|
Ekpyrotic
The ekpyrotic universe () is a cosmological model of the early universe that explains the origin of the large-scale structure of the cosmos. The model has also been incorporated in the cyclic universe theory (or ekpyrotic cyclic universe theory), which proposes a complete cosmological history, both the past and future. Origins The original ekpyrotic model was introduced by Justin Khoury, Burt Ovrut, Paul Steinhardt and Neil Turok in 2001. Steinhardt created the name based on the Ancient Greek word ekpyrosis (ἐκπύρωσις, "conflagration"), which refers to a Stoic cosmological model in which the universe is caught in an eternal cycle of fiery birth, cooling and rebirth. The theory addresses the fundamental question that remains unanswered by the Big Bang inflationary model, "What happened before the Big Bang?" The explanation, according to the ekpyrotic theory, is that the Big Bang was actually a big bounce, a transition from a previous epoch of contraction to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neil Turok
Neil Geoffrey Turok (born 16 November 1958) is a South African physicist. He holds the Higgs Chair of Theoretical Physics at the University of Edinburgh since 2020, and has been director emeritus of the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics since 2019. He specializes in mathematical physics and early-universe physics, including the cosmological constant and a cyclic model for the universe. Early life and career Turok was born on 16 November 1958 in Johannesburg, South Africa, to Mary (Butcher) and Byelorussian-born Ben Turok, who were activists in the anti-apartheid movement and the African National Congress. After graduating from Churchill College, Cambridge, Turok gained his doctorate from Imperial College, London, under the supervision of David Olive, one of the inventors of superstring theory. After a postdoctoral post at Santa Barbara, he was an associate scientist at Fermilab, Illinois. In 1992 he was awarded the Maxwell medal of the Institute of Physics for his c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burt Ovrut
Burt Ovrut is an American theoretical physicist best known for his work on heterotic string theory. He is currently Professor of Theoretical High Energy Physics at the University of Pennsylvania. Ovrut earned his Ph.D. in physics at the University of Chicago in 1978. His doctoral advisors were Benjamin W. Lee and Yoichiro Nambu, and his thesis was on an Sp(4) x U(1) Theory of the Weak and Electromagnetic Interactions. Ovrut is one of those who pioneered the use of M-theory to explain the Big Bang without the presence of a singularity. Together with Justin Khoury, Paul Steinhardt and Neil Turok, he introduced the notion of the Ekpyrotic Universe, "... a cosmological model in which the hot big bang universe is produced by the collision of a brane in the bulk space with a bounding orbifold plane, beginning from an otherwise cold, vacuous, static universe". Recently Burt Ovrut and his collaborators constructed a Calabi-Yau compactification that reproduces the Minimal Supersymmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Steinhardt
Paul Joseph Steinhardt (born December 25, 1952) is an American theoretical physicist whose principal research is in cosmology and condensed matter physics. He is currently the Albert Einstein Professor in Science at Princeton University, where he is on the faculty of both the Departments of Physics and of Astrophysical Sciences. Steinhardt is best known for his development of new theories of the origin, evolution and future of the universe. He is also well known for his exploration of a new form of matter, known as quasicrystals, which were thought to exist only as man-made materials until he co-discovered the first known natural quasicrystal in a museum sample. He subsequently led a separate team that followed up that discovery with several more examples of natural quasicrystals recovered from the wilds of the Kamchatka Peninsula in far eastern Russia. Several years later, he and collaborators reported the accidental synthesis of a previously unknown type of quasicrystal in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularity to some time between and seconds after the singularity. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The acceleration of this expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 80s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Alexei Starobinsky, Alan Guth, and Andrei Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation." It was developed further in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
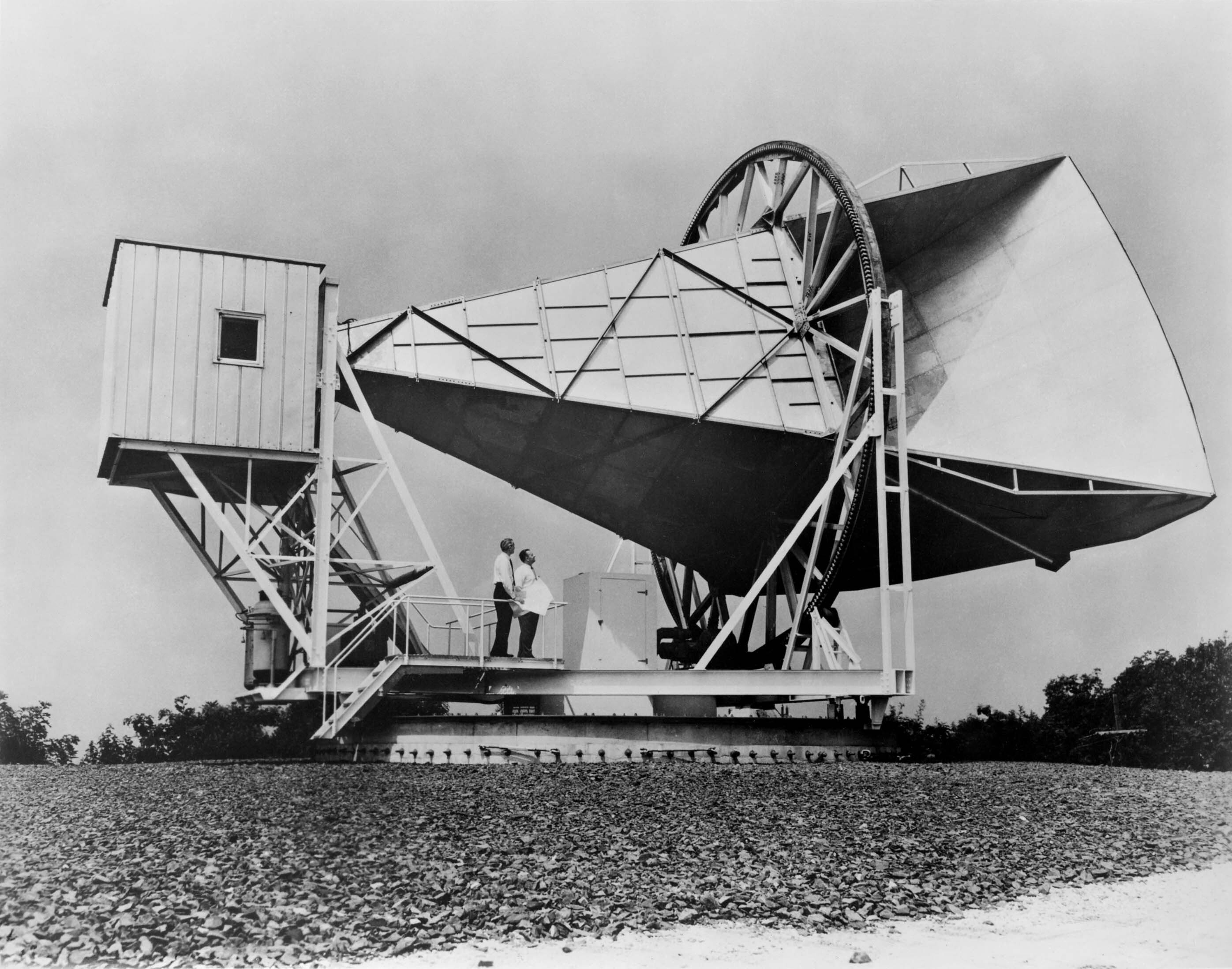
Cosmic Microwave Background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
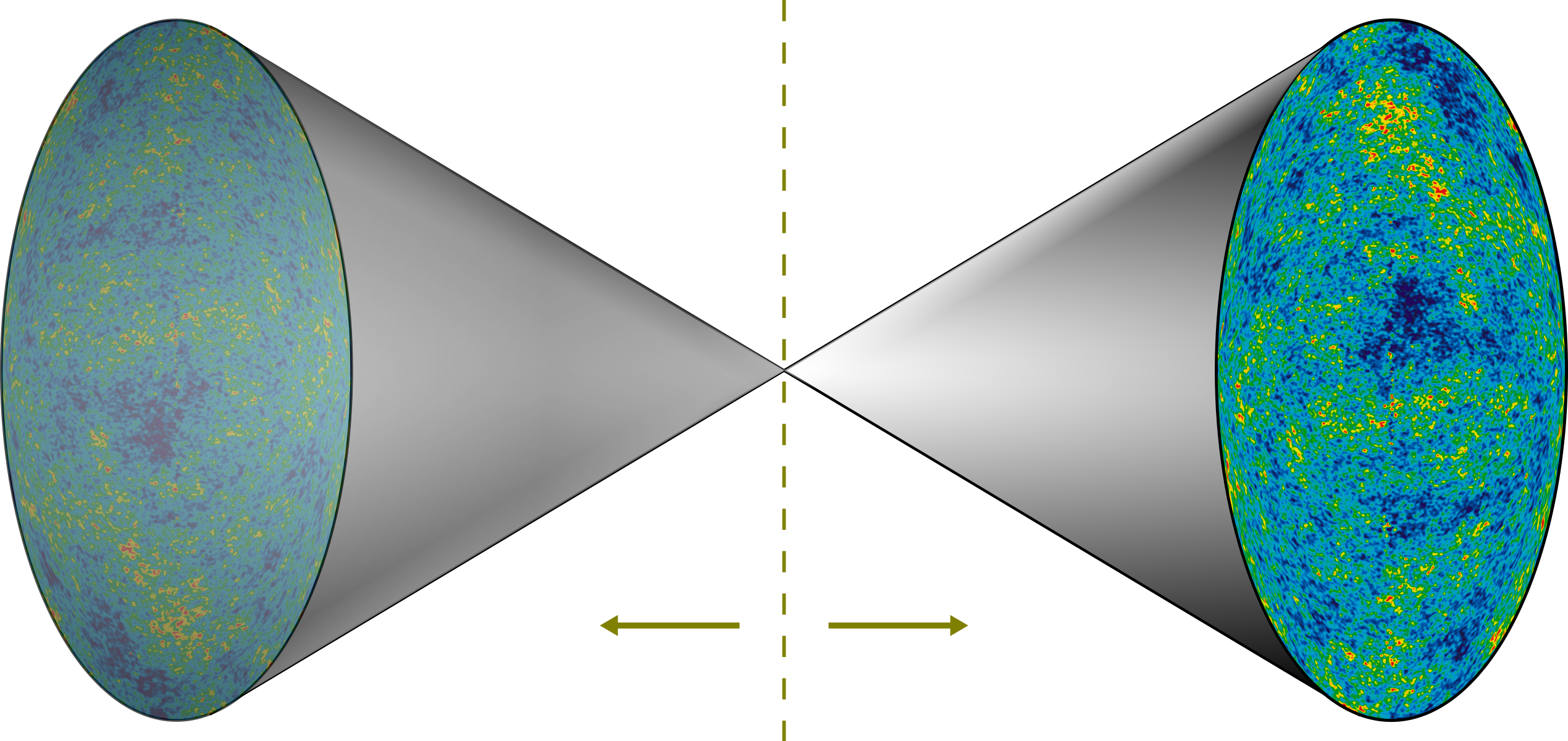
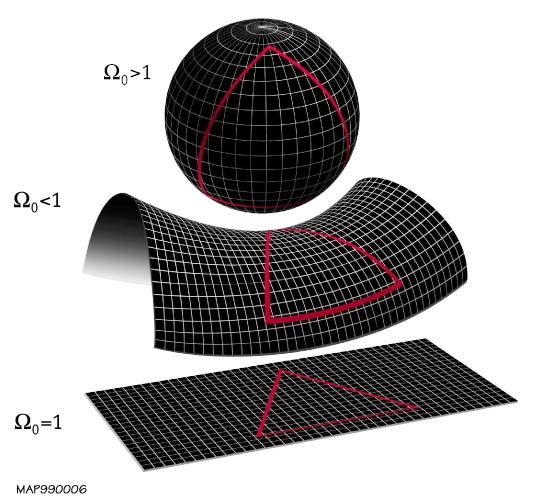
Shape Of The Universe
The shape of the universe, in physical cosmology, is the local and global geometry of the universe. The local features of the geometry of the universe are primarily described by its curvature, whereas the topology of the universe describes general global properties of its shape as a continuous object. The spatial curvature is defined by general relativity, which describes how spacetime is curved due to the effect of gravity. The spatial topology cannot be determined from its curvature, due to the fact that there exist locally indistinguishable spaces that may be endowed with different topological invariants. Cosmologists distinguish between the observable universe and the entire universe, the former being a ball-shaped portion of the latter that can, in principle, be accessible by astronomical observations. Assuming the cosmological principle, the observable universe is similar from all contemporary vantage points, which allows cosmologists to discuss properties of the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekpyrosis
Ekpyrosis (; grc, ἐκπύρωσις ''ekpýrōsis'', "conflagration") is a Stoicism, Stoic belief in the periodic destruction of the cosmos by a great conflagration every Great Year. The cosmos is then recreated (palingenesis) only to be destroyed again at the end of the new cycle. This form of wikt:catastrophe, catastrophe is the opposite of (κατακλυσμός, "inundation"), the destruction of the earth by water. The destruction of the universe was in the form of fire. The time frame of destruction was never defined or given by any of the Stoics. The fire destruction was to cleanse the universe. The cleansing of the universe was to help create a pure universe. The flames would destroy everything in the universe. Then, everything would be rebuilt in the exact same way in every detail before the fire. After so long, the process by fire would happen again and again. This cleansing of the universe is infinite. Causes There are three reasons that the belief was taught by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century Common Era, BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asserting that the practice of virtue is both necessary and sufficient to achieve Eudaimonia, (happiness, ): one flourishes by living an Ethics, ethical life. The Stoics identified the path to with a life spent practicing the cardinal virtues and living in accordance with nature. The Stoics are especially known for teaching that "virtue is the only good" for human beings, and that external things, such as health, wealth, and pleasure, are not good or called in themselves (''adiaphora'') but have value as "material for virtue to act upon". Alongside Aristotelian ethics, the Stoic tradition forms one of the major founding approaches to virtue ethics. The Stoics also held that certain destructive emotions resulted from errors of judgment, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Fluctuations
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation (also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation) is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space, as prescribed by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. They are minute random fluctuations in the values of the fields which represent elementary particles, such as electric and magnetic fields which represent the electromagnetic force carried by photons, W and Z fields which carry the weak force, and gluon fields which carry the strong force. Vacuum fluctuations appear as virtual particles, which are always created in particle-antiparticle pairs. Since they are created spontaneously without a source of energy, vacuum fluctuations and virtual particles are said to violate the conservation of energy. This is theoretically allowable because the particles annihilate each other within a time limit determined by the uncertainty principle so they are not directly observable. The uncertainty prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical group of multiple universes. Together, these universes comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. The different universes within the multiverse are called "parallel universes", "other universes", "alternate universes", or "many worlds". History of the concept According to some, the idea of infinite worlds was first suggested by the pre-Socratic Greek philosopher Anaximander in the sixth century BCE. However, there is debate as to whether he believed in multiple worlds, and if he did, whether those worlds were co-existent or successive. The first to whom we can definitively attribute the concept of innumerable worlds are the Ancient Greek Atomists, beginning with Leucippus and Democritus in the 5th century BCE, followed by Epicurus (341-270 BCE) and Lucretius (1st century BCE). In the third century BCE, the philosopher Chrysippus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_BEIC_6353768.jpg)