|
Emissions Target
A climate target, climate goal or climate pledge is a measurable commitment for climate policy and energy policy with the aim of limiting the climate change. Researchers within, among others, the UN climate panel have identified probable consequences of global warming for people and nature at different levels of warming. Based on this, politicians in a large number of countries have agreed on temperature targets for warming, which is the basis for scientifically calculated carbon budgets and ways to achieve these targets. This in turn forms the basis for politically decided global and national emission targets for greenhouse gases, targets for fossil-free energy production and efficient energy use, and for the extent of planned measures for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Many climate targets are implemented in national climate legislation. Calculation of Emissions Targets An emissions target or ''greenhouse gas emissions reduction target'' is a central policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries By Intended Year Of Climate Neutrality
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the country of Wales is a component of a multi-part sovereign state, the United Kingdom. A country may be a List of former sovereign states, historically sovereign area (such as Korea), a currently sovereign territory with a unified government (such as Senegal), or a non-sovereign geographic region associated with certain distinct political, ethnic, or cultural characteristics (such as the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country). The definition and usage of the word "country" is flexible and has changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Legislation
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caused by emissions from fossil fuels burning (coal, oil, and natural gas). Mitigation can reduce emissions by transitioning to sustainable energy sources, conserving energy, and increasing efficiency. In addition, can be removed from the atmosphere by enlarging forests, restoring wetlands and using other natural and technical processes, which are grouped together under the term of carbon sequestration. Solar energy and wind power have the highest climate change mitigation potential at lowest cost compared to a range of other options. Variable availability of sunshine and wind is addressed by energy storage and improved electrical grids, including long-distance electricity transmission, demand management and diversification of renewables. As low-carbon power is more widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Climate Change Conference
The United Nations Climate Change Conferences are yearly conferences held in the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). They serve as the formal meeting of the UNFCCC parties (Conference of the Parties, COP) to assess progress in dealing with climate change, and beginning in the mid-1990s, to negotiate the Kyoto Protocol to establish legally binding obligations for developed countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Starting in 2005 the conferences have also served as the "Conference of the Parties Serving as the Meeting of Parties to the Kyoto Protocol" (CMP); also parties to the convention that are not parties to the protocol can participate in protocol-related meetings as observers. From 2011 to 2015 the meetings were used to negotiate the Paris Agreement as part of the Durban platform, which created a general path towards climate action. Any final text of a COP must be agreed by consensus. The first UN Climate Change Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organisations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC informs governments about the state of knowledge of climate change. It does this by examining all the relevant scientific literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioenergy With Carbon Capture And Storage
Bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) is the process of extracting bioenergy from biomass and capturing and storing the carbon, thereby removing it from the atmosphere. The carbon in the biomass comes from the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) which is extracted from the atmosphere by the biomass when it grows. Energy is extracted in useful forms (electricity, heat, biofuels, etc.) as the biomass is utilized through combustion, fermentation, pyrolysis or other conversion methods. Some of the carbon in the biomass is converted to CO2 or biochar which can then be stored by geologic sequestration or land application, respectively, enabling carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and making BECCS a negative emissions technology (NET). The potential range of negative emissions from BECCS was estimated to be zero to 22 gigatonnes per year. , five facilities around the world were actively using BECCS technologies and were capturing approximately 1.5 million tonnes per year of CO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
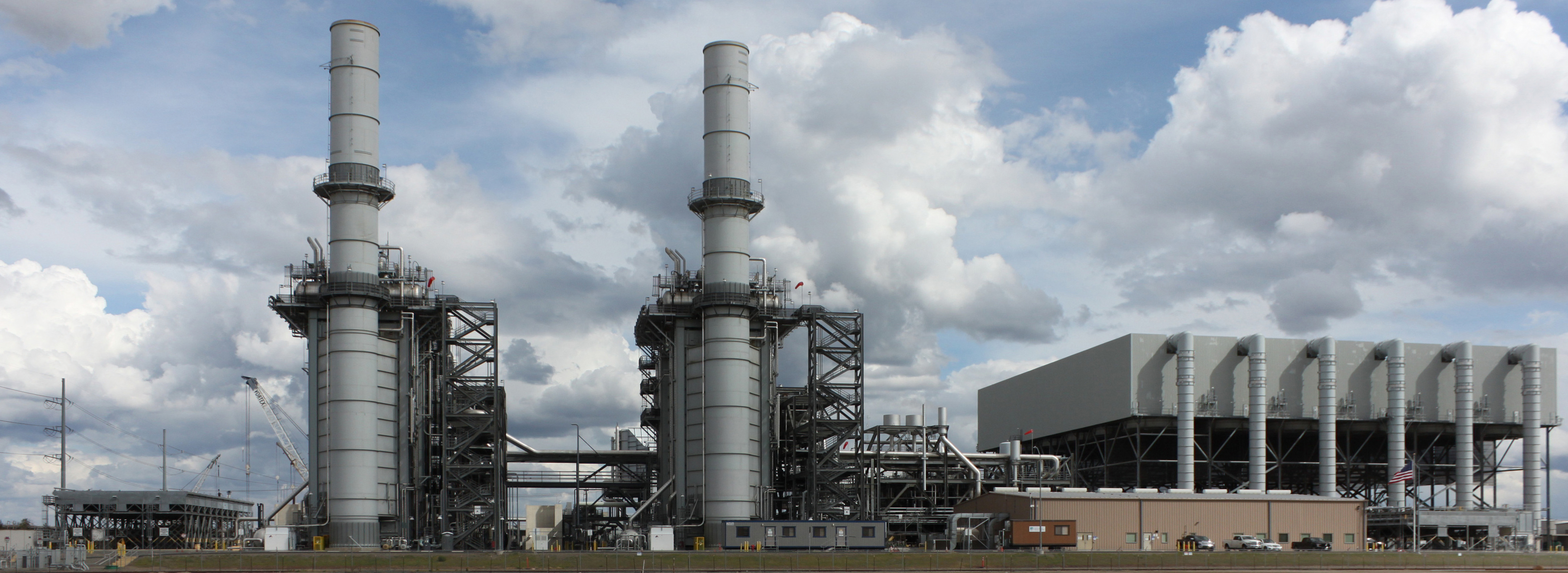
Combined Cycle Power Plant
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs. The principle is that after completing its cycle in the first engine, the working fluid (the exhaust) is still hot enough that a second subsequent heat engine can extract energy from the heat in the exhaust. Usually the heat passes through a heat exchanger so that the two engines can use different working fluids. By generating power from multiple streams of work, the overall efficiency can be increased by 50–60%. That is, from an overall efficiency of the system of say 34% for a simple cycle, to as much as 64% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Neutrality
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the "post-carbon economy"). The term is used in the context of carbon dioxide-releasing processes associated with transportation, energy production, agriculture, and industry. Although the term "carbon neutral" is used, a carbon footprint also includes other greenhouse gases, measured in terms of their carbon dioxide equivalence. The term climate-neutral reflects the broader inclusiveness of other greenhouse gases in climate change, even if CO2 is the most abundant. The term "net zero" is increasingly used to describe a broader and more comprehensive commitment to decarbonization and climate action, moving beyond carbon neutrality by including more activities under the scope of indirect emissions, and often including a science-based target on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emissions Trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission trading for and other greenhouse gases has been introduced in China, the European Union and other countries as a key tool for climate change mitigation. Other schemes include sulfur dioxide and other pollutants. In an emissions trading scheme, a central authority or governmental body allocates or sells a limited number (a "cap") of permits that allow a discharge of a specific quantity of a specific pollutant over a set time period. Polluters are required to hold permits in amount equal to their emissions. Polluters that want to increase their emissions must buy permits from others willing to sell them. Emissions trading is a type of flexible environmental regulation that allows organizations and markets to decide how best to meet po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), nitrous oxide (), and ozone (). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of . The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases. Human activities since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750) have increased the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide by over 50%, from 280 ppm in 1750 to 421 ppm in 2022. The last time the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide was this high was over 3 million years ago. This increase has occurred despite the absorption of more than half of the emissions by various natural carbon sinks in the carbon cycle. At current greenhouse gas emission rates, temperatures could incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emissions Budget
A carbon budget is "the maximum amount of cumulative net global anthropogenic carbon dioxide () emissions that would result in limiting global warming to a given level with a given probability, taking into account the effect of other anthropogenic climate forcers". When expressed relative to the pre-industrial period it is referred to as the Total Carbon Budget, and when expressed from a recent specified date it is referred to as the Remaining Carbon Budget. A carbon budget consistent with keeping warming below a specified limit is also referred to as an emissions budget, an emissions quota, or allowable emissions. An emissions budget may also be associated with objectives for other related climate variables, such as radiative forcing or sea level rise. Total or remaining carbon budgets are calculated by combining estimates of various contributing factors, including scientific evidence and value judgments or choices. Global carbon budgets can be further divided into national em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Removal
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR), also known as negative emissions, is a process in which carbon dioxide gas () is removed from the atmosphere and sequestered for long periods of time. Similarly, greenhouse gas removal (GGR) or negative greenhouse gas emissions is the removal of greenhouse gases (GHGs) from the atmosphere by deliberate human activities, i.e., in addition to the removal that would occur via natural carbon cycle or atmospheric chemistry processes.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary atthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.) IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


