|
Elicitor
Elicitors in plant biology are extrinsic or foreign molecules often associated with plant pests, diseases or synergistic organisms. Elicitor molecules can attach to special receptor proteins located on plant cell membranes. These receptors are able to recognize the molecular pattern of elicitors and trigger intracellular defence signalling via the Octadecanoid pathway. This response results in the enhanced synthesis of metabolites which reduce damage and increase resistance to pest, disease or environmental stress. This is an immune response known as pattern triggered immunity or PTI. PTI is effective against necrotrophic microorganisms. An example is chitosan which is found in insects, fungi and the shells of crustaceans. Chitosan is used in agriculture as a natural biocontrol agent, to improve plant health and increase crop yields. Effectors and Hormones Effectors and hormones are other signalling molecules often confused with elicitors. Elicitors and effectors differ from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitosan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked Glucosamine, D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit). It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crustaceans with an alkaline substance, such as sodium hydroxide. Chitosan has a number of commercial and possible biomedical uses. It can be used in agriculture as a seed treatment and biopesticide, helping plants to fight off fungal infections. In winemaking, it can be used as a fining agent, also helping to prevent spoilage. In industry, it can be used in a self-healing polyurethane paint coating. In medicine, it is useful in bandages to reduce bleeding and as an antibacterial agent; it can also be used to help deliver drugs through the skin. Manufacture and properties Chitosan is produced commercially by acetylation, deacetylation of chitin, which is the structural wikt:element, element in the exoskeleton of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elicitors
Elicitors in plant biology are extrinsic or foreign molecules often associated with plant pests, diseases or synergistic organisms. Elicitor molecules can attach to special receptor proteins located on plant cell membranes. These receptors are able to recognize the molecular pattern of elicitors and trigger intracellular defence signalling via the Octadecanoid pathway. This response results in the enhanced synthesis of metabolites which reduce damage and increase resistance to pest, disease or environmental stress. This is an immune response known as pattern triggered immunity or PTI. PTI is effective against necrotrophic microorganisms. An example is chitosan Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit). It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crustacean ... which is found in insects, fungi and the shells of crustaceans. Chitosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
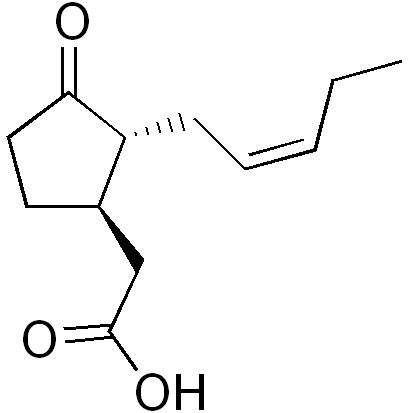
Octadecanoid Pathway
The octadecanoid pathway is a biosynthetic pathway for the production of the phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA), an important hormone for induction of defense genes. JA is synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid, which can be released from the plasma membrane by certain lipase enzymes. For example, in the wound defense response, phospholipase C will cause the release of alpha-linolenic acid for JA synthesis. In the first step, alpha-linolenic acid is oxidized by the enzyme lipoxygenase Lipoxygenases () are a family of (non-heme) iron-containing enzymes most of which catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene into cell signaling agents that serve diverse roles as auto .... This forms 13-hydroperoxylinolenic acid, which is then modified by a dehydrase and undergoes cyclization by allene oxide cyclase to form 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid. This undergoes reduction and three rounds of beta oxidation to form jasmonic acid. Footn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |