|
Exhaust Heat Management
Exhaust heat management is the means of lessening the damaging or performance-robbing effects of internal combustion engine exhaust heat by preventing heat from escaping from the exhaust system and into the engine compartment on automobiles. Overview The fact that exhausts often pass near important components means that ways of protecting these components from heat soak are especially important. As a result, heat management is used as a way of reflecting, dissipating or simply absorbing the heat. Heat shield is also useful to reduce under-bonnet temperatures which therefore reduces intake temperature, subsequently increasing power. Types There are many different types of heat management, some more effective than others. They range from basic solid heat shield to plasma sprayed ceramics. Heat shield Heat shield is one of the most widely used heat management options available due to its relative low price and ease to fit. In the past it has usually been custom made from rigid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high- temperature and high- pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons (piston engine), turbine blades ( gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle (jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
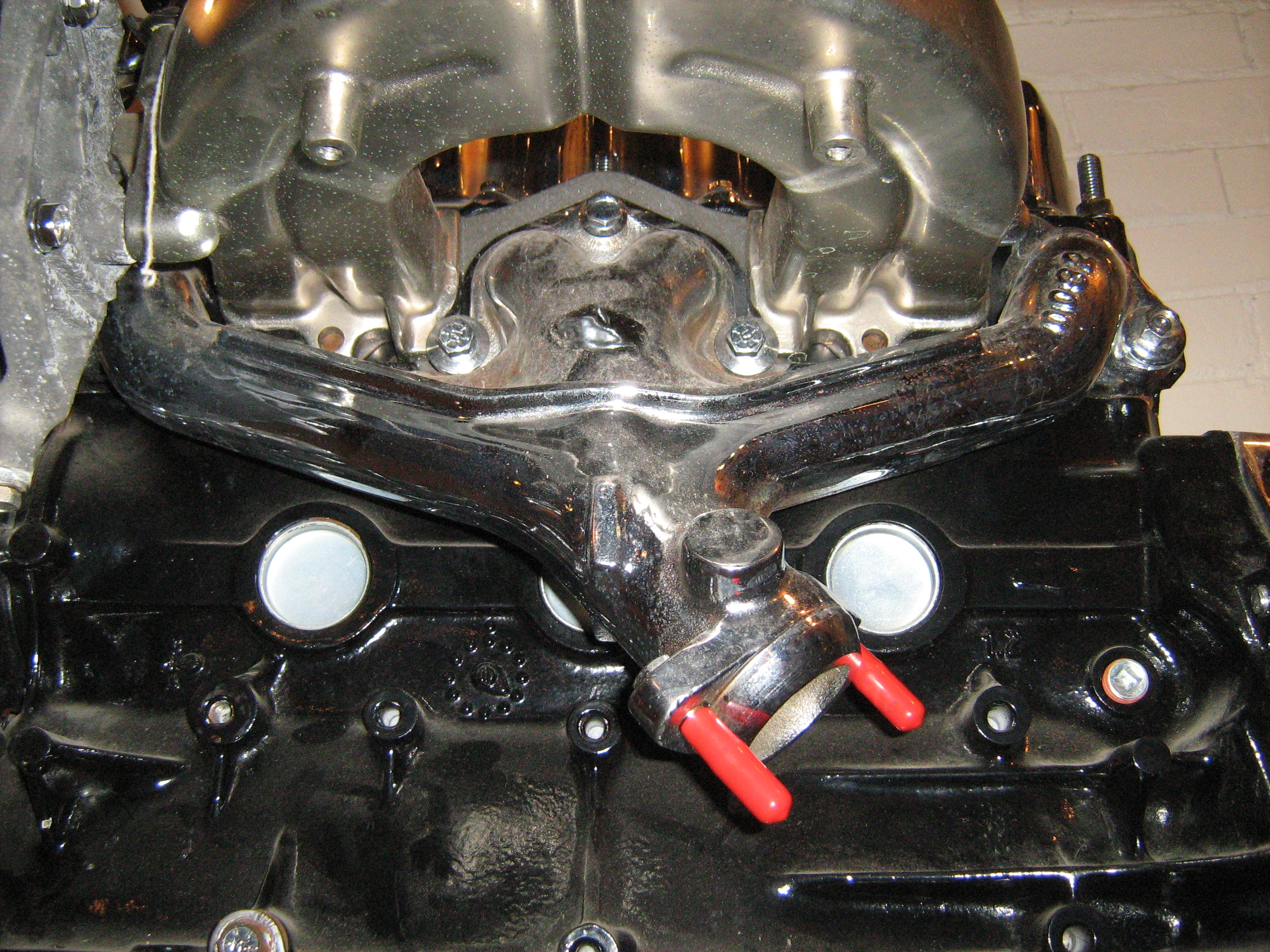
Exhaust System
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of: *Cylinder head and exhaust manifold *A turbocharger to increase engine power. *A catalytic converter to reduce air pollution. *A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise. Design criteria An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and/or noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most types of machines are very hot; the pipe must be heat-resistant, and it must not pass through or near anything that can burn or can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The ''law of reflection'' says that for specular reflection (for example at a mirror) the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected. In acoustics, reflection causes echoes and is used in sonar. In geology, it is important in the study of seismic waves. Reflection is observed with surface waves in bodies of water. Reflection is observed with many types of electromagnetic wave, besides visible light. Reflection of VHF and higher frequencies is important for radio transmission and for radar. Even hard X-rays and gamma rays can be reflected at shallow angles with special "grazing" mirrors. Reflection of light Reflection of light is either '' specular'' (mirror-like) or '' diffuse'' (retai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shield
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is also often used to refer to the thermal energy contained in a system as a component of its internal energy and that is reflected in the temperature of the system. For both uses of the term, heat is a form of energy. An example of formal vs. informal usage may be obtained from the right-hand photo, in which the metal bar is "conducting heat" from its hot end to its cold end, but if the metal bar is considered a thermodynamic system, then the energy flowing within the metal bar is called internal energy, not heat. The hot metal bar is also transferring heat to its surroundings, a correct statement for both the strict and loose meanings of ''heat''. Another example of informal usage is the term '' heat content'', used despite the fact that ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Barrier Coating
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are advanced materials systems usually applied to metallic surfaces operating at elevated temperatures, such as gas turbine or aero-engine parts, as a form of exhaust heat management. These 100 μm to 2 mm thick coatings of thermally insulating materials serve to insulate components from large and prolonged heat loads and can sustain an appreciable temperature difference between the load-bearing alloys and the coating surface. In doing so, these coatings can allow for higher operating temperatures while limiting the thermal exposure of structural components, extending part life by reducing oxidation and thermal fatigue. In conjunction with active film cooling, TBCs permit working fluid temperatures higher than the melting point of the metal airfoil in some turbine applications. Due to increasing demand for more efficient engines running at higher temperatures with better durability/lifetime and thinner coatings to reduce parasitic mass fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Typical Materials, engineered composite materials include: *Reinforced concrete and masonry *Composite wood such as plywood *Reinforced plastics, such as fibre-reinforced polymer or fiberglass *Ceramic matrix composites (composite armor, composite ceramic and metal matrices) *Metal matrix composites *and other Advanced composite materials (engineering), advanced composite materials There are various reasons where new material can be favoured. Typical examples include materials which are less ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula 1
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, which became the FIA Formula One World Championship in 1981, has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The word ''formula'' in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants' cars must conform. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as ''Grands Prix'', which take place worldwide on both purpose-built circuits and closed public roads. A points system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Each driver must hold a valid Super Licence, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA. The races must run on tracks graded "1" (formerly "A"), the highest grade-rating issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloured Ceramic Thermal Barrier Coating On Exhaust Component
Coloureds ( af, Kleurlinge or , ) refers to members of multiracial ethnic communities in Southern Africa who may have ancestry from more than one of the various populations inhabiting the region, including African, European, and Asian. South Africa's Coloured people are regarded as having some of the most diverse genetic background. Because of the vast combination of genetics, different families and individuals within a family may have a variety of different physical features. ''Coloured'' was a legally defined racial classification during apartheid referring to anyone not white or not a member of one the aboriginal groups of Africa on a cultural basis, which effectively largely meant those people of colour not speaking any indigenous languages. In the Western Cape, a distinctive Cape Coloured and affiliated Cape Malay culture developed. In other parts of Southern Africa, people classified as Coloured were usually the descendants of individuals from two distinct ethnicitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
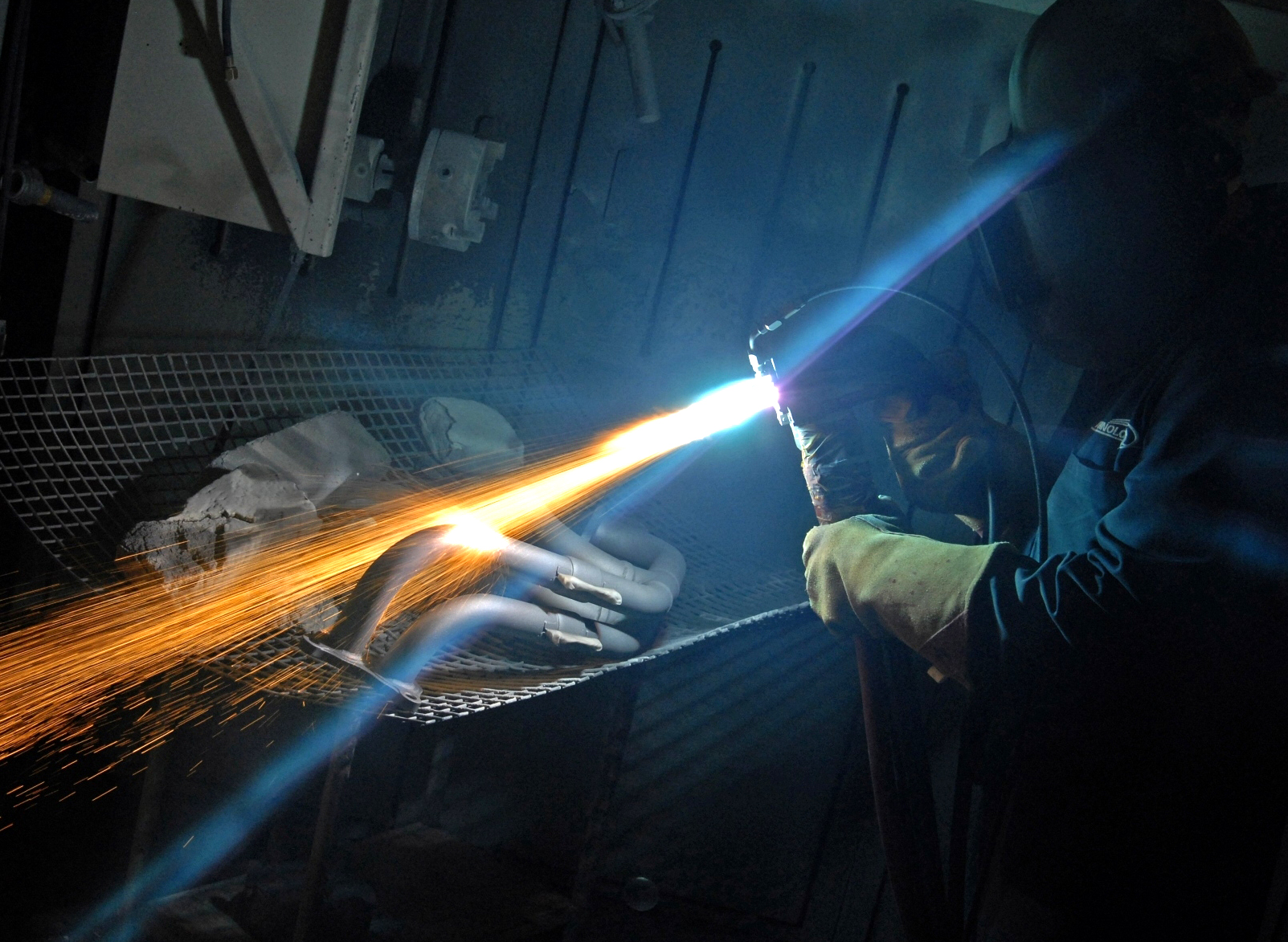
Plasma Spray
Thermal spraying techniques are coating processes in which melted (or heated) materials are sprayed onto a surface. The "feedstock" (coating precursor) is heated by electrical (plasma or arc) or chemical means (combustion flame). Thermal spraying can provide thick coatings (approx. thickness range is 20 microns to several mm, depending on the process and feedstock), over a large area at high deposition rate as compared to other coating processes such as electroplating, physical and chemical vapor deposition. Coating materials available for thermal spraying include metals, alloys, ceramics, plastics and composites. They are fed in powder or wire form, heated to a molten or semimolten state and accelerated towards substrates in the form of micrometer-size particles. Combustion or electrical arc discharge is usually used as the source of energy for thermal spraying. Resulting coatings are made by the accumulation of numerous sprayed particles. The surface may not heat up significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an ''exhaust plume''. It is a major component of motor vehicle emissions (and from stationary internal combustion engines), which can also include crankcase blow-by and evaporation of unused gasoline. Motor vehicle emissions contribute to air pollution and are a major ingredient in the creation of smog in some large cities. A 2013 study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) indicates that 53,000 early deaths occur per year in the United States alone because of vehicle emissions. According to another study from the same university, traffic fumes alone cause the death of 5,000 people every year just in the United Kingdom. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Spraying
Thermal spraying techniques are coating processes in which melted (or heated) materials are sprayed onto a surface. The "feedstock" (coating precursor) is heated by electrical (plasma or arc) or chemical means (combustion flame). Thermal spraying can provide thick coatings (approx. thickness range is 20 microns to several mm, depending on the process and feedstock), over a large area at high deposition rate as compared to other coating processes such as electroplating, physical and chemical vapor deposition. Coating materials available for thermal spraying include metals, alloys, ceramics, plastics and composites. They are fed in powder or wire form, heated to a molten or semimolten state and accelerated towards substrates in the form of micrometer-size particles. Combustion or electrical arc discharge is usually used as the source of energy for thermal spraying. Resulting coatings are made by the accumulation of numerous sprayed particles. The surface may not heat up significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zircotec
Zircotec is a high temperature coating and heat barrier manufacturer, based in Abingdon near Oxford, England. It uses plasma-sprayed ceramic materials to provide thermal and abrasive resistance to components - with a focus on automotive exhaust systems. Its best-known products include coloured thermal barrier coatings and Zircoflex - a flexible ceramic heatshield. History 1960-2003: Development at UKAEA Zircotec began life as part of the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, where its high temperature coatings and heat barrier processes were originally developed for the nuclear industry. It was based at the Atomic Energy Research Establishment near Harwell, Oxfordshire. At the time, this was the main centre for atomic energy research and development in the United Kingdom. In 1994, Zircotec's thermal barrier coatings were first used in a motorsport application. These coatings were applied to the exhaust systems of Subaru rally cars to lower in-cabin temperatures. After initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |