|
Economiser
Economizers (US and Oxford spelling), or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger. Stirling engine Robert Stirling's innovative contribution to the design of hot air engines of 1816 was what he called the 'Economiser'. Now known as the regenerator, it stored heat from the hot portion of the engine as the air passed to the cold side, and released heat to the cooled air as it returned to the hot side. This innovation improved the efficiency of Stirling engine enough to make it commercially successful in particular applications, and has since been a component of every air engine that is called a Stirling engine. Boilers In boilers, economizers are heat exchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
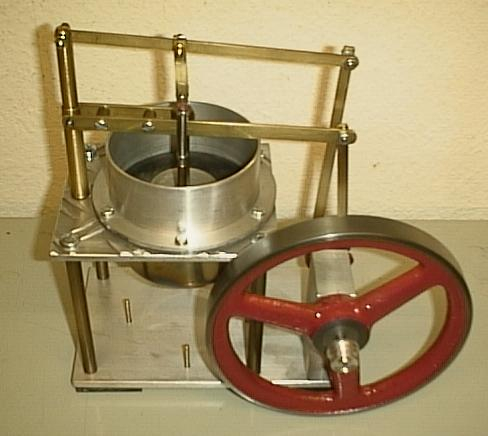
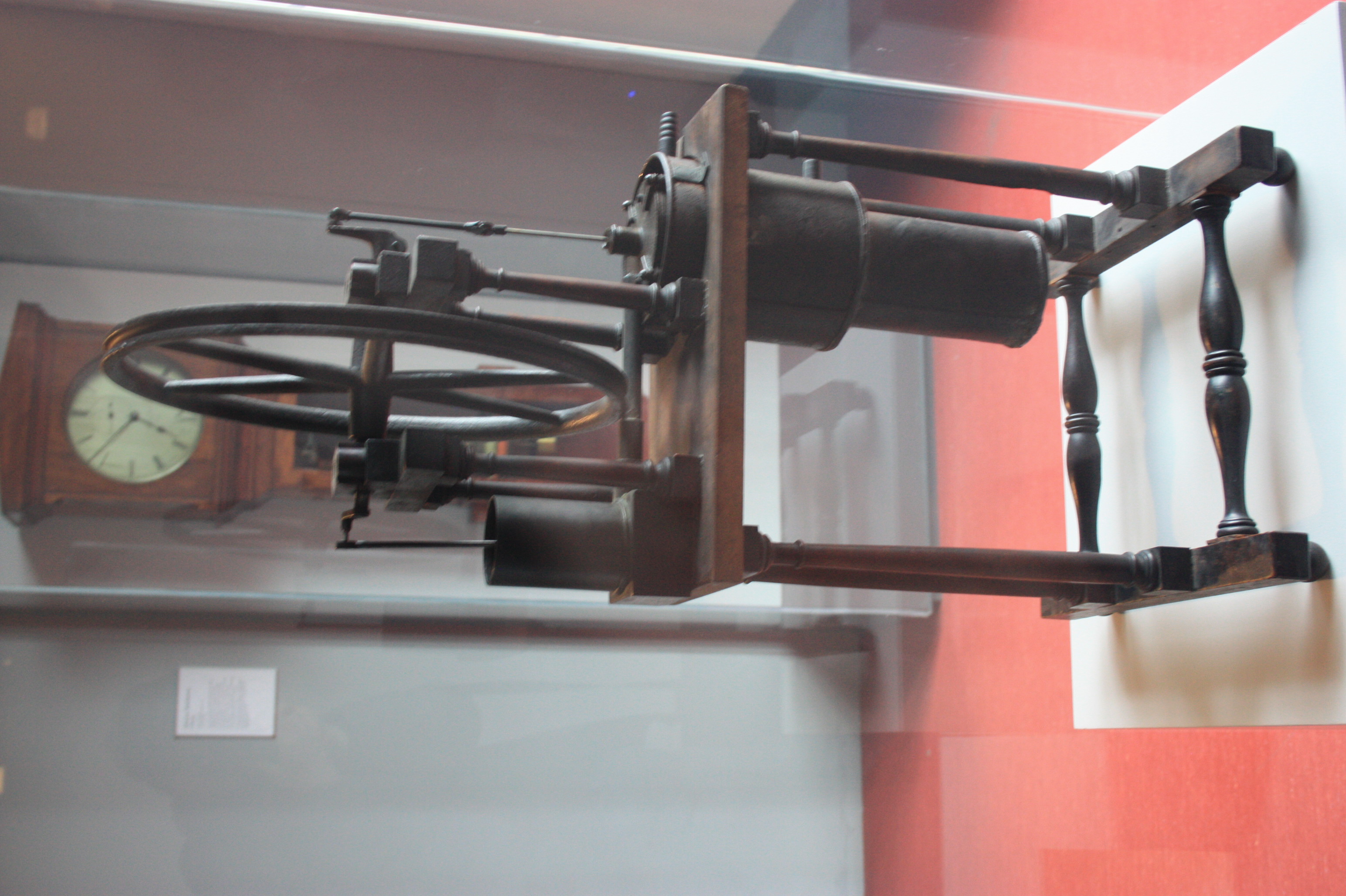
Stirling Engine
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas (the ''working fluid'') between different temperatures, resulting in a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical work. More specifically, the Stirling engine is a closed-cycle regenerative heat engine with a permanent gaseous working fluid. ''Closed-cycle'', in this context, means a thermodynamic system in which the working fluid is permanently contained within the system, and ''regenerative'' describes the use of a specific type of internal heat exchanger and thermal store, known as the ''regenerator''. Strictly speaking, the inclusion of the regenerator is what differentiates a Stirling engine from other closed-cycle hot air engines. In the Stirling engine, a gas is heated and expanded by energy supplied from outside the engine's interior space (cylinder). It is then shunted to a different location within the engine, where it is cooled and compressed. A piston (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stirling
Robert Stirling (25 October 1790 – 6 June 1878) was a Scottish clergyman and engineer. He invented the Stirling engine and was inducted into the Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame in 2014. Early life Robert Stirling was born at Fatal Fields, a location in Scotland near the village of Methven, Perthshire. A member of the Dublane side of the Stirling family, Robert was born to Patrick and Agnes Stirling. He was one of eight children that Patrick and Agnes shared. His grandfather was Michael Stirling, most famously known for his invention of the threshing machine. Robert's father, Patrick, also spent time experimenting and innovating with industrial agricultural equipment. Though Robert, like his father and grandfather, had a natural inclination for engineering, he began attending Edinburgh University in 1805 at the age of fifteen to study divinity in hopes of becoming a minister. His brother James, who would play a major role in Stirling's future engineering endeavours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Air Engine
A hot air engine (historically called an air engine or caloric engine) is any heat engine that uses the expansion and contraction of air under the influence of a temperature change to convert thermal energy into mechanical work. These engines may be based on a number of thermodynamic cycles encompassing both open cycle devices such as those of Sir George Cayley and John Ericsson and the closed cycle engine of Robert Stirling. Hot air engines are distinct from the better known internal combustion based engine and steam engine. In a typical implementation, air is repeatedly heated and cooled in a cylinder and the resulting expansion and contraction are used to move a piston and produce useful mechanical work. Definition The term "hot air engine" specifically excludes any engine performing a thermodynamic cycle in which the working fluid undergoes a phase transition, such as the Rankine cycle. Also excluded are conventional internal combustion engines, in which heat is added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
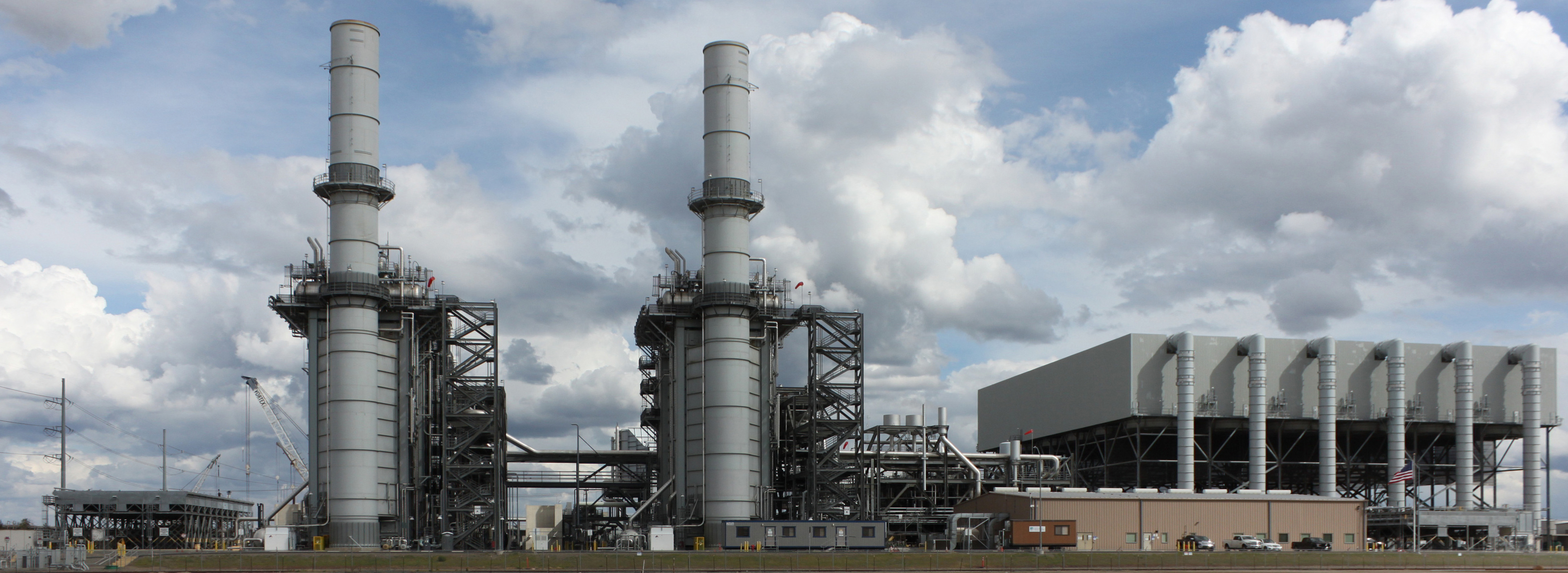
Combined Cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs. The principle is that after completing its cycle in the first engine, the working fluid (the exhaust) is still hot enough that a second subsequent heat engine can extract energy from the heat in the exhaust. Usually the heat passes through a heat exchanger so that the two engines can use different working fluids. By generating power from multiple streams of work, the overall efficiency can be increased by 50–60%. That is, from an overall efficiency of the system of say 34% for a simple cycle, to as much as 64% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
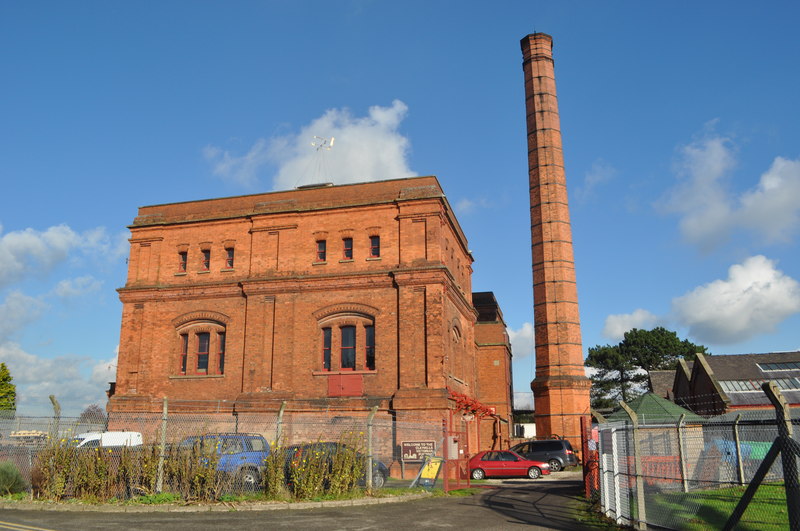
Claymills Pumping Station
Claymills Pumping Station is a restored Victorian sewage pumping station on the north side of Burton upon Trent, Staffordshire, England. It was designed by James Mansergh and used to pump sewage to the sewage farm at Egginton. The main pumping plant consists of four Woolf compound, rotative, beam pumping engines. These are arranged in mirror image pairs, in two separate engine houses, with a central boiler house (containing five Lancashire boilers with economisers) and chimney. The engines were built in 1885 by Gimson and Company of Leicester. All the engines are similar, and the following description is limited to only one, but applicable to all. The high-pressure cylinder is 24-inch bore by 6-foot stroke, and the low-pressure cylinder is 38-inch bore by 8-foot stroke. Steam is distributed by means of double beat 'Cornish' valves, mounted in upper and lower valve chests. The cylinders act on one end of the beam, via Watt's parallel motion. The beam itself is 26 feet 4 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
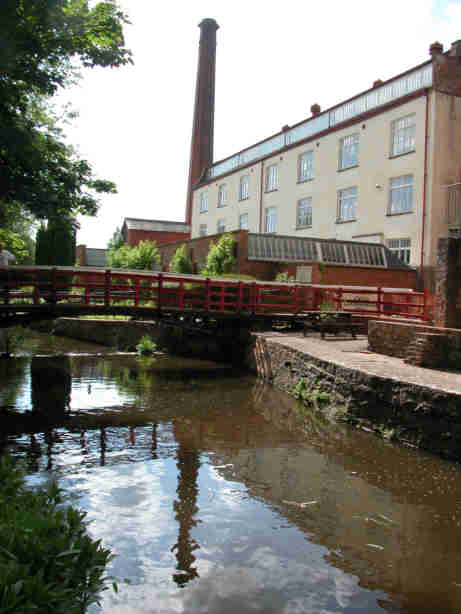
Coldharbour Mill Working Wool Museum
Coldharbour Mill, near the village of Uffculme in Devon, England, is one of the oldest woollen textile mills in the world, having been in continuous production since 1797. The mill was one of a number owned by Fox Brothers, and is designated by English Heritage as a Grade II* listed building. Location Coldharbour Mill can be found just off junction 27 of the M5 motorway near the village of Uffculme, and near to the border with Somerset. The headquarters for the mill was at Tonedale in Wellington. The water provided by the nearby River Culm was a prime factor in Thomas Fox's decision to purchase the existing grist mill. In 1797 he wrote to his brother "I have purchased the premises at Uffculme for eleven hundred guineas, which I do not think dear as they include about fifteen acres of very fine meadow land. The buildings are but middling, but the stream good."Fox, Hubert ''Quaker Homespun, The Life of Thomas Fox of Wellington, Serge Maker and Banker 1747-1821'' privately printed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke that may become airborne during pyrolysis and that are more properly identified as cokes or char. Soot causes various types of cancer and lung disease. Sources Soot as an airborne contaminant in the environment has many different sources, all of which are results of some form of pyrolysis. They include soot from coal burning, internal-combustion engines, power-plant boilers, hog-fuel boilers, ship boilers, central steam-heat boilers, waste incineration, local field burning, house fires, forest fires, fireplaces, and furnaces. These exterior sources also contribute to the indoor environment sources such as smoking of plant matter, cooking, oil lamps, candles, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Engineerium
The British Engineerium (formerly Brighton and Hove Engineerium) is an engineering and steam power museum in Hove, East Sussex. It is housed in the Goldstone Pumping Station, a set of High Victorian Gothic buildings started in 1866. The Goldstone Pumping Station supplied water to the local area for more than a century before it was converted to its present use. The site has been closed to the public since 2006, and in March 2018 the entire complex was put up for sale. At its greatest extent, between 1884 and 1952, the complex consisted of two boiler houses with condensing engines, a chimney, coal cellars, workshop, cooling pond, leat, and an underground reservoir. Situated on top of a naturally fissured chalk hollow, it provided vast quantities of water to the rapidly growing towns of Hove and its larger neighbour, the fashionable seaside resort of Brighton, for more than a century. As new sources of water were found elsewhere and more modern equipment installed to exploit t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Spelling
Oxford spelling (also ''Oxford English Dictionary'' spelling, Oxford style, or Oxford English spelling) is a spelling standard, named after its use by the University of Oxford, that prescribes the use of British spelling in combination with the suffix ''-ize'' in words like ''realize'' and ''organization'', in contrast to use of ''-ise'' endings. Oxford spelling is used by many British-based academic/science journals (for example, ''Nature'') and many international organizations (for example, the United Nations and its agencies).Three further examples:1. 2. 3. .All use British ''-our'' spellings with Oxford ''-ize/-ization'', except in proper names that have ''Organisation''. It is common for academic, formal, and technical writing for an international readership (see Usage). In digital documents, Oxford spelling may be indicated by the IETF language tag ''en-GB-oxendict'' (or historically by ''en-GB-oed''). Defining feature Oxford spelling uses the suffix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency (\eta_) is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, steam turbine, steam engine, boiler, furnace, refrigerator, ACs etc. For a heat engine, thermal efficiency is the ratio of the net work output to the heat input; in the case of a heat pump, thermal efficiency (known as the ''coefficient of performance'') is the ratio of net heat output (for heating), or the net heat removed (for cooling) to the energy input (external work). The efficiency of a heat engine is fractional as the output is always less than the input while the COP of a heat pump is more than 1. These values are further restricted by the Carnot theorem. Overview In general, energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of a device and the input, in energy terms. For thermal efficiency, the input, Q_, to the device is heat, or the heat-content of a fuel that is consumed. The des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)