|
Ex Parte Merryman
''Ex parte Merryman'', 17 F. Cas. 144 (C.C.D. Md. 1861) (No. 9487), is a well-known and controversial U.S. federal court case that arose out of the American Civil War. It was a test of the authority of the President to suspend "the privilege of the writ of ''habeas corpus''" under the Constitution's Suspension Clause, when Congress was in recess and therefore unavailable to do so itself.William H. Rehnquist, ''All the Laws But One'' (New York: Knopf, 1998), pp.27–39. More generally, the case raised questions about the ability of the executive branch to decline enforcement of judicial decisions when the executive believes them to be erroneous and harmful to its own legal powers. John Merryman was a prominent planter from Baltimore County, Maryland, who had been arrested at his rural plantation. Held prisoner in Fort McHenry in Baltimore harbor, he was kept inaccessible to the judiciary and to civilian legal authorities generally. U.S. Supreme Court Chief Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger B
Roger is a given name, usually masculine, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") and ', ' ("spear", "lance") (Hrōþigēraz). The name was introduced into England by the Normans. In Normandy, the Frankish name had been reinforced by the Old Norse cognate '. The name introduced into England replaced the Old English cognate '. ''Roger'' became a very common given name during the Middle Ages. A variant form of the given name ''Roger'' that is closer to the name's origin is ''Rodger''. Slang and other uses Roger is also a short version of the term "Jolly Roger", which refers to a black flag with a white skull and crossbones, formerly used by sea pirates since as early as 1723. From up to , Roger was slang for the word "penis". In ''Under Milk Wood'', Dylan Thomas writes "jolly, rodgered" suggesting both the sexual double entend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-chambers Opinion
{{no footnotes, date=March 2013 An in-chambers opinion is an opinion by a single justice or judge of a multi-member appellate court, rendered on an issue that the court's rules or procedures allow a single member of the court to decide. The judge is said to decide the matter "in chambers" because the decision can be issued from the judge's chambers without a formal court proceeding. Supreme Court of the United States Each Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States is assigned as the " Circuit Justice" to one or more of the 13 judicial circuits. The role of the Circuit Justice has changed over time, but has included addressing certain types of applications arising within the Circuit. Under current practice, the Circuit Justice for each circuit is responsible for dealing with certain types of applications that, under the Court's rules, may be addressed by a single Justice. These include emergency applications for stays (including requests for stays of execution in death-penalt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early stages of the American Civil War and conflicts with Native Americans. Scott was the Whig Party's presidential nominee in the 1852 election, but was defeated by Democrat Franklin Pierce. He was known as Old Fuss and Feathers for his insistence on proper military etiquette, as well as the Grand Old Man of the Army for his many years of service. Scott was born near Petersburg, Virginia, in 1786. After training as a lawyer and brief militia service, he joined the army in 1808 as a captain of the light artillery. In the War of 1812, Scott served on the Canadian front, taking part in the Battle of Queenston Heights and the Battle of Fort George, and was promoted to brigadier general in early 1814. He served with distinction in the Battle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Bates
Edward Bates (September 4, 1793 – March 25, 1869) was a lawyer and politician. He represented Missouri in the US House of Representatives and served as the U.S. Attorney General under President Abraham Lincoln. A member of the influential Bates family, he was the first US Cabinet appointee from a state west of the Mississippi River. Born in Goochland County, Virginia, in 1814 Bates moved to St. Louis, where he established a legal practice. He was appointed as the first attorney general of the state of Missouri in 1820. Over the next 30 years, he won election to a single term in Congress and served in both the Missouri House of Representatives and the Missouri Senate, becoming a prominent member of the Whig Party. He also represented Lucy Delaney in a successful freedom suit. After the breakup of the Whig Party in the early 1850s, he briefly joined the American Party before he became a member of the Republican Party. He was a candidate for president at the 1860 Republi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Attorney General
The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all legal matters. The attorney general is a statutory member of the Cabinet of the United States. Under the Appointments Clause of the United States Constitution, the officeholder is nominated by the president of the United States, then appointed with the advice and consent of the United States Senate. The attorney general is supported by the Office of the Attorney General, which includes executive staff and several deputies. Merrick Garland has been the United States attorney general since March 11, 2021. History Congress passed the Judiciary Act of 1789 which, among other things, established the Office of the Attorney General. The original duties of this officer were "to prosecute and conduct all sui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010. This city served as the seat of the Confederation Congress, formerly the Second Continental Congress, and temporary national capital of the United States in 1783–1784. At that time, General George Washington came before the body convened in the new Maryland State House and resigned his commission as commander of the Continental Army. A month later, the Congress ratified the Treaty of Paris of 1783, ending the American Revolutionary War, with Great Britain recognizing the independence of the United States. The city and state capitol was also the site of the 1786 An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Holliday Hicks
Thomas Holliday Hicks (September 2, 1798February 14, 1865) was a politician in the divided border-state of Maryland during the American Civil War. As governor, opposing the Democrats, his views accurately reflected the conflicting local loyalties. He was pro-slavery but anti-secession. Under pressure to call the General Assembly into special session, he held it in the pro-Union town of Frederick, where he was able to keep the state from seceding. In December 1862, Hicks was appointed to the U.S. Senate, where he endorsed Abraham Lincoln's re-election in 1864, but died soon afterwards. Early career Born in 1798 near East New Market, Maryland, Hicks began his political career as a Democrat when he was elected town constable and then, in 1824, elected Sheriff of Dorchester County. Later, he switched to the Whig Party and was elected to the House of Delegates in 1830 and re-elected in 1836. In 1837, the legislature elected him a member of the Governor's Council, the last to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George William Brown
George William Brown (October 13, 1812 – September 8, 1890) was an American politician, judge and academic. He was mayor of Baltimore from 1860 to 1861, professor in University of Maryland School of Law, and 2nd Chief Judge and Supreme Bench of Baltimore City. He was founder and president of the Bar Association of Baltimore City and the Library Company of the Baltimore Bar. Career Brown was admitted to the bar in 1834. Brown was a founder of the Library Company of the Baltimore Bar (1840) and from 1861 to 1874, he was its president. He was a founder of the Maryland Historical Society in 1844. The first digest of Maryland Court of Appeals decisions was compiled with his assistance and published in 1849. Brown was mayor of Baltimore, Maryland from 1860 to 1861 and a delegate to the Constitutional Convention in Baltimore in 1867. From 1871 to 1873, he was a University of Maryland School of Law professor from 1871 to 1873. He was elected in 1872 to serve as 2nd Chief Judge, Supreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
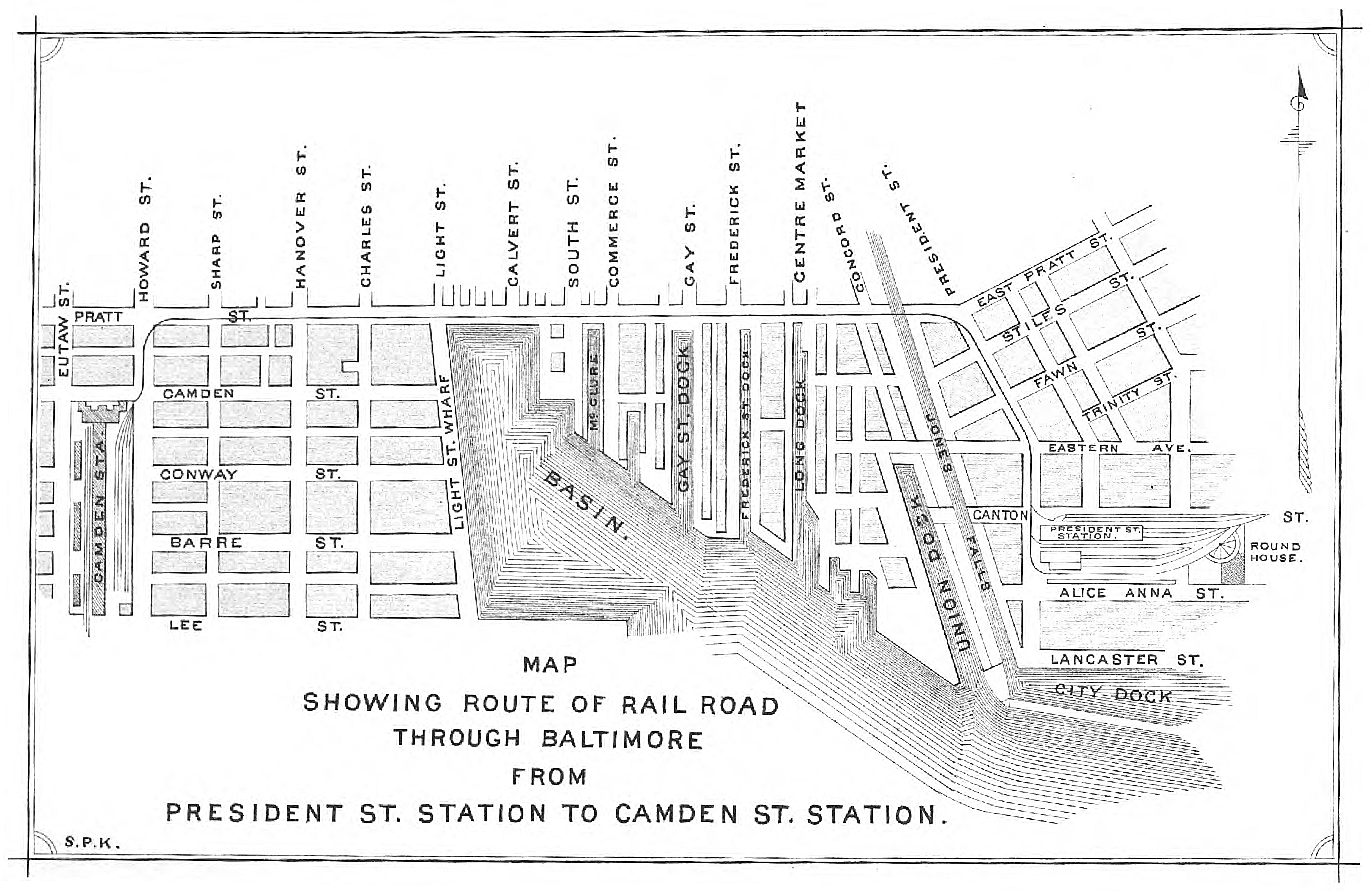
Baltimore Riot Of 1861
The Baltimore riot of 1861 (also called the "Pratt Street Riots" and the "Pratt Street Massacre") was a civil conflict on Friday, April 19, 1861, on Pratt Street, in Baltimore, Maryland. It occurred between antiwar "Copperhead" Democrats (the largest party in Maryland) and other Southern/Confederate sympathizers on one side, and on the other, members of Massachusetts and Pennsylvania state militia regiments en route to the national capital at Washington who had been called up for federal service. The fighting began at the President Street Station, spreading throughout President Street and subsequently to Howard Street, where it ended at the Camden Street Station. The riot produced the first deaths by hostile action in the American Civil War and is often called the "first bloodshed of the Civil War". Background In 1861, most Baltimoreans did not support a violent conflict with their southern neighbors, and some of them strongly sympathized with the Southern cause. In the prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a 2021 estimated population of 9,946,526. Prior to European colonization, the Baltimore region was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannock Native Americans, who were primarily settled further northwest than where the city was later built. Colonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington, D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |