|
Endellionite
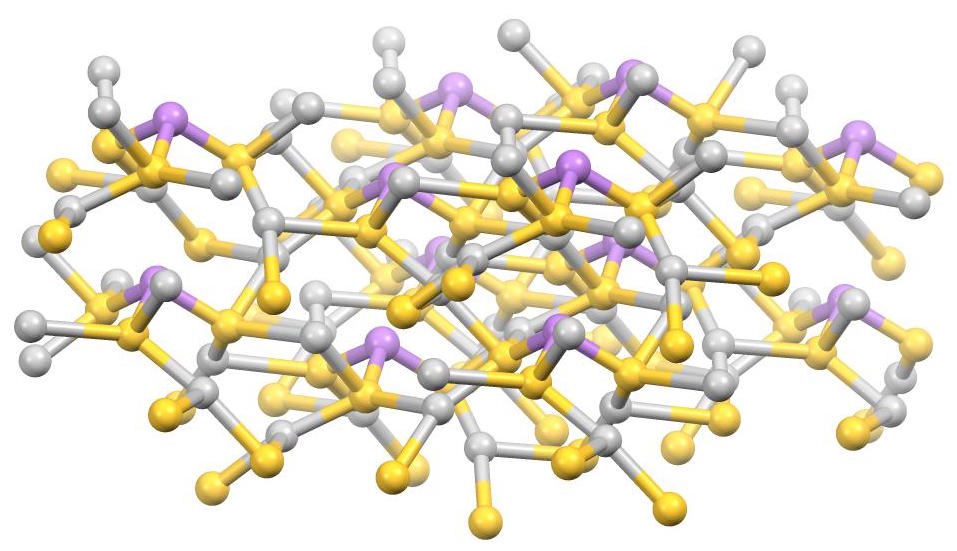
Bournonite is a sulfosalt mineral species, trithioantimoniate of lead and copper with the formula PbCuSbS3. It was first mentioned by Philip Rashleigh in 1797 as an ore of antimony and was more completely described in 1804 by French crystallographer and mineralogist Jacques Louis, Comte de Bournon (1751–1825), after whom it was named. The name given by Bournon himself (in 1813) was endellione, since used in the form endellionite, after St Endellion, the locality in Cornwall where the mineral was first found. The crystals are orthorhombic, and are generally tabular in habit owing to the predominance of the basal pinacoid; numerous smooth bright faces are often developed on the edges and corners of the crystals. They are usually twinned, the twin-plane being a face of the prism (m); the angle between the faces of this prism being nearly a right angle (86° 20′), the twinning gives rise to cruciform groups and when it is often repeated the group has the appearance of a cog-w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfosalt Mineral
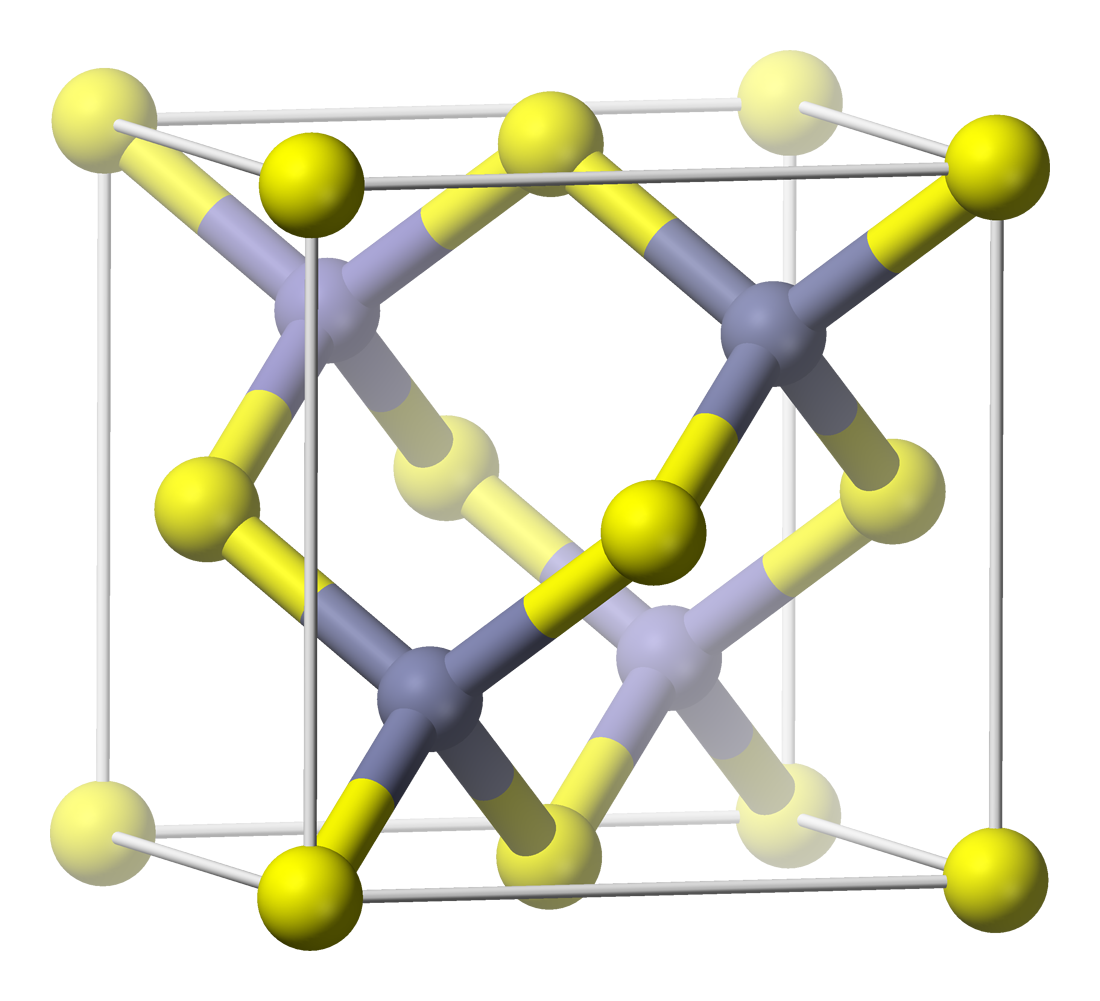
Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula , where *A represents a metal such as copper, lead, silver, iron, and rarely mercury (element), mercury, zinc, vanadium *B usually represents semi-metal such as arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and rarely germanium, or metals like tin and rarely vanadium *X is sulfur or rarely selenium and/or tellurium. The Strunz classification includes the sulfosalts in a ''sulfides and sulfosalts'' superclass. A group which have similar appearing formulas are the Sulfarsenide mineral, sulfarsenides (for example cobaltite (Co,Fe)AsS). In sulfarsenides the arsenic substitutes for sulfide anions whereas in the sulfosalts the arsenic substitutes for a metal cation.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut (1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York . About 200 sulfosalt minerals are known. Examples include: File:Proustite (long prismatic crystal) - Chanarcillo, Copiapo Province, Atacama Region, Chile.jpg, As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavnic
Cavnic ( hu, Kapnikbánya; german: Kapnik) is a former mining town located in the valley of the river Cavnic, east of Baia Mare, in Maramureș County, northern Romania. The town covers , at altitudes ranging from 500 to 1050 meters above sea level. History Cavnic was first documented in 1336, as ''Capnic''. It was named after the river, which got its name from a Slavic word, ''kopanе,'' which refers to digging. Mining activity in the area dates back to the Roman age. The town was destroyed by the Ottomans in 1460 and by the Tatars in 1717, but the Tatars invasion ended with their defeat from the people of Cavnic, making from it the last Tatar invasion to ever take place in the current territory of Romania. As a proof of the last Tatar invasion, the town hosts a 7.2 m tall obelisk on which a Latin inscription states "Anno 1717 usque hic fuerunt tartari" meaning "During the year 1717 the Tatars have arrived here". The obelisk is known among locals as "Tatar Pole" or "W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the mountains now known as the Dolomite Alps of northern Italy. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ions. Unless it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodochrosite
Rhodochrosite is a manganese carbonate mineral with chemical composition MnCO3. In its (rare) pure form, it is typically a rose-red color, but impure specimens can be shades of pink to pale brown. It streaks white, and its Mohs hardness varies between 3.5 and 4. Its specific gravity is between 3.5 and 3.7. It crystallizes in the trigonal system, and cleaves with rhombohedral carbonate cleavage in three directions. Crystal twinning often is present. It is transparent to translucent with refractive indices of ''nω''=1.814 to 1.816, ''nε''=1.596 to 1.598. It is often confused with the manganese silicate, rhodonite, but is distinctly softer. It is officially listed as one of the National symbols of Argentina. Rhodochrosite forms a complete solid solution series with iron carbonate (siderite). Calcium, (as well as magnesium and zinc, to a limited extent) frequently substitutes for manganese in the structure, leading to lighter shades of red and pink, depending on the degree of substit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). It takes its name from the Greek word σίδηρος ''sideros,'' "iron". It is a valuable iron mineral, since it is 48% iron and contains no sulfur or phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium and manganese commonly substitute for the iron resulting in the siderite-smithsonite, siderite- magnesite and siderite-rhodochrosite solid solution series. Siderite has Mohs hardness of 3.75-4.25, a specific gravity of 3.96, a white streak and a vitreous lustre or pearly luster. Siderite is antiferromagnetic below its Néel temperature of 37 K which can assist in its identification. It crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system, and are rhombohedral in shape, typically with curved and striated faces. It also occurs in masses. Color ranges from yellow to dark brown or black, the latter being due to the presence of manganese. Siderite is commonly found in hydrothermal veins, and is associated with barite, fluorite, galena, and others. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinkenite
Zinkenite is a steel-gray metallic sulfosalt mineral composed of lead antimony sulfide Pb9 Sb22 S42. Zinkenite occurs as acicular needle-like crystals. It was first described in 1826 for an occurrence in the Harz Mountains, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany and named after its discoverer, German mineralogist and mining geologist, Johann Karl Ludwig Zinken Johann, typically a male given name, is the German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin form of the Greek name ''Iōánnēs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew name '' Yochanan'' () in turn from its extended form (), meaning "Yahweh is Gracious ... (1790–1862).http://www.mindat.org/min-4417.html Mindat References Lead minerals Antimony minerals Sulfosalt minerals Hexagonal minerals Minerals in space group 173 {{sulfide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stibnite
Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2 S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the Greek στίβι ''stibi'' through the Latin ''stibium'' as the former name for the mineral and the element antimony. Structure Stibnite has a structure similar to that of arsenic trisulfide, As2S3. The Sb(III) centers, which are pyramidal and three-coordinate, are linked via bent two-coordinate sulfide ions. However, some studies suggest that the actual coordination polyhedra of antimony are SbS7, with (3+4) coordination at the M1 site and (5+2) at the M2 site. Some of the secondary bonds impart cohesion and are connected with packing. Stibnite is grey when fresh, but can turn superficially black due to oxidation in air. Properties The melting point of Sb2S3 is . The band gap is 1.88 eV at room temperature and it is a photoco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcopyrite
Chalcopyrite ( ) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black. On exposure to air, chalcopyrite tarnishes to a variety of oxides, hydroxides, and sulfates. Associated copper minerals include the sulfides bornite (Cu5FeS4), chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu9S5); carbonates such as malachite and azurite, and rarely oxides such as cuprite (Cu2O). Is rarely found in association with native copper. Chalcopyrite is a conductor of electricity. Etymology The name chalcopyrite comes from the Greek words , which means copper, and ', which means striking fire. It was sometimes historically referred to as "yellow copper". Identification Chalcopyrite is often confused with pyrite and gold since all three of these minerals have a yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedrite
Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: . It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, the antimony rich phase is more common. Other elements also substitute in the structure, most notably iron and zinc, along with less common silver, mercury and lead. Bismuth also substitutes for the antimony site and ''bismuthian tetrahedrite'' or ''annivite'' is a recognized variety. The related, silver dominant, mineral species freibergite, although rare, is notable in that it can contain up to 18% silver. Mineralogy Tetrahedrite gets its name from the distinctive tetrahedron shaped cubic crystals. The mineral usually occurs in massive form, it is a steel gray to black metallic mineral with Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and specific gravity of 4.6 to 5.2. Tetrahedrite occurs in low to moderate temperature hydrothermal veins and in some co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |