|
Ecteniniid
Ecteniniidae is an extinct family (biology), family of probainognathian cynodonts from the Triassic of South America. They are notable for their large size, as well as for being among the first synapsids with specializations towards cursoriality. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Martínez ''et al.'' (2013): References Prehistoric probainognathians Late Triassic first appearances Late Triassic extinctions Prehistoric therapsid families {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
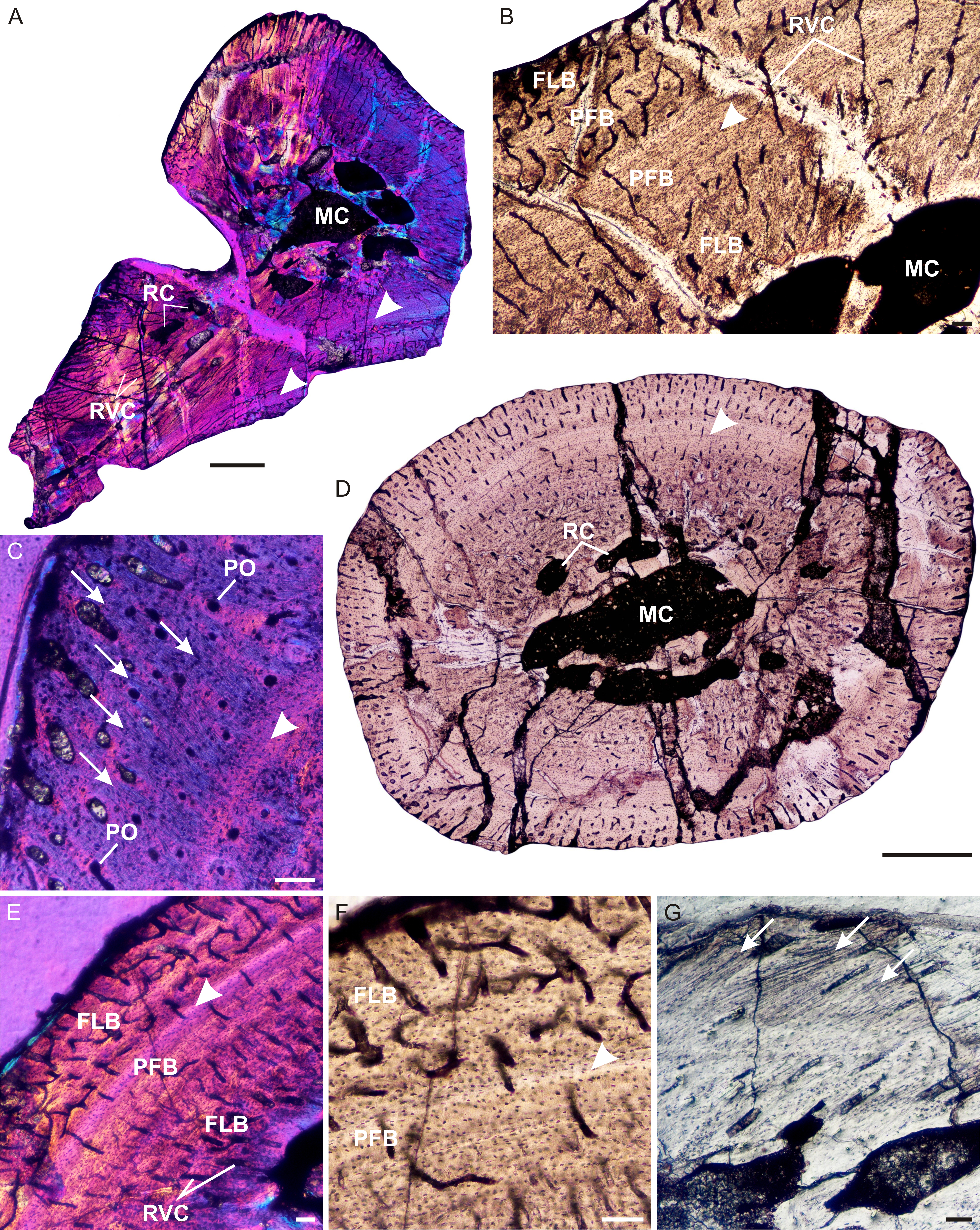
Trucidocynodon
''Trucidocynodon'' is an extinct genus of ecteniniid cynodonts from Upper Triassic of Brazil. It contains a single species, ''Trucidocynodon riograndensis''. Fossils of ''Trucidocynodon'' were discovered in Santa Maria Formation outcrops in Paleorrota geopark Agudo. ''T. riograndensis'' was similar to '' Ecteninion lunensis'' from the Upper Triassic Ischigualasto formation of Argentina, but differed in several respects, including its larger size. It is known from a nearly complete holotype skeleton as well as a referred skull. The holotype skeleton had an estimated length of 1.2 meters (4 feet), while the referred skull was 17% larger than that of the holotype. ''Trucidocynodon'' is considered one of the largest known carnivorous cynodonts from the Triassic, as well as one of the largest probainognathians in the entire Mesozoic. A biomechanical study has argued that ''Trucidocynodon'' not only had erect limbs, but that it also possibly had digitigrade forelimbs, being among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trucidocynodon Riograndensis
''Trucidocynodon'' is an extinct genus of ecteniniid cynodonts from Upper Triassic of Brazil. It contains a single species, ''Trucidocynodon riograndensis''. Fossils of ''Trucidocynodon'' were discovered in Santa Maria Formation outcrops in Paleorrota geopark Agudo, Rio Grande do Sul, Agudo. ''T. riograndensis'' was similar to ''Ecteninion lunensis'' from the Upper Triassic Ischigualasto, Ischigualasto formation of Argentina, but differed in several respects, including its larger size. It is known from a nearly complete holotype skeleton as well as a referred skull. The holotype skeleton had an estimated length of 1.2 meters (4 feet), while the referred skull was 17% larger than that of the holotype. ''Trucidocynodon'' is considered one of the largest known carnivorous cynodonts from the Triassic, as well as one of the largest probainognathians in the entire Mesozoic. A Biomechanics, biomechanical study has argued that ''Trucidocynodon'' not only had erect limbs, but that it also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probainognathia
Probainognathia is one of the two major subgroups of the clade Eucynodontia, the other being Cynognathia. The earliest forms were carnivorous and insectivorous, though some groups eventually also evolved herbivorous diets. The earliest and most basal probainognathian is the Middle Triassic (Anisian) aged ''Lumkuia'', from South Africa, though probainognathians would not become prominent until the mid Norian stage of the Late Triassic. Three groups survived the extinction at the end of Triassic: Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae, which both survived until the Jurassic—the latter even into the Cretaceous (''Montirictus'' and '' Xenocretosuchus'')—and Mammaliaformes, which includes the mammals. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Ruta, Botha-Brink, Mitchell and Benton (2013) showing one hypothesis of cynodont relationships: See also * Evolution of mammals * List of prehistoric mammals This is an incomplete list of prehistoric mammals. It does not include extant mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probainognathia
Probainognathia is one of the two major subgroups of the clade Eucynodontia, the other being Cynognathia. The earliest forms were carnivorous and insectivorous, though some groups eventually also evolved herbivorous diets. The earliest and most basal probainognathian is the Middle Triassic (Anisian) aged ''Lumkuia'', from South Africa, though probainognathians would not become prominent until the mid Norian stage of the Late Triassic. Three groups survived the extinction at the end of Triassic: Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae, which both survived until the Jurassic—the latter even into the Cretaceous (''Montirictus'' and '' Xenocretosuchus'')—and Mammaliaformes, which includes the mammals. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Ruta, Botha-Brink, Mitchell and Benton (2013) showing one hypothesis of cynodont relationships: See also * Evolution of mammals * List of prehistoric mammals This is an incomplete list of prehistoric mammals. It does not include extant mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diegocanis
''Diegocanis'' is an extinct genus of cynodonts from the Late Triassic (Carnian The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series (or earliest age of the Late Triassic Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by t ...) of Argentina. The type species, ''Diegocanis elegans'', was named in 2013 from fossils found in the Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin. ''Diegocanis'' was classified within a new family of probainognathian cynodonts called Ecteniniidae, along with the genera ''Ecteninion'' and ''Trucidocynodon''.Martínez et al., 2013 References Bibliography * Prehistoric probainognathians Prehistoric cynodont genera Carnian genera Late Triassic synapsids of South America Triassic Argentina Fossils of Argentina Ischigualasto Formation Fossil taxa described in 2013 {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritylodon
''Tritylodon'' (Greek for 3 cusped tooth) is an extinct genus of tritylodonts, one of the most advanced group of cynodont therapsids. They lived in the Early Jurassic and possibly Late Triassic periods along with dinosaurs. They also shared many characteristics with mammals, and were once considered mammals because of overall skeleton construction. That was changed due to them retaining the vestigial reptilian jawbones and a different skull structure. Tritylodons are now regarded as non-mammalian synapsids. Characteristics If a living ''Tritylodon'' were to be seen today, it would look a lot like a large rodent. They were about long but there is no certainty about the exact weight. Their method of chewing food, a grinding motion with the bottom teeth sliding against the top teeth, resembled that of rodents as well. The bottom teeth were much like a set of cusps and the top teeth were a set of matching grooves that matched perfectly allowing this motion. There were large inciso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligokyphus
''Oligokyphus'' ("few cusps") is an extinct genus of advanced herbivorous cynodonts of the late Triassic to early Jurassic periods. Originally considered to be an early mammal, it is now classified as a Mammaliamorph (nearly a mammal) because ''Oligokyphus'' does not have the mammalian jaw attachments and it retains a vestigial joint between the quadrate bone and the squamosal bone in the skull. Discovery and naming ''Oligokyphus'' was named by Edwin Hennig in 1922 on the basis of two teeth from Württemberg, Germany. The name of the genus is derived from Greek "few" and "hump", and is a calque of Paucituberculata, the group in which ''Oligokyphus'' was initially classified, from Latin into Greek. Like ''Tritylodon'', ''Oligokyphus'' was originally classified as a mammal. Hennig initially recognized two species, which he named ''Oligokyphus triserialis'' and ''Oligokyphus biserialis'' based on the number of rows of cusps, though he acknowledged this distiction as provisional. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritylodontidae
Tritylodontidae ("three-knob teeth", named after the shape of their cheek teeth) is an extinct family of small to medium-sized, highly specialized mammal-like cynodonts, bearing several mammalian traits like erect limbs, endothermy and details of the skeleton. They were the last-known family of the non-mammaliaform synapsids, persisting into the Early Cretaceous. Most tritylodontids are thought to have been herbivorous, feeding on vegetation, such as stems, leaves, and roots, although at least one may have had a more omnivorous diet. Tritylodontid fossils are found in the Americas, South Africa, and Eurasia—they appear to have had an almost global distribution, including Antarctica. Description The skull of tritylodontids had a high sagittal crest. They retained the primitive condition of the joint between the quadrate bone of the skull and the articular bone of the lower jaw—the retention of the joint is one of the reasons they are technically regarded to not be mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynognathia
Cynognathia ("dog jaw") is one of two major clades of cynodonts, the other being Probainognathia. Cynognathians included the large carnivorous genus ''Cynognathus'' and the herbivorous traversodontids. Cynognathians can be identified by several synapomorphies including a very deep zygomatic arch that extends above the middle of the orbit. Cynognathian fossils are currently known from Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Taxonomy *Suborder Cynodontia **Infraorder Eucynodontia ***(unranked) Cynognathia ****Family Cynognathidae *****''Cynognathus'' ****(unranked) Gomphodontia *****Family Diademodontidae ******''Diademodon'' ******'' Titanogomphodon'' *****(unranked) Neogomphodontia ******Family Trirachodontidae *******Subfamily Trirachodontinae ********''Langbergia'' ********'' Trirachodon'' *******Subfamily Sinognathinae ********''Beishanodon'' ********'' Sinognathus'' ********''Cricodon'' ******Family Traversodontidae *******'' Etjoia'' *******'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therioherpeton
''Therioherpeton'' is an extinct genus of small, carnivorous cynodonts belonging to the clade Prozostrodontia, which lived in what is now Brazil during the Late Triassic. Its type species is ''Therioherpeton cargnini''. It was named in 1975 by the palaeontologists José Bonaparte and Mário Costa Barberena based on remains collected in the ''Hyperodapedon'' Assemblage Zone of the Santa Maria Formation in the Paraná Basin.''Therioherpeton'' site, Faixa Nova at Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online r ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prozostrodon
''Prozostrodon'' is an extinct genus of advanced cynodonts that was closely related to the ancestors of mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated middle to late Triassic. It was originally described as a species of ''Thrinaxodon'' and was probably fairly similar to that genus in overall build. The holotype has a skull length of 6.7 cm, indicating the whole animal may have been the size of a cat, though there is some doubt as to whether the find represents an adult individual. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a small carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey. Later analysis indicated ''Prozostrodon'' was more closely related to the mammals than to the ''Thrinaxodon'' species, and it was given its own genus. Cladistic analysis indicates its closest relatives gave rise to the first mammaliaforms and therefore to the crown group mammals. The holotype of ''Prozostrodon'' was found in the Geopark of Paleorrota, Santa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |