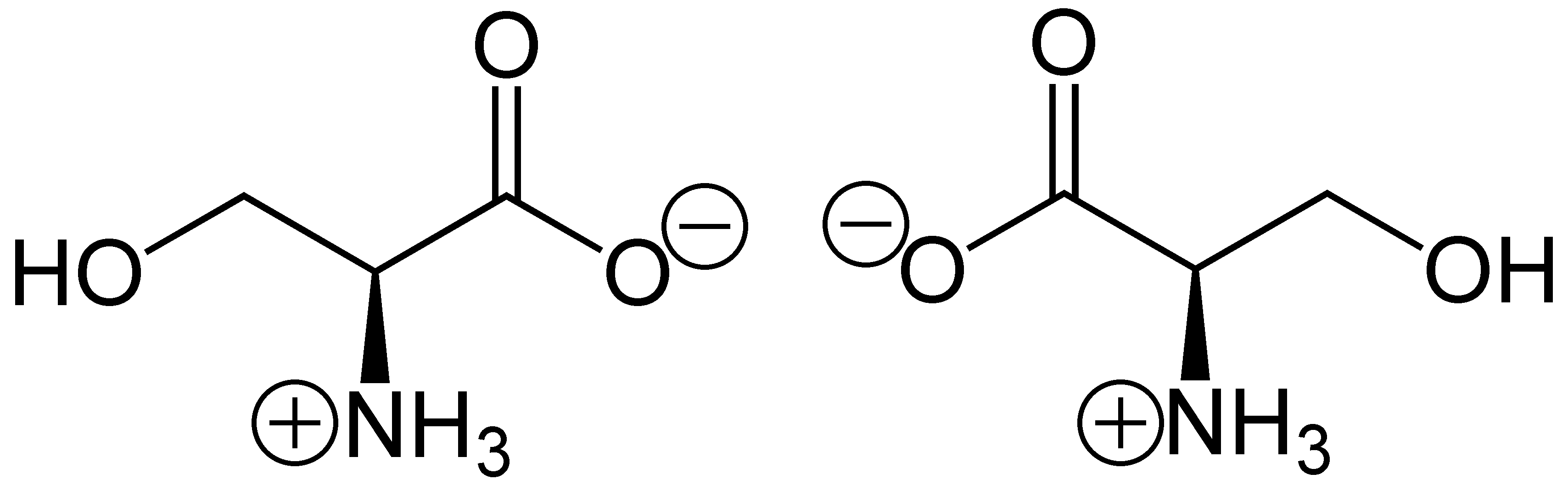|
Extensin
Extensins are a family of flexuous, rodlike, hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) of the plant cell wall. They are highly abundant proteins. There are around 20 extensions in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. They form crosslinked networks in the young cell wall. Typically they have two major diagnostic repetitive peptide motifs, one hydrophilic and the other hydrophobic, with potential for crosslinking. Extensins are thought to act as self-assembling amphiphiles essential for cell-wall assembly and growth by cell extension and expansion. The name "extensin" encapsulates the hypothesis that they are involved in cell extension.Lamport,D.T.A. (1963) Oxygen fixation into hydroxyproline of plant cell wall protein. J.Biol.Chem., 238, 1438-1440. Hydrophilic motif This pentapeptide consists of serine (Ser) and four hydroxyprolines (Hyp): Ser-Hyp-Hyp-Hyp-Hyp. Hydroxyproline is unusual not only as a cyclic amino acid that restricts peptide flexibility but as an amino acid with no codon, bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensin Peroxidase
Extensins are a family of flexuous, rodlike, hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) of the plant cell wall. They are highly abundant proteins. There are around 20 extensions in '' Arabidopsis thaliana''. They form crosslinked networks in the young cell wall. Typically they have two major diagnostic repetitive peptide motifs, one hydrophilic and the other hydrophobic, with potential for crosslinking. Extensins are thought to act as self-assembling amphiphiles essential for cell-wall assembly and growth by cell extension and expansion. The name "extensin" encapsulates the hypothesis that they are involved in cell extension.Lamport,D.T.A. (1963) Oxygen fixation into hydroxyproline of plant cell wall protein. J.Biol.Chem., 238, 1438-1440. Hydrophilic motif This pentapeptide consists of serine (Ser) and four hydroxyprolines (Hyp): Ser-Hyp-Hyp-Hyp-Hyp. Hydroxyproline is unusual not only as a cyclic amino acid that restricts peptide flexibility but as an amino acid with no codon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
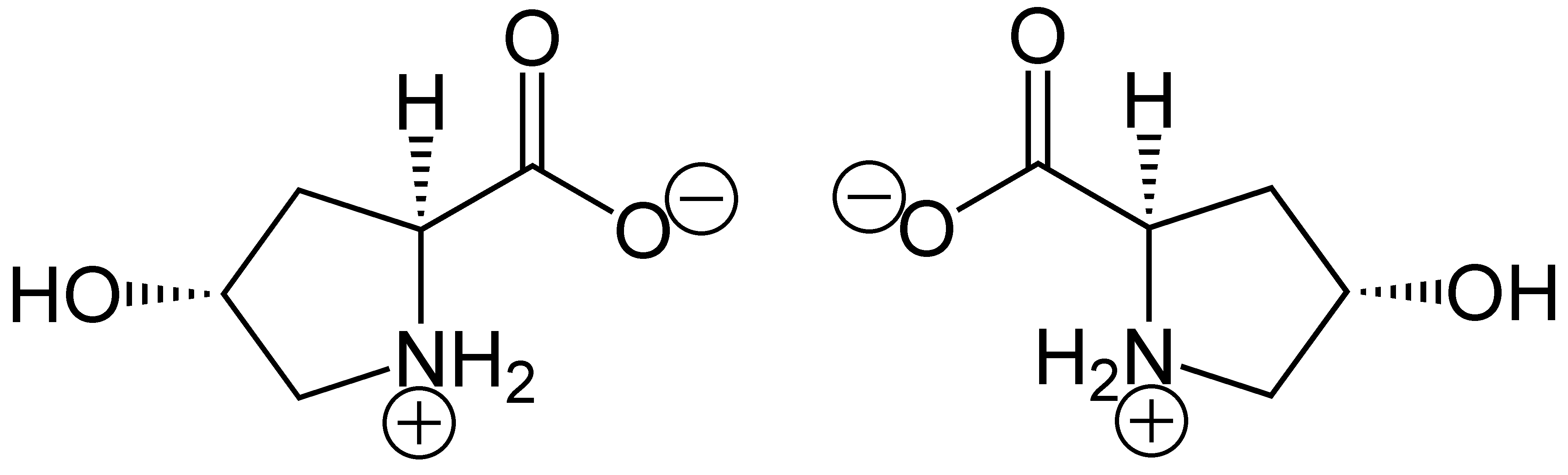
Hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank. Structure and discovery In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelatin. In 1905, Hermann Leuchs synthesized a racemic mixture of 4-hydroxyproline. Hydroxyproline differs from proline by the presence of a hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the gamma carbon atom. Production and function Hydroxyproline is produced by hydroxylation of the amino acid proline by the enzyme prolyl hydroxylase following protein synthesis (as a post-translational modification). The enzyme catalyzed reaction takes place in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Although it is not directly incorporated into proteins, hydroxyproline comprises roughly 4% of all amino acids found in animal tissue, an amount greater than seven other amino acids that are translationally incorporated. Animals Collagen Hydroxyproline is a major compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic secondary amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Proteins
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphne Osborne
Daphne J. Osborne (7 March 1930 – 16 June 2006) was a British botanist. Her research in the field of plant physiology spanned five decades and resulted in over two hundred papers, twenty of which were published in ''Nature''. Her obituary in ''The Times'' described her scientific achievements as "legendary"; that from the Botanical Society of America attributed her success to "her wonderful intellectual style, combined with her proclivity for remarkable and perceptive experimental findings". Her research focused on plant hormones, seed biology and plant DNA repair. She is best known for her work on the gas ethylene, in particular for demonstrating that ethylene is a natural plant hormone, and that it is the major regulator of ageing and the shedding of leaves and fruits. She also originated the concept of the target cell as a model for understanding plant hormone action. Education and career Born in India, where her father was a colonial administrator, Osborne attend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a Hydrophobe, hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code#Codons, codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-arabinose
Arabinose is an aldopentose – a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde (CHO) functional group. For biosynthetic reasons, most saccharides are almost always more abundant in nature as the "D"-form, or structurally analogous to D-glyceraldehyde.The D/L nomenclature does not refer to the molecule's optical rotation properties but to its structural analogy to glyceraldehyde. However, L-arabinose is in fact more common than D-arabinose in nature and is found in nature as a component of biopolymers such as hemicellulose and pectin. The L-arabinose operon, also known as the araBAD operon, has been the subject of much biomolecular research. The operon directs the catabolism of arabinose in ''E. coli'', and it is dynamically activated in the presence of arabinose and the absence of glucose. A classic method for the organic synthesis of arabinose from glucose is the Wohl degradation. : Etymology Arabinose gets its name from gum arabic, from whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
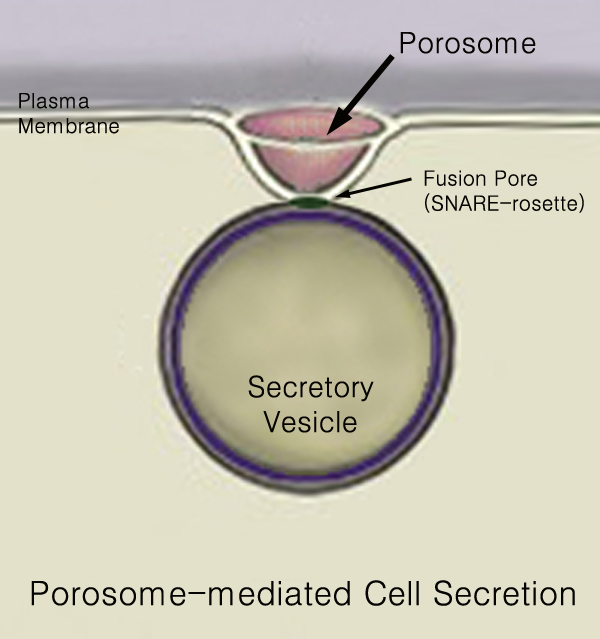
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiphile
An amphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'') properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Common amphiphilic substances are soaps, detergents, and lipoproteins. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes. Amphiphiles are the basis for a number of areas of research in chemistry and biochemistry, notably that of lipid polymorphism. Organic compounds containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of the molecule are called bolaamphiphilic. The micelles they form in the aggregate are prolate. Structure The lipophilic group is typically a large hydrocarbon moiety, such as a long chain of the form CH3(CH2)n, with n > 4. The hydrophilic group falls into one of the following categories: # charged groups #* anionic. Examples, with the lipophilic part of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the constitutive components are molecules, the process is termed molecular self-assembly. Self-assembly can be classified as either static or dynamic. In ''static'' self-assembly, the ordered state forms as a system approaches equilibrium, reducing its free energy. However, in ''dynamic'' self-assembly, patterns of pre-existing components organized by specific local interactions are not commonly described as "self-assembled" by scientists in the associated disciplines. These structures are better described as "self-organized", although these terms are often used interchangeably. Self-assembly in chemistry and materials science Self-assembly in the classic sense can be defined as ''the spontaneous and reversible organization of molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |