|
Emerging Diseases
An emerging infectious disease (EID) is an infectious disease whose incidence has increased recently (in the past 20 years), and could increase in the near future. The minority that are capable of developing efficient transmission between humans can become major public and global concerns as potential causes of epidemics or pandemics. Their many impacts can be economic and societal, as well as clinical. EIDs have been increasing steadily since at least 1940. For every decade since 1940, there has been a consistent increase in the number of EID events from wildlife-related zoonosis. Human activity is the primary driver of this increase, with loss of biodiversity a leading mechanism. Emerging infections account for at least 12% of all human pathogens. EIDs can be caused by newly identified microbes, including novel species or strains of virus (e.g. novel coronaviruses, ebolaviruses, HIV). Some EIDs evolve from a known pathogen, as occurs with new strains of influenza. EIDs may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Examples Of Emerging And Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to: Entertainment * Global (Paul van Dyk album), ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003 * Global (Bunji Garlin album), ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007 * Global (Humanoid album), ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989 * Global (Todd Rundgren album), ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015 * Bruno J. Global, a character in the anime series ''The Super Dimension Fortress Macross'' Companies and brands Television * Global Television Network, in Canada ** Global BC, on-air brand of CHAN-TV, a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Okanagan, on-air brand of CHBC-TV, a television station in Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada ** Global Toronto, a television station in Toronto ** Global Edmonton ** Global Calgary ** Global Montreal ** Global Maritimes ** Canwest Global, former parent company of Global Television Network * Global TV (Venezuela), a regional channel in Venezuela Other industries * Global (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergent Virus
An emergent virus (or emerging virus) is a virus that is either newly Viral evolution, appeared, notably increasing in incidence (epidemiology), incidence/geographic range limit, geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious diseases and raise public health challenges globally, given their potential to cause disease outbreak, outbreaks of disease which can lead to epidemics and pandemics. As well as causing disease, emergent viruses can also have severe economy, economic implications. Recent examples include the SARS-related coronaviruses, which have caused the 2002-2004 SARS outbreak, 2002-2004 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV-1) and the COVID-19 pandemic, 2019–21 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-CoV-2). Other examples include the human immunodeficiency vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ResearchGate
ResearchGate is a European commercial social networking site for scientists and researchers to share papers, ask and answer questions, and find collaborators. According to a 2014 study by ''Nature'' and a 2016 article in ''Times Higher Education'', it is the largest academic social network in terms of active users, although other services have more registered users, and a 2015–2016 survey suggests that almost as many academics have Google Scholar profiles. While reading articles does not require registration, people who wish to become site members need to have an email address at a recognized institution or to be manually confirmed as a published researcher in order to sign up for an account. Members of the site each have a user profile and can upload research output including papers, data, chapters, negative results, patents, research proposals, methods, presentations, and software source code. Users may also follow the activities of other users and engage in discussions with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-species Transmission
Cross-species transmission (CST), also called interspecies transmission, host jump, or spillover, is the transmission of an infectious pathogen, such as a virus, between hosts belonging to different species. Once introduced into an individual of a new host species, the pathogen may cause disease for the new host and/or acquire the ability to infect other individuals of the same species, allowing it to spread through the new host population. The phenomenon is most commonly studied in virology, but cross-species transmission may also occur with bacterial pathogens or other types of microorganisms. Steps involved in the transfer of pathogens to new hosts include contact between the pathogen and the host; the successful infection of an initial individual host, which may lead to amplification and an outbreak; and the adaptation of the pathogen, within either the original or new host, which may render it capable of spreading efficiently between individuals in populations of the new host. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. Typically, the first infected human transmits the infectious agent to at least one other human, who, in turn, infects others. Major modern diseases such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Most strains of influenza that infect humans are human diseases, although many strains of bird flu and swine flu are zoonoses; these viruses occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 1918 Spanish flu or the 2009 swine flu. ''Taenia solium'' infection is one of the neglected tropical diseases with public health and veterinary concern in ende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndemic
A syndemic or synergistic epidemic is the aggregation of two or more concurrent or sequential epidemics or disease clusters in a population with biological interactions, which exacerbate the prognosis and burden of disease. The term was developed by Merrill Singer in the early 1990s to call attention to the synergistic nature of the health and social problems facing the poor and underserved. Syndemics develop under health disparity, caused by poverty, stress, or structural violence and are studied by epidemiologists and medical anthropologists concerned with public health, community health and the effects of social conditions on health. The syndemic approach departs from the biomedical approach to diseases to diagnostically isolate, study, and treat diseases as distinct entities separate from other diseases and independent of social contexts. Definition A syndemic is a synergistic epidemic. The term was developed by Merrill Singer in the mid-1990s, culminating in a 2009 tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-communicable Diseases
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others. NCDs may be chronic or acute. Most are non-infectious, although there are some non-communicable infectious diseases, such as parasitic diseases in which the parasite's life cycle does not include direct host-to-host transmission. NCDs are the leading cause of death globally. In 2012, they caused 68% of all deaths (38 million) up from 60% in 2000. About half were under age 70 and half were women. Risk factors such as a person's background, lifestyle and environment increase the likelihood of certain NCDs. Every year, at least 5 million people die because of tobacco use and about 2.8 million die from being overweight. High cholesterol accounts for roughly 2.6 million deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''red measles'', and ''English measles''. Both rubella, also known as ''German measles'', and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses. Mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
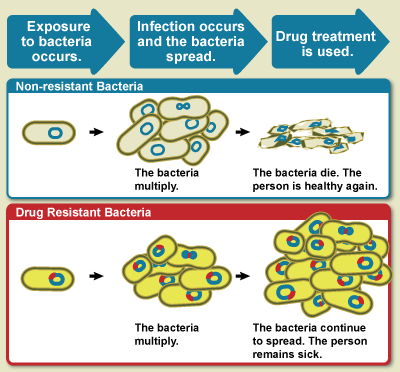
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |