|
Entecavir
Entecavir (ETV), sold under the brand name Baraclude, is an antiviral medication used in the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. In those with both HIV/AIDS and HBV antiretroviral medication should also be used. Entecavir is taken by mouth as a tablet or solution. Common side effects include headache, nausea, high blood sugar, and decreased kidney function. Severe side effects include enlargement of the liver, high blood lactate levels, and liver inflammation if the medication is stopped. While there appears to be no harm from use during pregnancy, this use has not been well studied. Entecavir is in the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) family of medications. It prevents the hepatitis B virus from multiplying by blocking reverse transcriptase. Entecavir was approved for medical use in 2005. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Available as a generic medication in the United States. Medical uses Entecavir is mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is '' acute'' if it resolves within six months, and '' chronic'' if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer. Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus ''hepatovirus A'', '' B'', '' C'', '' D'', and '' E''. Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever virus. Other common causes of hepatitis include heavy alcohol use, certain medications, toxins, other infections, autoimmune diseases, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocyclic Nucleoside
Carbocyclic nucleosides (also referred to as carbanucleosides) are nucleoside analogues in which a methylene group has replaced the oxygen atom of the furanose ring. These analogues have the nucleobase attached at a simple alkyl carbon rather than being part of a hemiaminal ether linkage. As a result, they have increased chemical stability. They also have increased metabolic stability because they are unaffected by phosphorylases and hydrolases that cleave the glycosidic bond between the nucleobase and furanose ring of nucleosides. They retain many of the biological properties of the original nucleosides with respect to recognition by various enzymes and receptors. Carbocyclic nucleosides were originally limited to a five-membered ring system, matching the ring-size of the nucleosides; however, this term has been broadened to three-, four-, and six-membered rings. Natural products The 5-membered ring carbocyclic nucleosides aristeromycin, the analog of adenosine, and neplano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses. Mechanism of action When HIV infects a cell, reverse transcriptase copies the viral single stranded RNA genome into a double-stranded viral DNA. The viral DNA is then integrated into the host chromosomal DNA, which then allows host cellular processes, such as transcription and translation, to reproduce the virus. RTIs block reverse transcriptase's enzymatic function and prevent completion of synthesis of the double-stranded viral DNA, thus preventing HIV from multiplying. A similar process occurs with other types of viruses. The hepatitis B virus, for example, carries its genetic material in the form of DNA, and employs an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase to replicate. Some of the same compounds used as RTIs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
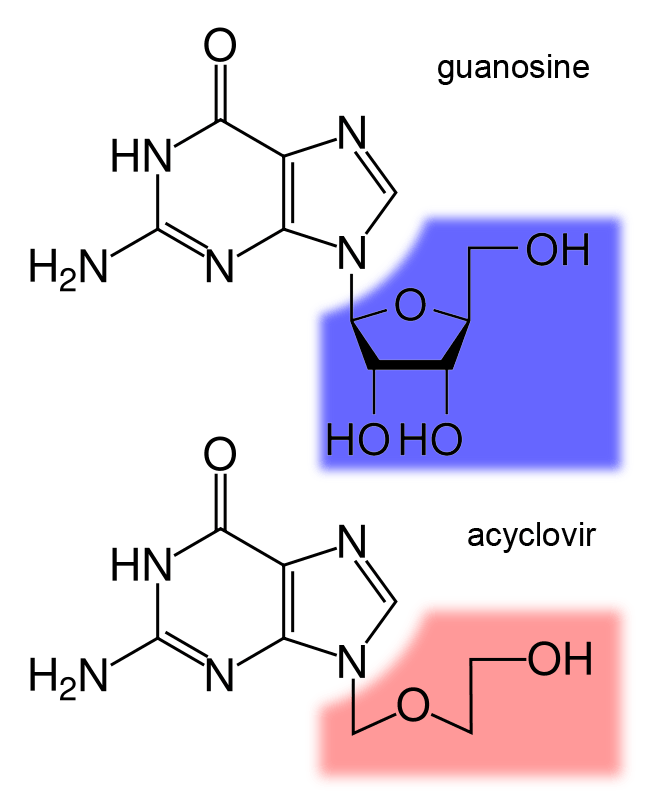
Nucleoside Analog
Nucleoside analogues are nucleosides which contain a nucleic acid analogue and a sugar. Nucleotide analogs are nucleotides which contain a nucleic acid analogue, a sugar, and a phosphate group with one to three phosphates. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues can be used in therapeutic drugs, including a range of antiviral products used to prevent viral replication in infected cells. The most commonly used is acyclovir, although its inclusion in this category is uncertain, because it acts as a nucleoside but contains no actual sugar, as the sugar ring is replaced by an open-chain structure. Nucleotide and nucleoside analogues can also be found naturally. Examples include ddhCTP (3ʹ-deoxy-3′,4ʹdidehydro-CTP) produced by the human antiviral protein viperin and sinefungin (a S-Adenosyl methionine analogue) produced by some ''Streptomyces''. Function These agents can be used against hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, herpes simplex, and HIV. Once they are phosphoryl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
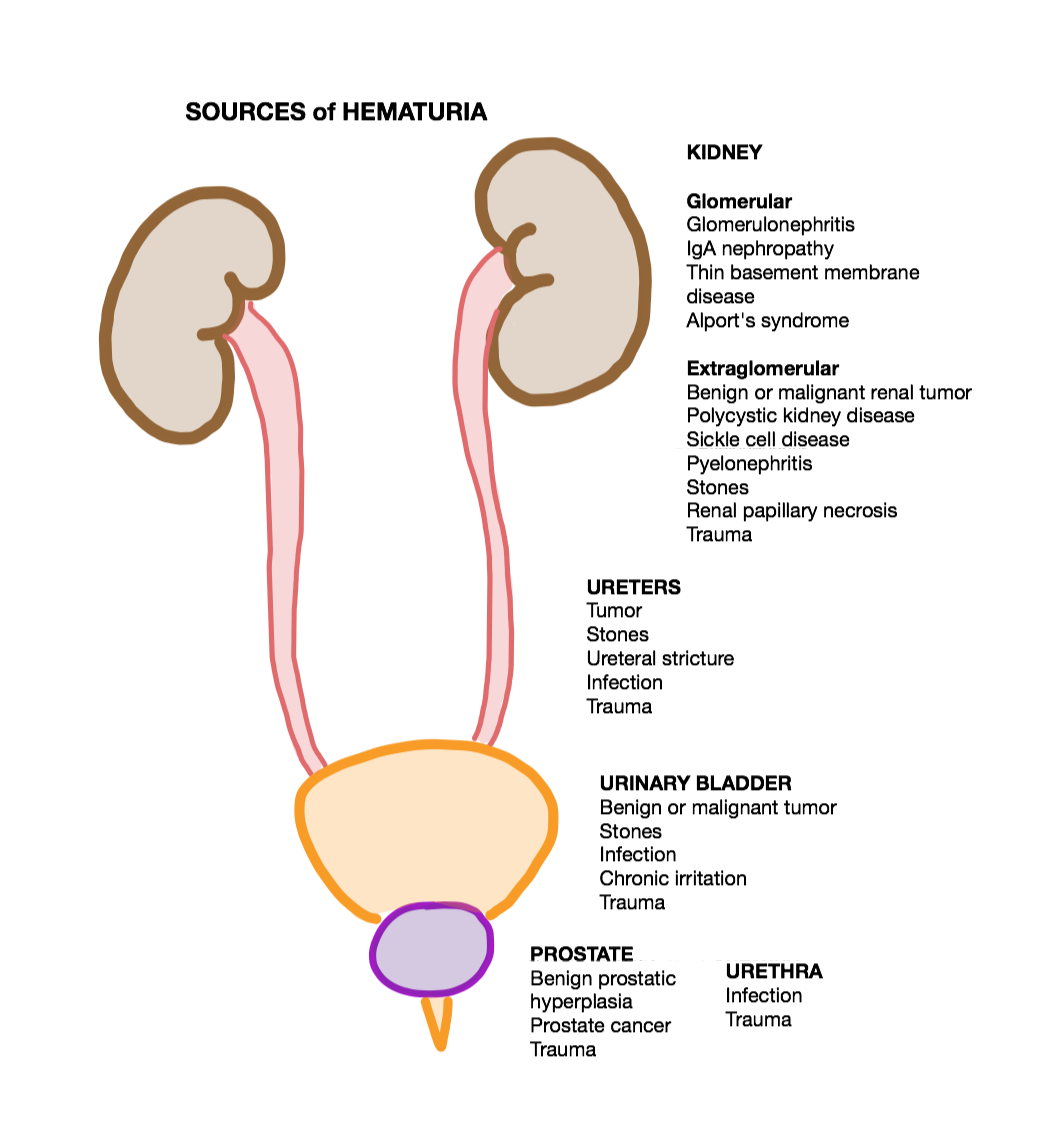
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamivudine
Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible. It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2. It is typically used in combination with other antiretrovirals such as zidovudine and abacavir. Lamivudine may be included as part of post-exposure prevention in those who have been potentially exposed to HIV. Lamivudine is taken by mouth as a liquid or tablet. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headaches, feeling tired, and cough. Serious side effects include liver disease, lactic acidosis, and worsening hepatitis B among those already infected. It is safe for people over three months of age and can be used during pregnancy. The medication can be taken with or without food. Lamivudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor and works by blocking the HIV reverse transcriptase and hepatitis B virus polymerase. Lamivudine was pate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm. Viral production / replication Viruses multiply only in living cells. The host cell must provide the energy and synthetic machinery and the low- molecular-weight precursors for the synthesis of viral proteins and nucleic acids. The virus replication occurs in seven stages, namely; # Attachment # Entry, # Uncoating, # Transcription / mRNA production, # Synthesis of virus components, # Virion assembly and # Release (Liberation Stage). Attachment It is the first step of viral replicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcription
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogue (chemical)
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |