|
Early Warning Systems
An early warning system is a warning system that can be implemented as a chain of information communication systems and comprises sensors, event detection and decision subsystems for early identification of hazards. They work together to forecast and signal disturbances that adversely affect the stability of the physical world, providing time for the response system to prepare for the adverse event and to minimize its impact. To be effective, early warning systems need to actively involve the communities at risk, facilitate public education and awareness of risks, effectively disseminate alerts, and warnings and ensure there is constant state of preparedness. A complete and effective early warning system supports four main functions: risk analysis, monitoring and warning; dissemination and communication; and a response capability. Application Risk analysis involves systematically collecting data and undertaking risk assessments of predefined hazards and vulnerabilities. Monit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TWS 295 Sirens, Saudi Arabia Warning System
{{Disambiguation ...
TWS may refer to: * '' Captain America: The Winter Soldier'' – a 2014 film * Texas World Speedway – a road-racing track in College Station, Texas * The Weekly Standard * The White Stripes – an American rock band * ''The White Stripes'' (album) – 1999 debut album by The White Stripes * The Wilberforce Society – a Cambridge-based think tank * The Wilderness Society (Australia) * The Wilderness Society (United States) * The Williams School * Thermal weapon sight * Toad the Wet Sprocket * Track while scan – a radar mode * True wind speed; see Apparent wind#Apparent wind in sailing * True Wireless Stereo; see Headphones#True wireless * Tsunami warning system A tsunami warning system (TWS) is used to detect tsunamis in advance and issue the warnings to prevent loss of life and damage to property. It is made up of two equally important components: a network of sensors to detect tsunamis and a communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Prediction
Earthquake prediction is a branch of the science of seismology concerned with the specification of the time, location, and magnitude of future earthquakes within stated limits, and particularly "the determination of parameters for the ''next'' strong earthquake to occur in a region". Earthquake prediction is sometimes distinguished from '' earthquake forecasting'', which can be defined as the probabilistic assessment of ''general'' earthquake hazard, including the frequency and magnitude of damaging earthquakes in a given area over years or decades. Not all scientists distinguish "prediction" and "forecast", but the distinction is useful. Prediction can be further distinguished from earthquake warning systems, which upon detection of an earthquake, provide a real-time warning of seconds to neighboring regions that might be affected. In the 1970s, scientists were optimistic that a practical method for predicting earthquakes would soon be found, but by the 1990s continuing failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Communication System
An emergency communication system (ECS) is any system (typically computer-based) that is organized for the primary purpose of supporting one-way and two-way communication of emergency information between both individuals and groups of individuals. These systems are commonly designed to convey information over multiple types of devices, from signal lights to text messaging to live, streaming video, forming a unified communication system intended to optimize communications during emergencies. Contrary to emergency notification systems, which generally deliver emergency information in one direction, emergency communication systems are typically capable of both initiating and receiving information between multiple parties. These systems are often made up of both input devices, sensors, and output/communication devices. Therefore, the origination of information can occur from a variety of sources and locations, from which the system will disseminate that information to one or more target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
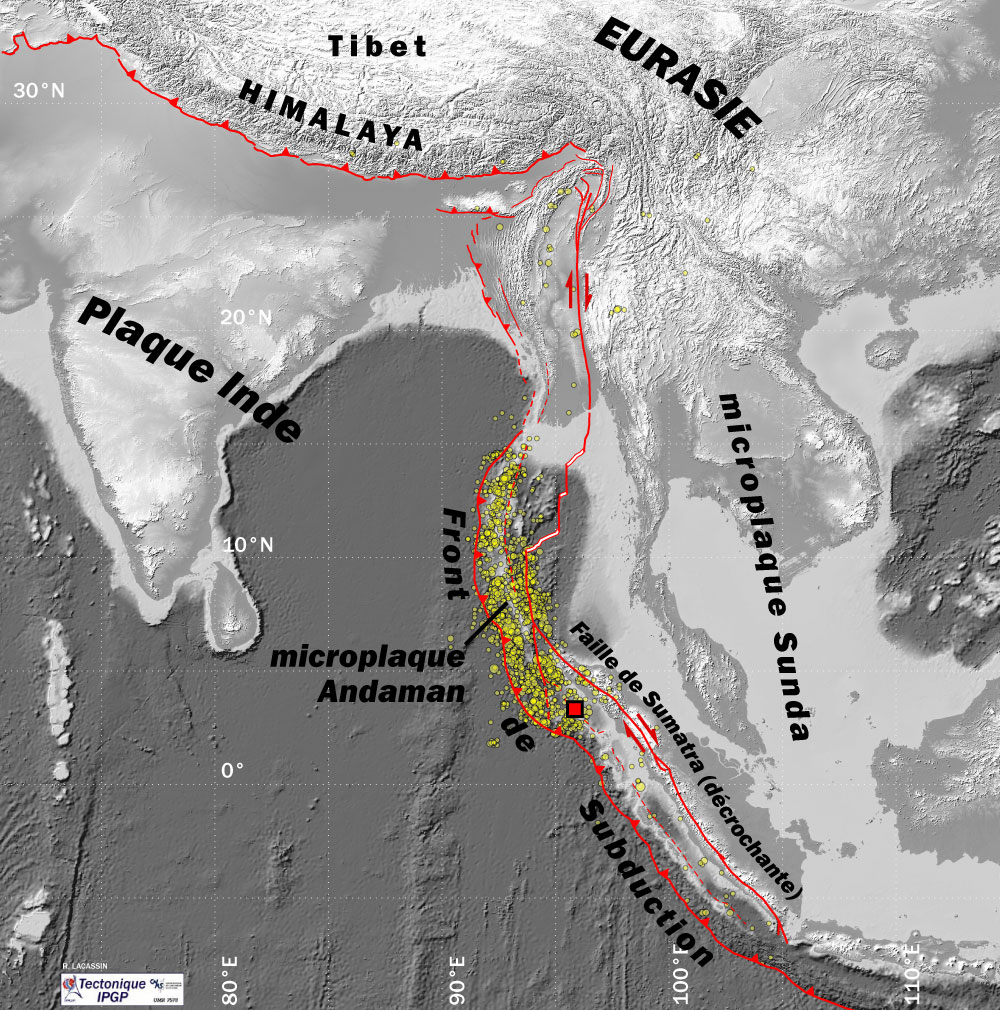
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contaminants Of Emerging Concern
Contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) is a term used by water quality professionals to describe pollutants that have been detected in environmental monitoring samples, that may cause ecological or human health impacts, and typically are not regulated under current environmental laws. Sources of these pollutants include agriculture, urban runoff and ordinary household products (such as soaps and disinfectants) and pharmaceuticals that are disposed to sewage treatment plants and subsequently discharged to surface waters. Examples of emerging contaminants are 1,4-Dioxane, food additives, pharmaceuticals, and natural & synthetic hormones. CECs have the ability to enter the water cycle after being discharged as waste through the process of runoff making its way into rivers, directly through effluent discharge, or by the process of seepage and infiltration into the water table, eventually entering the public water supply system. Emerging contaminants are known to cause endocrine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Agency
The Environment Agency (EA) is a non-departmental public body, established in 1996 and sponsored by the United Kingdom government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England (and until 2013 also Wales). Based in Bristol, the Environment Agency is responsible for flood management, regulating land and water pollution, and conservation. Roles and responsibilities Purpose The Environment Agency's stated purpose is, "to protect or enhance the environment, taken as a whole" so as to promote "the objective of achieving sustainable development" (taken from the Environment Act 1995, section 4). Protection of the environment relates to threats such as flood and pollution. The vision of the agency is of "a rich, healthy and diverse environment for present and future generations". Scope The Environment Agency's remit covers almost the whole of England, about 13 million h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Degradation
Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment (biophysical), environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution. It is defined as any change or disturbance to the environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable. Environmental concerns can be defined as the negative effects of any human activity on the environment. The biological as well as the physical features of the environment are included. Some of the primary environmental challenges that are causing great worry are air pollution, water pollution, natural environment pollution, rubbish pollution, and so o Environmental degradation is one of the ten threats officially cautioned by the High-level Panel on Threats, Challenges and Change, high-level PaneI on Threats, Challenges and Change of the United Nations. The United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Risk Management
Climate risk management (CRM) is a term describing the strategies involved in mitigating climate risk, through the work of various fields including climate change adaptation, disaster management and sustainable development. Major international conferences and workshops include: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, World Meteorological Organization - Living With Climate. Definition Climate risk management is a generic term referring to an approach to climate-sensitive decision making. The approach seeks to promote sustainable development by reducing the vulnerability associated with climate risk. CRM involves strategies aimed at maximizing positive and minimizing negative outcomes for communities in fields such as agriculture, food security, water resources, and health. Climate risk management covers a broad range of potential actions, including: early-response systems, strategic diversification, dynamic resource-allocation rules, financial instruments (such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to current or expected effects of climate change.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) InClimate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029. For humans, adaptation aims to moderate or avoid harm, and exploit opportunities; for natural systems, humans may intervene to help adjustment. Adaptation actions can be either incremental (actions where the central aim is to maintain the essence and integrity of a system) or transformative (actions that chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level Rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year. Climate scientists expect further acceleration during the 21st century. Climate change heats (and therefore expands) the ocean and melts land-based ice sheets and glaciers. Between 1993 and 2018, the thermal expansion of water contributed 42% to sea level rise; melting of temperate glaciers, 21%; Greenland, 15%; and Antarctica, 8%. Over the next 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


