|
Ectopia (medicine)
An ectopia () is a displacement or malposition of an organ or other body part, which is then referred to as ectopic ({{IPAc-en, ɛ, k, ˈ, t, ɒ, p, ɪ, k). Most ectopias are congenital, but some may happen later in life. Examples * Ectopic ACTH syndrome, also known as small-cell carcinoma. * Ectopic calcification, a pathologic deposition of calcium salts in tissues or bone growth in soft tissues * Cerebellar tonsillar ectopia, aka Chiari malformation, a herniation of the brain through the foramen magnum, which may be congenital or caused by trauma. * Ectopic cilia, a hair growing where it isn't supposed to be, commonly an eyelash on an abnormal spot on the eyelid, distichia * Ectopia cordis, the displacement of the heart outside the body during fetal development *Ectopic enamel, a tooth abnormality, where enamel is found in an unusual location, such as at the root of a tooth *Ectopic expression, the expression of a gene in an abnormal place in an organism * Ectopic hormone, a hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (biology)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Recombination
Ectopic recombination is an atypical form of recombination in which crossing over occurs at non-homologous, rather than along homologous, loci. //This needs to be edited, as it is 1)incorrect and 2)contradicts what's written below, namely the need of ~2kbp of homologous sequence (which is correct). Suggested edit: replace "non-homologous" by "non-allelic"// Such recombination often results in dramatic chromosomal rearrangement, which is generally harmful to the organism.Montgomery, E., B. Charlesworth, and C. H. Langley. 1987. A test for the role of natural selection in the stabilization of transposable element copy number in a population of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Res. 49:31–41 Some research, however, has suggested that ectopic recombination can result in mutated chromosomes that benefit the organism. Ectopic recombination can occur during both meiosis and mitosis, although it is more likely occur during meiosis. It occurs relatively frequently—in at least one yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions the fetus is unable to survive. Overall, ectopic pregnancies are very rare, annually affecting less than 2% of pregnancies worldwide. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include pelvic inflammatory disease, often due to chlamydia infection; tobacco smoking; prior tubal surgery; a history of infertility; and the use of assisted reproductive technology. Those who have previously had an ectopic pregnancy are at much higher risk of having another one. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tube, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Ectropion
Cervical ectropion is a condition in which the cells from the 'inside' of the cervical canal, known as glandular cells (or columnar epithelium), are present on the 'outside' of the vaginal portion of the cervix. The cells on the 'outside' of the cervix are typically squamous epithelial cells. Where the two cells meet is called the transformation zone, also known as the stratified squamous epithelium. Cervical ectropion can be grossly indistinguishable from early cervical cancer and must be evaluated by a physician to determine risks and prognosis. It may be found incidentally when a vaginal examination (or pap smear test) is done. The area may look red because the glandular cells are red. While many women are born with cervical ectropion, it can be caused by a number of reasons, such as: *Hormonal changes, meaning it can be common in young women *Using oral contraceptives *Pregnancy. Signs and symptoms Cervical ectropion can be associated with excessive, non-purulent vaginal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Beat
Ectopic beat is a disturbance of the cardiac rhythm frequently related to the electrical conduction system of the heart, in which beats arise from fibers or group of fibers outside the region in the heart muscle ordinarily responsible for impulse formation (''i.e.'', the sinoatrial node). An ectopic beat can be further classified as either a premature ventricular contraction (PVC), or a premature atrial contraction (PAC). Some patients describe this experience as a "flip" or a "jolt" in the chest, or a "heart hiccup", while others report dropped or missed beats. Ectopic beats are more common during periods of psychological stress, exercise or debility; they may also be triggered by consumption of some food like carbohydrates, strong cheese, or chocolate. It is a form of cardiac arrhythmia in which ectopic foci within either ventricular or atrial myocardium, or from finer branches of the electric transduction system, cause additional beats of the heart. Some medications may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
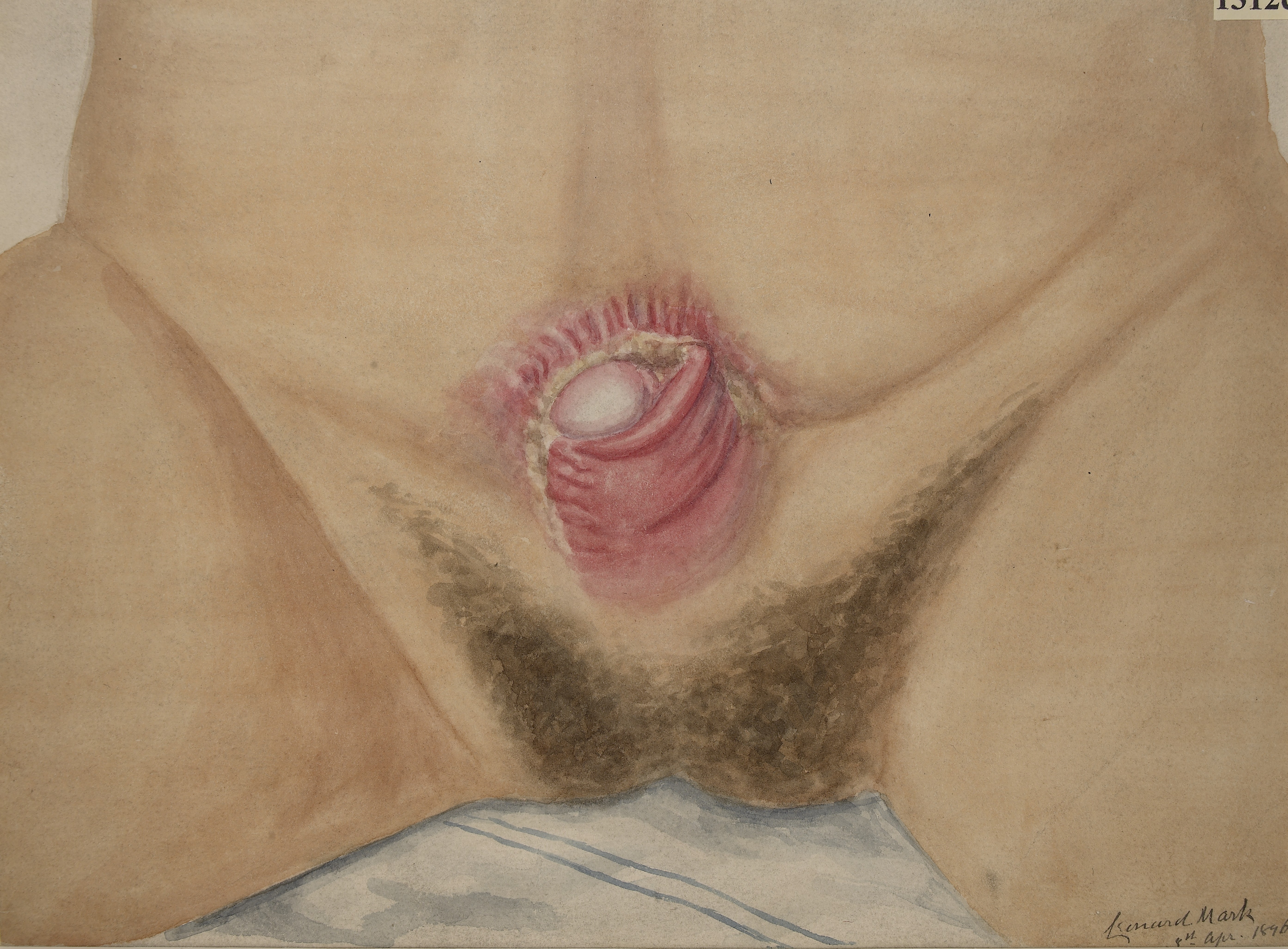
Ectopia Vesicae
Bladder exstrophy is a congenital anomaly that exists along the spectrum of the exstrophy-epispadias complex, and most notably involves protrusion of the urinary bladder through a defect in the abdominal wall. Its presentation is variable, often including abnormalities of the bony pelvis, pelvic floor, and genitalia. The underlying embryologic mechanism leading to bladder exstrophy is unknown, though it is thought to be in part due to failed reinforcement of the cloacal membrane by underlying mesoderm. Exstrophy means the inversion of a hollow organ. Signs and symptoms The classic manifestation of bladder exstrophy presents with: * A defect in the abdominal wall occupied by both the exstrophied bladder as well as a portion of the urethra * A flattened puborectal sling * Separation of the pubic symphysis * Shortening of a pubic rami * External rotation of the pelvis. Females frequently have a displaced and narrowed vaginal orifice, a bifid clitoris, and divergent labia. Caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Ureter
Ectopic ureter (or ureteral ectopia) is a medical condition where the ureter, rather than terminating at the urinary bladder, terminates at a different site. In males this site is usually the urethra, in females this is usually the urethra or vagina. It can be associated with renal dysplasia, frequent urinary tract infections, and urinary incontinence (usually continuous drip incontinence). Ectopic ureters are found in 1 of every 2000–4000 patients, and can be difficult to diagnose, but are most often seen on CT scans. Ectopic ureter is commonly a result of a duplicated renal collecting system, a duplex kidney The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ... with 2 ureters. In this case, usually one ureter drains correctly to the bladder, with the duplicated ureter presentin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Tooth
An ectopic tooth, also known as an impacted tooth, is a tooth that develops in an abnormal position and fails to erupt into its normal location in the oral cavity. Ectopic teeth can cause a variety of symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and infection, and they can lead to more serious complications if left untreated. This condition can affect both deciduous teeth and permanent teeth, although it is more common in the permanent teeth. Ectopic teeth may commonly occur within the dentate region of the jaws. Other common sites for ectopic teeth include the maxillary sinus, the nasal cavity, the mandibular condyle, and the palate. The cause of ectopic teeth is not always clear, but it may be related to genetic factors or developmental abnormalities. Diagnosis of ectopic teeth typically involves a comprehensive dental examination, including X-rays and other imaging tests. Treatment options for ectopic teeth depend on the location and severity of the condition, as well as the ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Thyroid
Thyroid dysgenesis is a cause of congenital hypothyroidism where the thyroid is missing, ectopic, or severely underdeveloped. It should not be confused with iodine deficiency, or with other forms of congenital hypothyroidism, such as thyroid dyshormonogenesis, where the thyroid is present but not functioning correctly. Congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis can be associated with PAX8. __TOC__ Ectopic thyroid An ''ectopic thyroid'', also called ''accessory thyroid gland'', is a form of thyroid dysgenesis in which an entire or parts of the thyroid located in another part of the body than what is the usual case. A completely ectopic thyroid gland may be located anywhere along the path of the descent of the thyroid during its embryological development, although it is most commonly located at the base of the tongue, just posterior to the foramen cecum of the tongue. In this location, an aberrant or ectopic thyroid gland is known as a ''lingual thyroid''. If the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Thymus
Ectopic thymus is a condition where thymus tissue is found in an abnormal location. It usually does not cause symptoms, but may leads to a mass in the neck that may compress the trachea and the esophagus. It is thought to be the result of either a failure of descent or a failure of involution of normal thymus tissue. It may be diagnosed with radiology, such as an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. If it causes illness, surgery can be used to remove it. Recurrence after surgery is very unlikely. Signs and symptoms Ectopic thymus most often does not cause symptoms. It is most frequently discovered as a soft mass or swelling in the neck of infants and children. However, when symptoms do occur they are most commonly due to compression of nearby structures such as the trachea and esophagus. This can lead to hoarse voice, stridor, difficulty breathing and/or difficulty swallowing. Pain is uncommon. Cause During embryological development, the thymus is formed from the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Testis
A ectopic testis is a testicle that, although not an undescended testicle, has taken a non-standard path through the body and ended up in an unusual location. The positions of the ectopic testis may be: in the lower part of the abdomen, front of thigh, femoral canal, skin of penis or behind the scrotum. The testis is usually developed, and accompanied by an indirect inguinal hernia. It may be divorced from the epididymis which may lie in the scrotum. See also * Cryptorchidism * Orchiopexy Orchiopexy (or orchidopexy) is a surgery to move and/or permanently fix a testicle into the scrotum. While orchiopexy typically describes the operation to surgically correct an undescended testicle, it is also used to resolve testicular torsion. ... References External links {{Medical resources , DiseasesDB = , ICD9 = , ICDO = , OMIM = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , eMedicine_mult = , MeshI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Ectopia
Ectopic kidney describes a kidney that is not located in its usual position. It results from the kidney failing to ascend from its origin in the true pelvis or from a superiorly ascended kidney located in the thorax The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea .... It has an incidence of approximately 1/900. See also * Crossed dystopia References External links Nephrology Congenital disorders of urinary system Kidney anatomy {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |