|
Equal-loudness Contour
An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure level, over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours. By definition, two sine waves of differing frequencies are said to have equal-loudness level measured in phons if they are perceived as equally loud by the average young person without significant hearing impairment. The Fletcher–Munson curves are one of many sets of equal-loudness contours for the human ear, determined experimentally by Harvey Fletcher and Wilden A. Munson, and reported in a 1933 paper entitled "Loudness, its definition, measurement and calculation" in the ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America''. Fletcher–Munson curves have been superseded and incorporated into newer standards. The definitive curves are those defined in ISO 226 from the International O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Of Pain
The threshold of pain or pain threshold is the point along a curve of increasing perception of a stimulus at which pain begins to be felt. It is an entirely subjective phenomenon. A distinction must be maintained between the stimulus (an external thing that can be directly measured, such as with a thermometer) and the person's or animal's resulting pain perception (an internal, subjective thing that can sometimes be measured indirectly, such as with a visual analog scale). Although an IASP document defines "pain threshold" as "the minimum intensity of a stimulus that is perceived as painful", it then goes on to say (contradictorily in letter although not in spirit) that: Traditionally the threshold has often been defined, as we defined it formerly, as the least stimulus intensity at which a subject perceives pain. Properly defined, the threshold is really the experience of the patient, whereas the intensity measured is an external event. It has been common usage for most pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighting Curve
A weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. An important example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A-, B-, C-, and D-weighting as defined in IEC 61672 are used. Unweighted measurements of sound pressure do not correspond to perceived loudness because the human ear is less sensitive at low and high frequencies, with the effect more pronounced at lower sound levels. The four curves are applied to the measured sound level, for example by the use of a weighting filter in a sound level meter, to arrive at readings of loudness in phons or in decibels (dB) above the threshold of hearing (see A-weighting). Weighting curves in electronic engineering, audio, and broadcasting Although A-weighting with a slow RMS detector, as commonly used in sound level meters is frequently used when measuring noise in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Band
In audiology and psychoacoustics the concept of critical bands, introduced by Harvey Fletcher in 1933 and refined in 1940, describes the frequency bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth of the "auditory filter" created by the cochlea, the sense organ of hearing within the inner ear. Roughly, the critical band is the band of audio frequency, audio frequencies within which a second tone will interfere with the perception of the first tone by auditory masking. Psychophysiology, Psychophysiologically, Beat (acoustics), beating and Roughness (psychophysics), auditory roughness sensations can be linked to the inability of the auditory frequency-analysis mechanism to resolve inputs whose frequency difference is smaller than the critical bandwidth and to the resulting irregular "tickling" of the mechanical system (basilar membrane) that resonates in response to such inputs. Critical bands are also closely related to auditory masking phenomena – reduced audibility of a sound signal when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Measurement
In acoustics, noise measurement can be for the purpose of measuring environmental noise or measuring noise in the workplace. Applications include monitoring of construction sites, aircraft noise, road traffic noise, entertainment venues and neighborhood noise. One of the definitions of noise covers all "unwanted sounds". When sound levels reach a high enough intensity, the sound, whether it is wanted or unwanted, may be damaging to hearing. Environmental noise monitoring is the measurement of noise in an outdoor environment caused by transport (e.g. motor vehicles, aircraft, and trains), industry (e.g. machines) and recreational activities (e.g. music). The laws and limits governing environmental noise monitoring differ from country to country. At the very least, noise may be annoying or displeasing or may disrupt the activity or balance of human or animal life, increasing levels of aggression, hypertension and stress. In the extreme, excessive levels or periods of noise can have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Harmonic Distortion
The total harmonic distortion (THD or THDi) is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present in a signal and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency. Distortion factor, a closely related term, is sometimes used as a synonym. In audio systems, lower distortion means that the components in a loudspeaker, amplifier or microphone or other equipment produce a more accurate reproduction of an audio recording. In radio communications, devices with lower THD tend to produce less unintentional interference with other electronic devices. Since harmonic distortion can potentially widen the frequency spectrum of the output emissions from a device by adding signals at multiples of the input frequency, devices with high THD are less suitable in applications such as spectrum sharing and spectrum sensing. In power systems, lower THD implies lower peak currents, less heating, lower electromagnetic emissions, and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
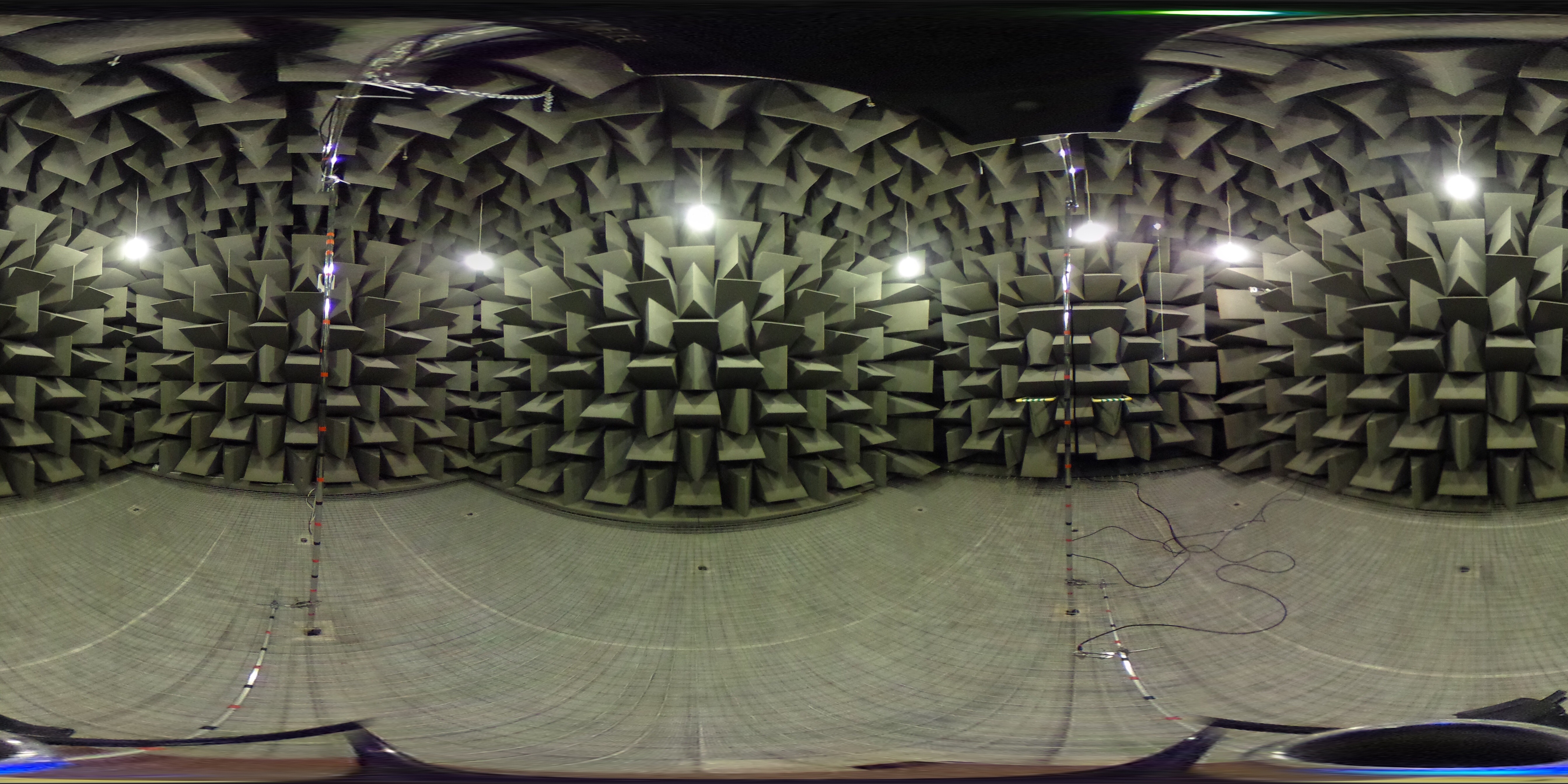
Anechoic Chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective" or "without echoes") is a room designed to stop reflection (physics), reflections or Echo (phenomenon), echoes of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reverberation, reflected sounds), in effect simulating being outside in a free field. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to other radio frequency (RF) and sonar anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kellogg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-related Transfer Function
A head-related transfer function (HRTF) is a response that characterizes how an ear receives a sound from a point in space. As sound strikes the listener, the size and shape of the head, ears, ear canal, density of the head, size and shape of nasal and oral cavities, all transform the sound and affect how it is perceived, boosting some frequencies and attenuating others. Generally speaking, the HRTF boosts frequencies from 2–5 kHz with a primary resonance of +17 dB at 2,700 Hz. But the response curve is more complex than a single bump, affects a broad frequency spectrum, and varies significantly from person to person. A pair of HRTFs for two ears can be used to synthesize a binaural sound that seems to come from a particular point in space. It is a transfer function, describing how a sound from a specific point will arrive at the ear (generally at the outer end of the auditory canal). Some consumer home entertainment products designed to reproduce surround so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinna (anatomy)
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna (Latin for 'wing' or ' fin', : pinnae), a term that is used more in zoology. Structure The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components: * '' antihelix'' forms a 'Y' shape where the upper parts are: ** ''Superior crus'' (to the left of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) ** ''Inferior crus'' (to the right of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) * ''Antitragus'' is below the ''tragus'' * ''Aperture'' is the entrance to the ear canal * ''Auricular sulcus'' is the depression behind the ear next to the head * ''Concha'' is the hollow next to the ear canal * Conchal angle is the angle that the back of the ''concha'' makes with the side of the head * ''Crus'' of the helix is just above the ''tragus'' * ''Cymba conchae'' is the narrowest end of the ''concha'' * External auditory meatus is the ear canal * ''Fossa triangularis'' is the depression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Shadow
A head shadow (or acoustic shadow) is a region of reduced amplitude of a sound because it is obstructed by the head. It is an example of diffraction. Sound may have to travel through and around the head in order to reach an ear. The obstruction caused by the head can account for attenuation (reduced amplitude) of overall intensity as well as cause a filtering effect. The filtering effects of head shadowing are an essential element of sound localisation—the brain weighs the relative amplitude, timbre, and phase of a sound heard by the two ears and uses the difference to interpret directional information. The shadowed ear, the ear further from the sound source, receives sound slightly later (up to approximately 0.7 ms later) than the unshadowed ear, and the timbre, or frequency spectrum In signal processing, the power spectrum S_(f) of a continuous time signal x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components f composing that signal. According to Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stapedius Muscle
The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ... in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or stirrup bone of the middle ear. Structure The stapedius emerges from a pinpoint foramen or opening in the apex of the pyramidal eminence (a hollow, cone-shaped prominence in the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity), and inserts into the neck of the stapes. Nerve supply The stapedius is supplied by the nerve to stapedius, a branch of the facial nerve. Function The stapedius dampens the vibrations of the stapes by pulling on the neck of that bone. As one of the muscles involved in the acoustic reflex it prevents excess movement of the stapes, helping to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |