|
Electrically-assisted Turbocharger
An electrically-assisted turbocharger (EAT) is an arrangement where an electric motor assists the gas-driven turbocharger in providing forced induction, particular at times when exhaust gas flow is insufficient to produce the desired boost. Some systems integrate the motor inside a turbocharger, while others use a separate electric supercharger. Systems BorgWarner BorgWarner tested the idea in the 1990s, but never produced a part for production vehicles because of high power consumption, until the Mercedes-Benz M256 engine (2017), which used a 48-volt electrical system. , BorgWarner markets two EAT solutions: a standalone "electric compressor" (i.e. supercharger) named eBooster and a turbocharger with a single-shaft motor attached named eTurbo. Garrett Motion In October 2019, Garrett Motion announced its first electric turbocharger for market passenger vehicles, with expected launch in 2021. The design adds an electric motor between the turbocharger's turbine wheel and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive-E
The Volvo Engine Architecture (VEA) is a family of straight-three and straight-four automobile petrol and diesel engines produced by Volvo Cars in Skövde, Sweden, since 2013, Zhangjiakou, China since 2016 and Tanjung Malim, Malaysia since 2022 by Proton. Volvo markets all engines under the ''Drive–E'' designation, while Geely groups the three-cylinder variants with its other engines under the ''G-power'' name. These engines are some of the few ever put into production as twincharged engines, in the company of the Lancia Delta Integrale and concept Jaguar CX-75. History Development of the new engine family began in 2006, with the decision to only produce four-cylinder engines being finalised in 2007. The intention was to produce smaller, more economical and environmentally friendly engines that would be fitted to every Volvo model. In 2008 Volvo began to upgrade its Skövde engine plant and invested roughly 2 billion SEK into development and tooling for the VEA. In the autu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
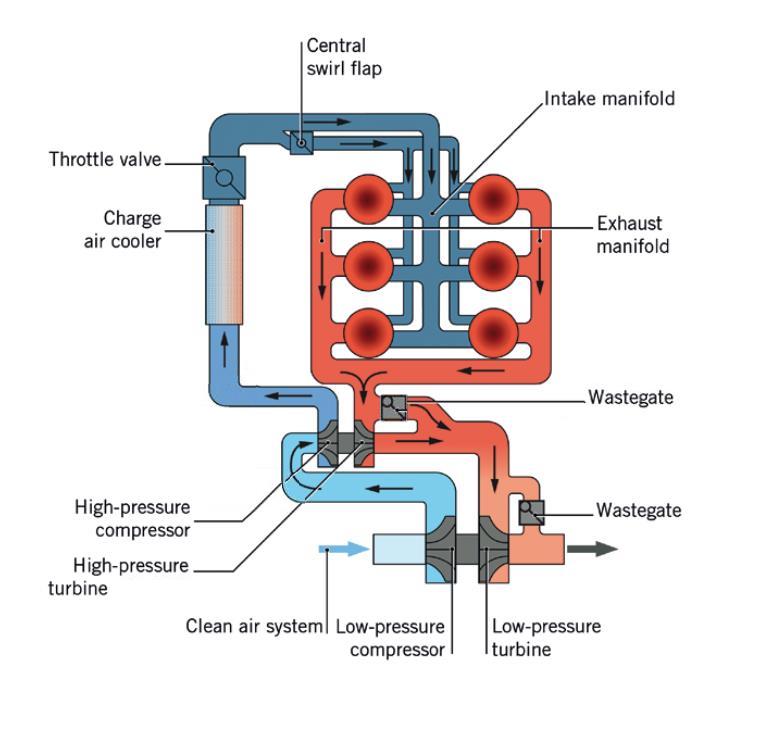
Turbochargers
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger, |
Engine Technology
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superchargers
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and/or increase power outputs. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.Gordon R. Selmon, ''Magnetoelectric Devices'', John Wiley and Sons, 1966 no ISBN pp. 391-393 Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids. History Alternating current generating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo XC90
The Volvo XC90 is a mid-size luxury SUV manufactured and marketed by Volvo Cars since 2002 and now in its second generation. The first generation was introduced at the 2002 North American International Auto Show and used the Volvo P2 platform shared with the first generation Volvo S80 and other large Volvo cars. It was manufactured at Volvo's Torslandaverken. Volvo moved production equipment of the first generation to China and ended Swedish production at the end of 2014, renaming the car as the Volvo XC Classic (or Volvo XC90 Classic). At the end of 2014, the second generation XC90 was introduced. It is based on a new global platform, the Scalable Product Architecture (SPA). Both generations of the XC90 have won ''Motor Trend''s SUV of the Year award in their debuts. In late 2022, the electric-only EX90 was introduced as the successor of the XC90. First generation (2002) In January 2001, Volvo débuted its ''Adventure Concept Car'' at the North American International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-turbo
Twin-turbo (not to be confused with a twincharger setup, which is a combination of a supercharger and a turbocharger) refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture (or intake air, in the case of a direct-injection engine). The most common layout features two identical or mirrored turbochargers in parallel, each processing half of a V engine's produced exhaust through independent piping. The two turbochargers can either be matching or different sizes. Types and combinations There are three types of turbine setups used for twin-turbo setups: * Parallel * Sequential * Series These can be applied to any of the five types of compressor setups (which theoretically could have 15 different setups): * Compound Compressors * Staged Compound Compressors * Staged Sequential Compressors * Parallel Sequential Compressors * Parallel Compressors Parallel A parallel configuration refers to using two equally-sized turbochargers which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volkswagen Group Diesel Engines
List of Volkswagen Group diesel engines. The compression-ignition diesel engines listed below are currently used by various marques of automobiles and commercial vehicles of the German automotive concern, Volkswagen Group,ETKA official factory data and also in Volkswagen Marine and Volkswagen Industrial Motor applications. All listed engines operate on the four-stroke cycle, and unless stated otherwise, use a wet sump lubrication system, and are water-cooled. Previous Volkswagen Group Diesel engines are in the list of discontinued Volkswagen Group diesel engines article. Three- and four-cylinder EA111 diesels The EA111 series of internal combustion engines was introduced in the mid-1970s in the Audi 50, and shortly after in the original Volkswagen Polo. They are a series of water-cooled inline three- and inline four-cylinder petrol and Diesel engines, with a variety of displacements. They feature an overhead camshaft with a crossflow cylinder head design and directly dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be powered by AC or DC, be Brushed motor, brushed or Brushless motor, brushless, single-phase, Two-phase electric power, two-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_2.5_T_wagon_(2011-11-18)_02.jpg)