|
EIF1AX
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-chromosomal (eIF1A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF1AX'' gene. This gene encodes an essential eukaryotic translation initiation factor. The protein is a component of the 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC), which mediates the recruitment of the small 40S ribosomal subunit to the 5' cap of messenger RNAs. Function eIF1A is a small protein (17 kDa in budding yeast) and a component of the 43S preinitiation complexes (PIC). eIF1A binds near the ribosomal A-site, in a manner similar to the functionally related bacterial counterpart IF1. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been recurrently seen associated to cases of uveal melanoma with disomy 3. eIF1A is mutated in thyroid cancers. Interactions EIF1AX has been shown to interact with IPO13. See also * Eukaryotic initiation factors Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
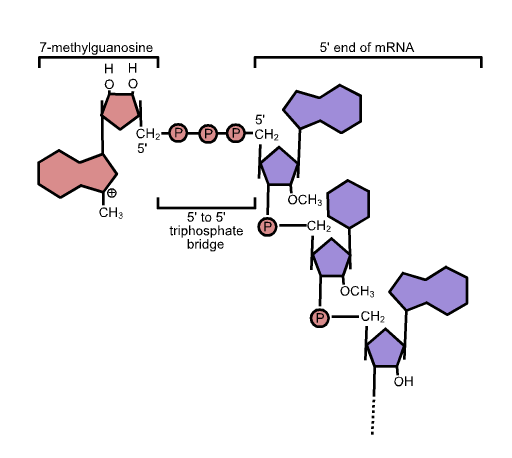
Five-prime Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-site
The A-site (A for aminoacyl) of a ribosome is a binding site for charged t-RNA molecules during protein synthesis. One of three such binding sites, the A-site is the first location the t-RNA binds during the protein synthesis process, the other two sites being P-site (peptidyl) and E-site The E-site is the third and final binding site for t-RNA in the ribosome during translation, a part of protein synthesis. The "E" stands for exit, and is accompanied by the P-site (for peptidyl) which is the second binding site, and the A-site ( ... (exit). References Ribosomal RNA {{Genetics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-1
Bacterial initiation factor 1 is a bacterial initiation factor. IF1 associates with the 30S ribosomal subunit in the A site and prevents an aminoacyl-tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypept ... from entering. It modulates IF2 binding to the ribosome by increasing its affinity. It may also prevent the 50S subunit from binding, stopping the formation of the 70S subunit. It also contains a β-domain fold common for nucleic acid binding proteins. IF1– IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling. References {{GeneticTranslation Molecular biology Protein biosynthesis Gene expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
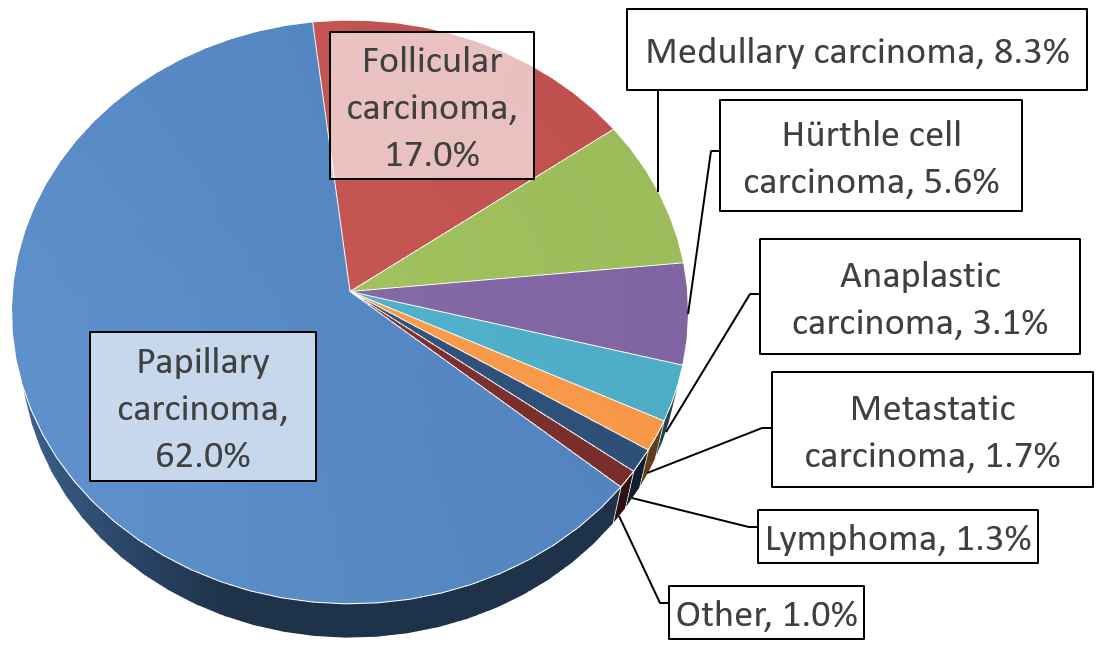
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer. Risk factors include radiation exposure at a young age, having an enlarged thyroid, and family history. The four main types are papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Diagnosis is often based on ultrasound and fine needle aspiration. Screening people without symptoms and at normal risk for the disease is not recommended as of 2017. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy including radioactive iodine, chemotherapy, thyroid hormone, targeted therapy, and watchful waiting. Surgery may involve removing part or all of the thyroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPO13
Importin-13 is a protein encoded by the IPO13 gene in humans. Importin-13 is a member of the importin-β family of nuclear transport receptors (NTRs) and was first identified as a transport receptor in 2000. According to PSI-blast based secondary structure PREDiction (PSIPRED), importin-13 contains 38 α-helices. Importin-13 accommodates a range of cargoes due to its flexible superhelical structure and a cargo binding and release system that is distinct from other importin-like transport receptors. IPO13 is broadly expressed in a variety of tissues in the human body, including the heart, cornea, fetal lung, brain, endometrial carcinoma, and testes. Nucleocytoplasmic transport In eukaryotic cells, macromolecules larger than ~40 kDa are actively transported between the nuclear and cytosolic compartment through nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) via soluble transport receptors. Importin-β-like factors are the largest class of NTRs and are classified as importins or exportins based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |