the early 1990s, and the idea of using this type of diagram to help document Balanced Scorecard was discussed in a paper by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1996. The strategy map idea featured in several books and articles during the late 1990s by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton. Their original book in 1996, "The Balanced Scorecard, Translating strategy into action", contained diagrams which are later called strategy maps, but at this time they did not refer to them as such. Kaplan & Norton's second book, The Strategy Focused Organization, explicitly refers to strategy maps and includes a chapter on how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategy Gap
A strategy gap refers to the gap between the current performance of an organisation and its desired performance as expressed in its mission, Goal, objectives, goals and the strategy for achieving them. Mckeown argues that a strategic gap may be transformed into a strategic stretch. Often unseen, the strategy gap is a threat to the future performance—and even survival—of an organisation and is guaranteed to impact upon the efficiency and effectiveness of senior executives and their management teams. The strategy gap is considered to be real and exists within most organisations. An article in ''Fortune magazine, Fortune'' magazine (June 1999 edition) stated that some 70% of CEOs' failures were the result of poor execution rather than poor strategies. There are various schools of thought on what causes the gap between vision and execution, and how the strategy gap might be avoided. In 2005, Paul R. Niven, a thought leader in performance management systems, pinpointed four sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Performance Indicators
A performance indicator or key performance indicator (KPI) is a type of performance measurement. KPIs evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity (such as projects, programs, products and other initiatives) in which it engages. KPIs provide a focus for strategic and operational improvement, create an analytical basis for decision making and help focus attention on what matters most. Often success is simply the repeated, periodic achievement of some levels of operational goal (e.g. zero defects, 10/10 customer satisfaction), and sometimes success is defined in terms of making progress toward strategic goals. Accordingly, choosing the right KPIs relies upon a good understanding of what is important to the organization. What is deemed important often depends on the department measuring the performance – e.g. the KPIs useful to finance will differ from the KPIs assigned to sales. Since there is a need to understand well what is important, various techniques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Information Systems
An executive information system (EIS), also known as an executive support system (ESS), is a type of Management information system , management support system that facilitates and supports senior executive information and decision-making needs. It provides easy information access, access to internal and external information relevant to organizational goals. It is commonly considered a specialized form of decision support system (DSS).Power, D. J., Decision Support Systems: Concepts and Resources for Managers, Greenwood/Quorum, 2002. EIS emphasizes graphical displays and easy-to-use user interfaces. They offer strong reporting and drill-down capabilities. In general, EIS are enterprise-wide DSS that help top-level executives analyze, compare, and highlight trends in important variable (math), variables so that they can monitor performance and identify opportunities and problems. EIS and data warehousing technologies are converging in the marketplace. The term EIS lost popularity in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |