|
Ethnohistorian
Ethnohistory is the study of cultures and indigenous peoples customs by examining historical records as well as other sources of information on their lives and history. It is also the study of the history of various ethnic groups that may or may not still exist. The term is most commonly used in writing about the history of the Americas. Ethnohistory uses both historical and ethnographic data as its foundation. Its historical methods and materials go beyond the standard use of documents and manuscripts. Practitioners recognize the use of such source material as maps, music, paintings, photography, folklore, oral tradition, site exploration, archaeological materials, museum collections, enduring customs, language, and placenames. Historical development Scholars studying the history of Mexico's indigenous have a long tradition, dating back to the colonial era; they used alphabetic texts and other sources to write the history of Mexico's indigenous peoples. The ''Handbook of Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original peoples. The term ''Indigenous'' was first, in its modern context, used by Europeans, who used it to differentiate the Indigenous peoples of the Americas from the European settlers of the Americas and from the Sub-Saharan Africans who were brought to the Americas as enslaved people. The term may have first been used in this context by Sir Thomas Browne in 1646, who stated "and although in many parts thereof there be at present swarms of ''Negroes'' serving under the ''Spaniard'', yet were they all transported from ''Africa'', since the discovery of ''Columbus''; and are not indigenous or proper natives of ''America''." Peoples are usually described as "Indigenous" when they maintain traditions or other aspects of an early culture that is asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodology
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal. In the context of research, this goal is usually to discover new knowledge or to verify pre-existing knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting this data. The study of methods involves a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods to assess their advantages and disadvantages relative to different research goals and situations. This way, a methodology can help make the research process efficient and reliable by guiding researchers on which method to employ at each step. These descriptions and evaluations of methods often depend on philosophical background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnoarchaeology
Ethnoarchaeology is the ethnographic study of peoples for archaeological reasons, usually through the study of the material remains of a society (see David & Kramer 2001). Ethnoarchaeology aids archaeologists in reconstructing ancient lifeways by studying the material and non-material traditions of modern societies. Ethnoarchaeology also aids in the understanding of the way an object was made and the purpose of what it is being used for. Archaeologists can then infer that ancient societies used the same techniques as their modern counterparts given a similar set of environmental circumstances. One good example of ethnoarchaeology is that of Brian Hayden (1987), whose team examined the manufacture of Mesoamerican quern-stones, providing valuable insights into the manufacture of prehistoric quern-stones. Many other studies have focused on the manufacture and use of ceramics, architecture, food, fiber, and other types of material culture. In the best cases, these studies have involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, society, culture, nation, religion, or social treatment within their residing area. The term ethnicity is often times used interchangeably with the term nation, particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism, and is separate from the related concept of races. Ethnicity may be construed as an inherited or as a societally imposed construct. Ethnic membership tends to be defined by a shared cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language, or dialect, symbolic systems such as religion, mythology and ritual, cuisine, dressing style, art, or physical appearance. Ethnic groups may share a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, depending on group identification, with many groups having mixed genetic ancestry. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. Ethnography in simple terms is a type of qualitative research where a person puts themselves in a specific community or organization in attempt to learn about their cultures from a first person point-of-view. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation—on the researcher participating in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Codices
Maya codices (singular ''codex'') are folding books written by the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in Maya hieroglyphic script on Mesoamerican bark paper. The folding books are the products of professional scribes working under the patronage of deities such as the Tonsured Maize God and the Howler Monkey Gods. Most of the codices were destroyed by conquistadors and Catholic priests in the 16th century. The codices have been named for the cities where they eventually settled. The Dresden codex is generally considered the most important of the few that survive. The Maya made paper from the inner bark of a certain wild fig tree, '' Ficus cotinifolia''. This sort of paper was generally known by the word ''huun'' in Mayan languages (the Aztec people far to the north used the word '' āmatl'' for paper). The Maya developed their ''huun''-paper around the 5th century, which is roughly the same time that the codex became predominant over the scroll in the Roman world. Maya paper was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Codices
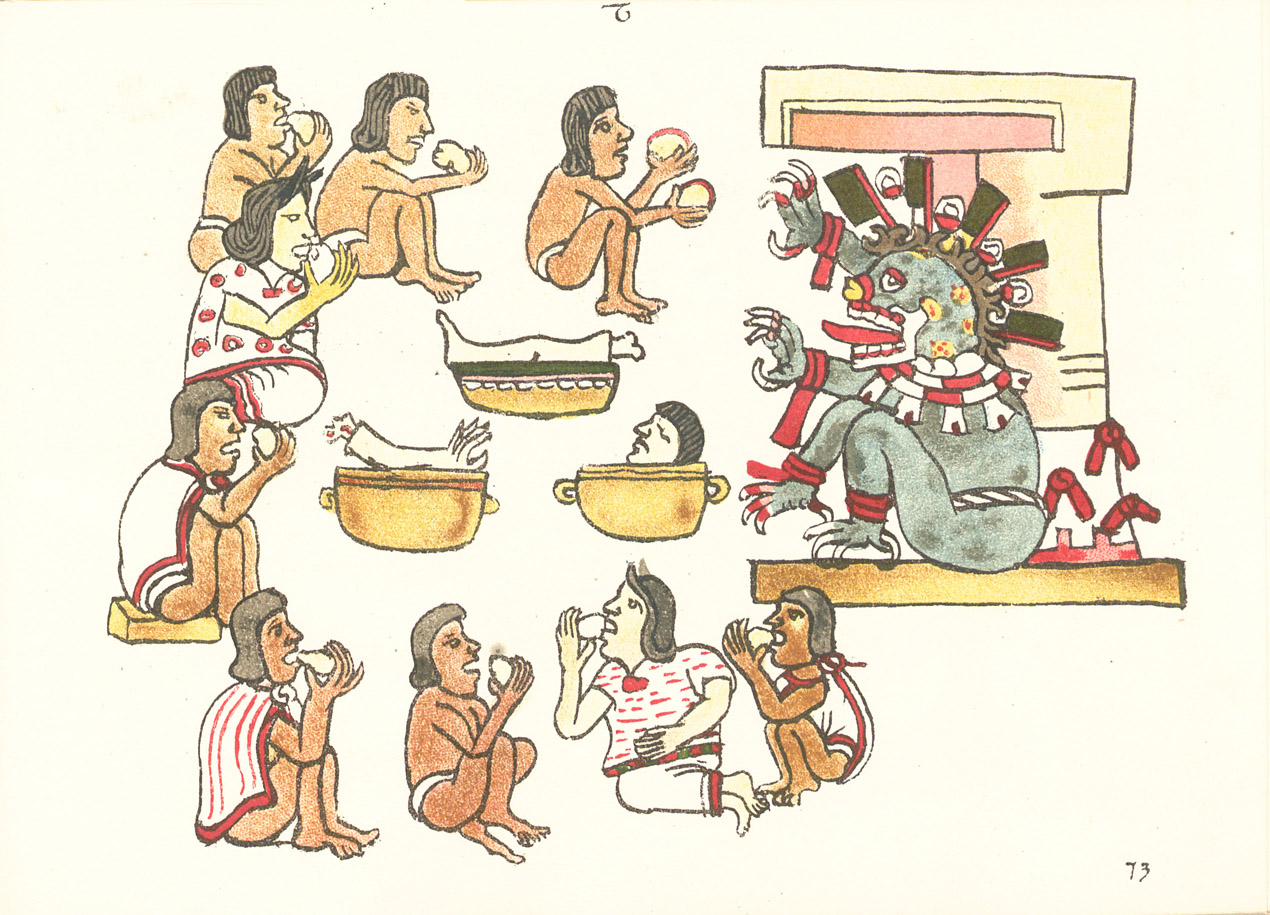
Aztec codices ( nah, Mēxihcatl āmoxtli , sing. ''codex'') are Mesoamerican manuscripts made by the pre-Columbian Aztec, and their Nahuatl-speaking descendants during the colonial period in Mexico. History Before the start of the Spanish colonization of the Americas, the Mexica and their neighbors in and around the Valley of Mexico relied on painted books and records to document many aspects of their lives. Painted manuscripts contained information about their history, science, land tenure, tribute, and sacred rituals. According to the testimony of Bernal Díaz del Castillo, Moctezuma had a library full of such books, known as ''amatl'', or ''amoxtli,'' kept by a ''calpixqui'' or nobleman in his palace, some of them dealing with tribute. After the conquest of Tenochtitlan, indigenous nations continued to produce painted manuscripts, and the Spaniards came to accept and rely on them as valid and potentially important records. The native tradition of pictorial document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diachronic
Synchrony and diachrony are two complementary viewpoints in linguistic analysis. A ''synchronic'' approach (from grc, συν- "together" and "time") considers a language at a moment in time without taking its history into account. Synchronic linguistics aims at describing a language at a specific point of time, often the present. In contrast, a ''diachronic'' (from "through" and "time") approach, as in historical linguistics, considers the development and evolution of a language through history. For example, the study of Middle English—when the subject is temporally limited to a sufficiently homogenous form—is synchronic focusing on understanding how a given stage in the history of English functions as a whole. The diachronic approach, by contrast, studies language change by comparing the different stages. The terms synchrony and diachrony are often associated with historical linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, who considered the synchronic perspective as systematic but argu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holistic
Holism () is the idea that various systems (e.g. physical, biological, social) should be viewed as wholes, not merely as a collection of parts. The term "holism" was coined by Jan Smuts in his 1926 book '' Holism and Evolution''."holism, n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, September 2019, www.oed.com/view/Entry/87726. Accessed 23 October 2019. While his ideas had racist connotations, the modern use of the word generally refers to treating a person as an integrated whole, rather than as a collection of separate systems. For example, well-being may be regarded as not merely physical health, but also psychological and spiritual well-being. Meaning The exact meaning of "holism" depends on context. Jan Smuts originally used "holism" to refer to the tendency in nature to produce wholes from the ordered grouping of unit structures. However, in common usage, "holism" usually refers to the idea that a whole is greater than the sum of its parts.J. C. Poynton (1987) SMUTS'S HOLISM AND EVO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
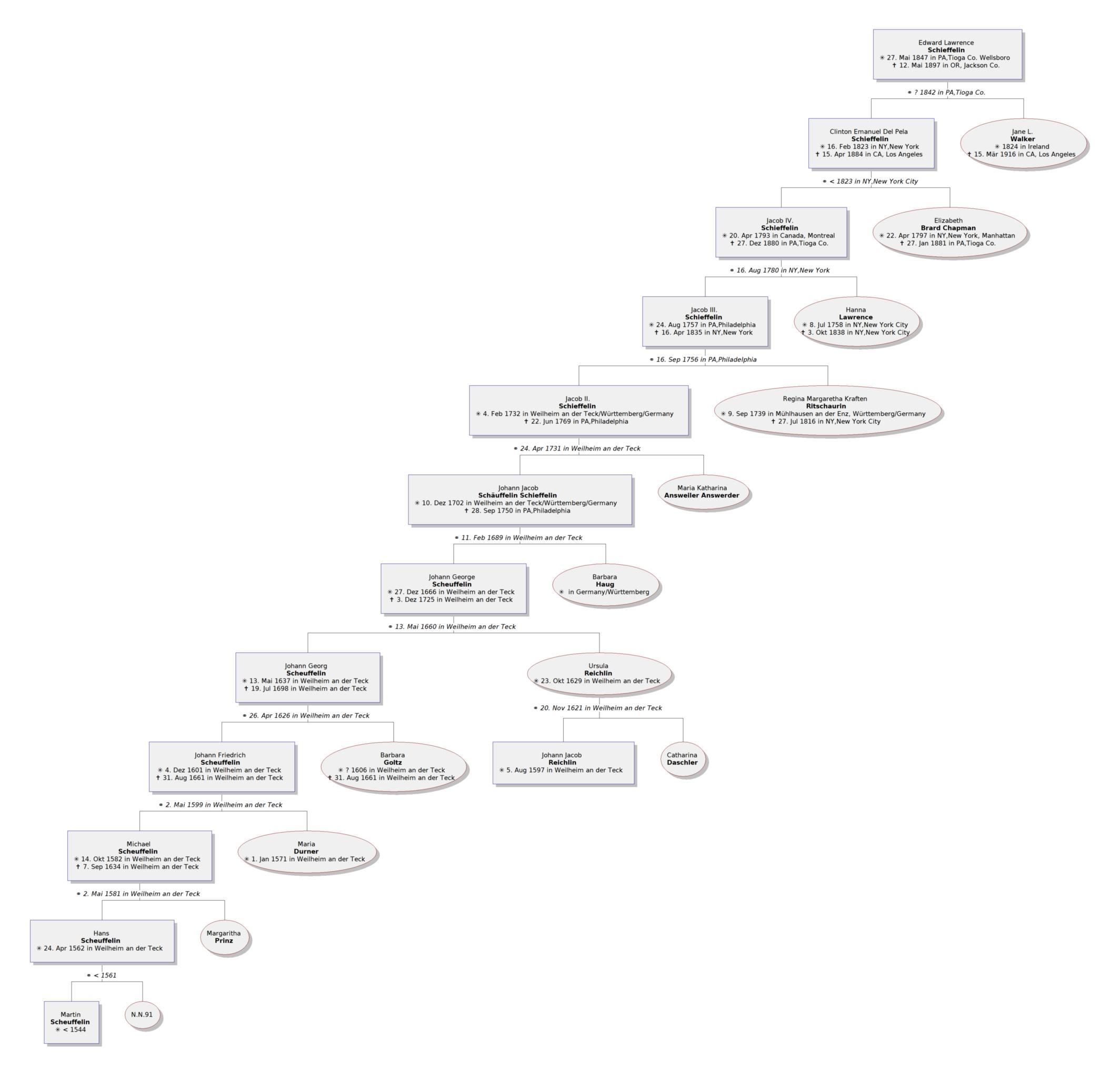
Ed Schieffelin
Edward Lawrence Schieffelin (1847–1897) was an U.S. Army Indian Scouts, Indian scout and prospecting, prospector who discovered silver in the Arizona Territory, which led to the founding of Tombstone, Arizona. He partnered with his brother Al and mining engineer Richard Gird in a gentleman's agreement, handshake deal that produced millions of dollars in wealth for all three men. During the course of Tombstone's mining history, about US $85,000,000 in silver was produced from its mines. Early life Ed Schieffelin was born in a coal-mining region of Wellsboro, Pennsylvania, the son of a prominent New York and Pennsylvania family, in 1847. His great-grandfather Jacob Schieffelin, Sr., born in 1757, joined the Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalist army and served as Henry Hamilton (governor), Henry Hamilton's secretary during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. Schieffelin was captured in 1779 and held prisoner in Williamsburg, Virginia. He escaped to Canada, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Axtell
James L. Axtell (born December 20, 1941 in Endicott, New York) is an American historian. He was a professor of history at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. Axtell, whose interests lie in American Indian history and the history of higher education, was the William R. Kenan, Jr. Professor of Humanities. He was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, a ... in 2004. Axtell retired at the end of the spring 2008 semester, although he taught a class at Princeton University in the fall of 2009. |




.jpg)