|
Endophenotype
In genetic epidemiology, endophenotype (or intermediate phenotype) is a term used to separate behavioral symptoms into more stable phenotypes with a clear genetic connection. The concept was coined by Bernard John and Kenneth R. Lewis in a 1966 paper attempting to explain the geographic distribution of grasshoppers. They claimed that the particular geographic distribution could not be explained by the obvious and external "exophenotype" of the grasshoppers, but instead must be explained by their microscopic and internal "endophenotype". The next major use of the term was in psychiatric genetics, to bridge the gap between high-level symptom presentation and low-level genetic variability, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms. It is therefore more applicable to more heritable disorders, such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Since then, the concept has expanded to many other fields, such as the study of ADHD, addiction, Alzheimer's disease, obesity and cystic fibrosis. Some ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatric Genetics
Psychiatric genetics is a subfield of behavioral neurogenetics and behavioral genetics which studies the role of genetics in the development of mental disorders (such as alcoholism, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and autism). The basic principle behind psychiatric genetics is that genetic polymorphisms (as indicated by linkage to e.g. a single nucleotide polymorphism) are part of the causation of psychiatric disorders. Psychiatric genetics is a somewhat new name for the old question, "Are behavioral and psychological conditions and deviations inherited?". The goal of psychiatric genetics is to better understand the causes of psychiatric disorders, to use that knowledge to improve treatment methods, and possibly also to develop personalized treatments based on genetic profiles (see pharmacogenomics). In other words, the goal is to transform parts of psychiatry into a neuroscience-based discipline. Recent advances in molecular biology allowed for the identification of hundreds o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates synaptic plasticity by enhancing the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. It also stimulates dendrite and dendritic spine development and regulates the continuing migration of neuroblasts generated in adult neurogenesis sites like the subventricular and subgranular zones. It is found not only in the brain but also in the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, Fallopian tube, breast and in comparatively lower levels across a range of anatomical regions. Reelin has been suggested to be implicated in pathogenesis of several brain diseases. The expression of the protein has been found to be significantly lower in schizophrenia and psychoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FABP7
Fatty acid binding protein 7, brain (FABP7; also brain lipid binding protein, BLBP), is a human gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a brain fatty acid binding protein. Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. FABPs are thought to play roles in fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. FABP7 is expressed, during development, in radial glia by the activation of Notch receptors. Reelin was shown to induce FABP7 expression in neural progenitor cells via Notch-1 activation. According to one study, FABP7 binds DHA with the highest affinity among all of the FABPs. Role in pathology FABP7 maps onto human chromosome 6q22.31, a schizophrenia linkage region corroborated by a meta-analysis. As of 2008, two studies have been conducted into FABP7 as a possible risk gene for schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction, and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society. Although people with ADHD struggle to focus on tasks they are not particularly interested in completing, they are often able to maintain an unusually prolonged and intense level of attention for tasks they do find interesting or rewarding; this is known as hyperfocus. The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases. Genetic factors play an imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use often alters brain function in ways that perpetuate craving, and weakens (but does not completely negate) self-control. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological (and thus involuntary) factors that are implicated in addiction's development. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use despite negative consequences. Habits and patterns associated with addiction are typically characterized by immediate gratification (short-term reward), coupled with delayed deleterious effects (long-term costs). Exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probands
In medical genetics and other medical fields, a proband, proposito (male proband), or proposita (female proband)Bennett, RL. The Language of the Pedigree. In: ''The Practical Guide to the Genetic Family History''. Wiley-Liss. is a particular subject (human or other animal) being studied or reported on. On pedigrees, the proband is noted with a square (male) or circle (female) shaded accordingly. Denoting the proband is important, so the relationship to other individuals can be seen and patterns established. In most cases, the proband is the first affected family member who seeks medical attention for a genetic disorder. Among the ancestors of the proband, other subjects may manifest the disease, but the proband typically refers to the member seeking medical attention or being studied, even if affected ancestors are known. Often, affected ancestors are unknown due to the lack of information regarding those individuals or about the disease at the time they lived. Other ancestors mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHRNA7
Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7, also known as nAChRα7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CHRNA7'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR). Function The nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are members of a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast signal transmission at synapses. The nAChRs are thought to be hetero-pentamers composed of homologous subunits. The proposed structure for each subunit is a conserved N-terminal extracellular domain followed by three conserved transmembrane domains, a variable cytoplasmic loop, a fourth conserved transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal extracellular region. The protein encoded by this gene forms a homo-oligomeric channel, displays marked permeability to calcium ions and is a major component of brain nicotinic receptors that are blocked by, and highly sensitive to, alpha-bungarotoxin. Once this receptor binds acety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
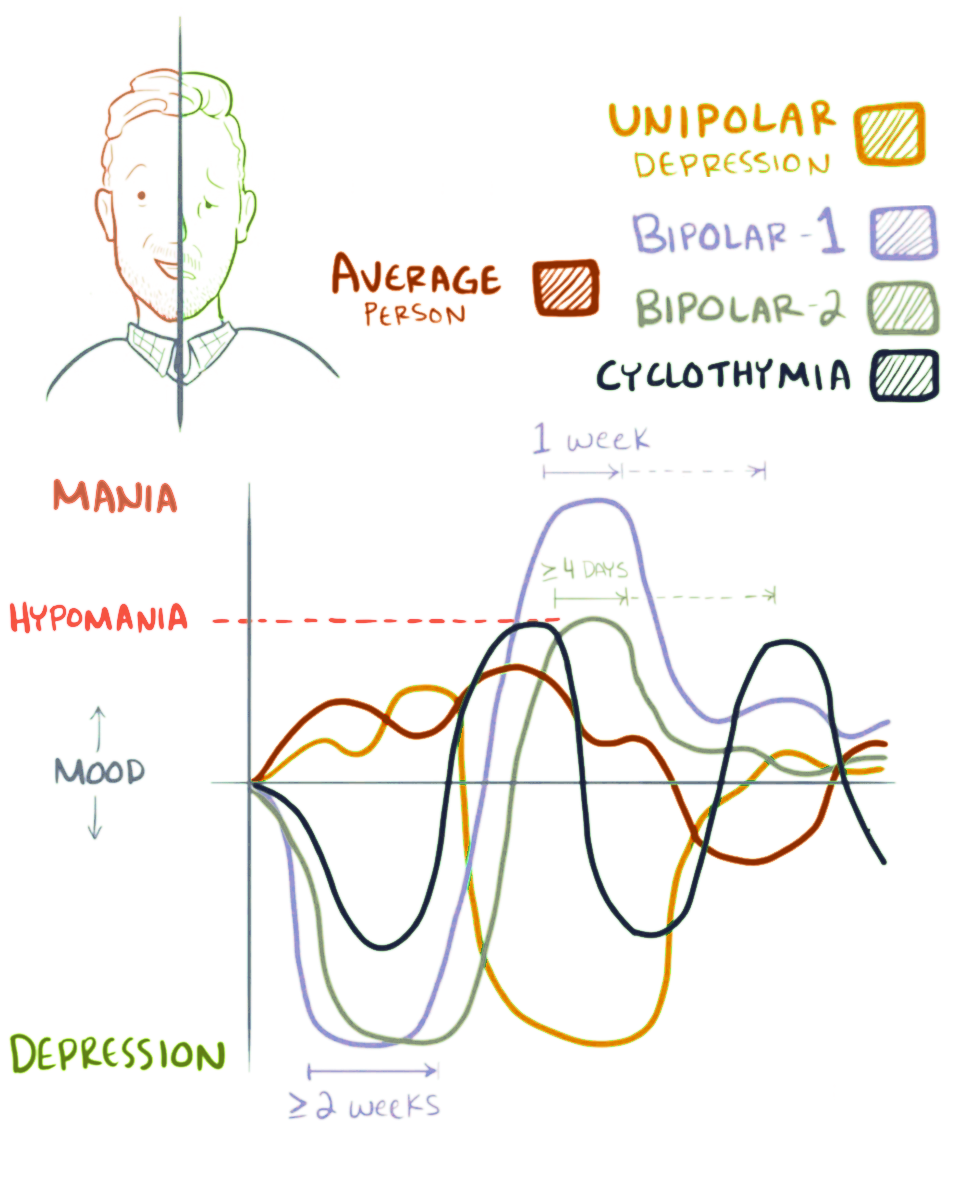
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Perception
Facial perception is an individual's understanding and interpretation of the face. Here, perception implies the presence of consciousness and hence excludes automated facial recognition systems. Although facial recognition is found in other species, this article focuses on facial perception in humans. The perception of facial features is an important part of social cognition. Information gathered from the face helps people understand each other's identity, what they are thinking and feeling, anticipate their actions, recognize their emotions, build connections, and communicate through body language. Developing facial recognition is a necessary building block for complex societal constructs. Being able to perceive identity, mood, age, sex, and race lets people mold the way we interact with one another, and understand our immediate surroundings. Though facial perception is mainly considered to stem from visual intake, studies have shown that even people born blind can learn fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Epidemiology
Genetic epidemiology is the study of the role of genetic factors in determining health and disease in families and in populations, and the interplay of such genetic factors with environmental factors. Genetic epidemiology seeks to derive a statistical and quantitative analysis of how genetics work in large groups. Definition The use of the term ''Genetic epidemiology'' emerged in the mid-1980s as a new scientific field. In formal language, genetic epidemiology was defined by Newton Morton, one of the pioneers of the field, as "a science which deals with the etiology, distribution, and control of disease in groups of relatives and with inherited causes of disease in populations". It is closely allied to both molecular epidemiology and statistical genetics, but these overlapping fields each have distinct emphases, societies and journals. One definition of the field closely follows that of behavior genetics, defining genetic epidemiology as "the scientific discipline that deal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
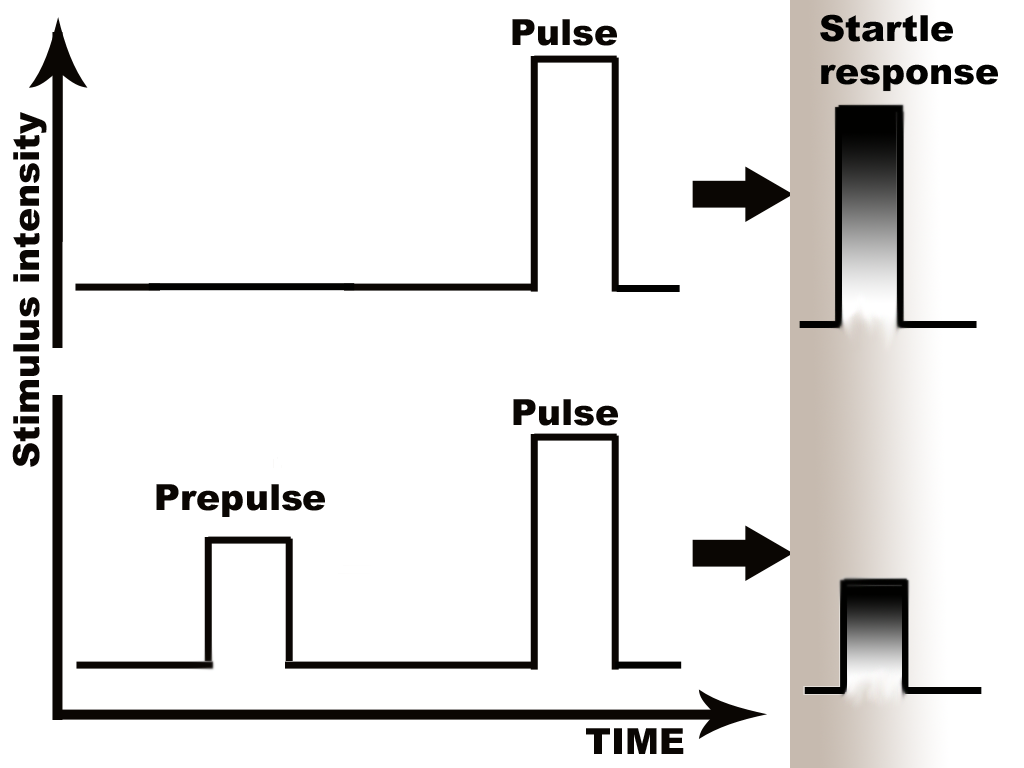
Prepulse Inhibition
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) is a neurological phenomenon in which a weaker prestimulus (prepulse) inhibits the reaction of an organism to a subsequent strong reflex-eliciting stimulus (pulse), often using the startle reflex. The stimuli are usually acoustic, but tactile stimuli (e.g. via air puffs onto the skin) and light stimuli are also used. When prepulse inhibition is high, the corresponding one-time startle response is reduced. The reduction of the amplitude of startle reflects the ability of the nervous system to temporarily adapt to a strong sensory stimulus when a preceding weaker signal is given to warn the organism. PPI is detected in numerous species including mice and humans. Although the extent of the adaptation affects numerous systems, the most comfortable to measure are the muscular reactions, which are normally diminished as a result of the nervous inhibition. Deficits of prepulse inhibition manifest in the inability to filter out the unnecessary information; they h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow ( hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |