|
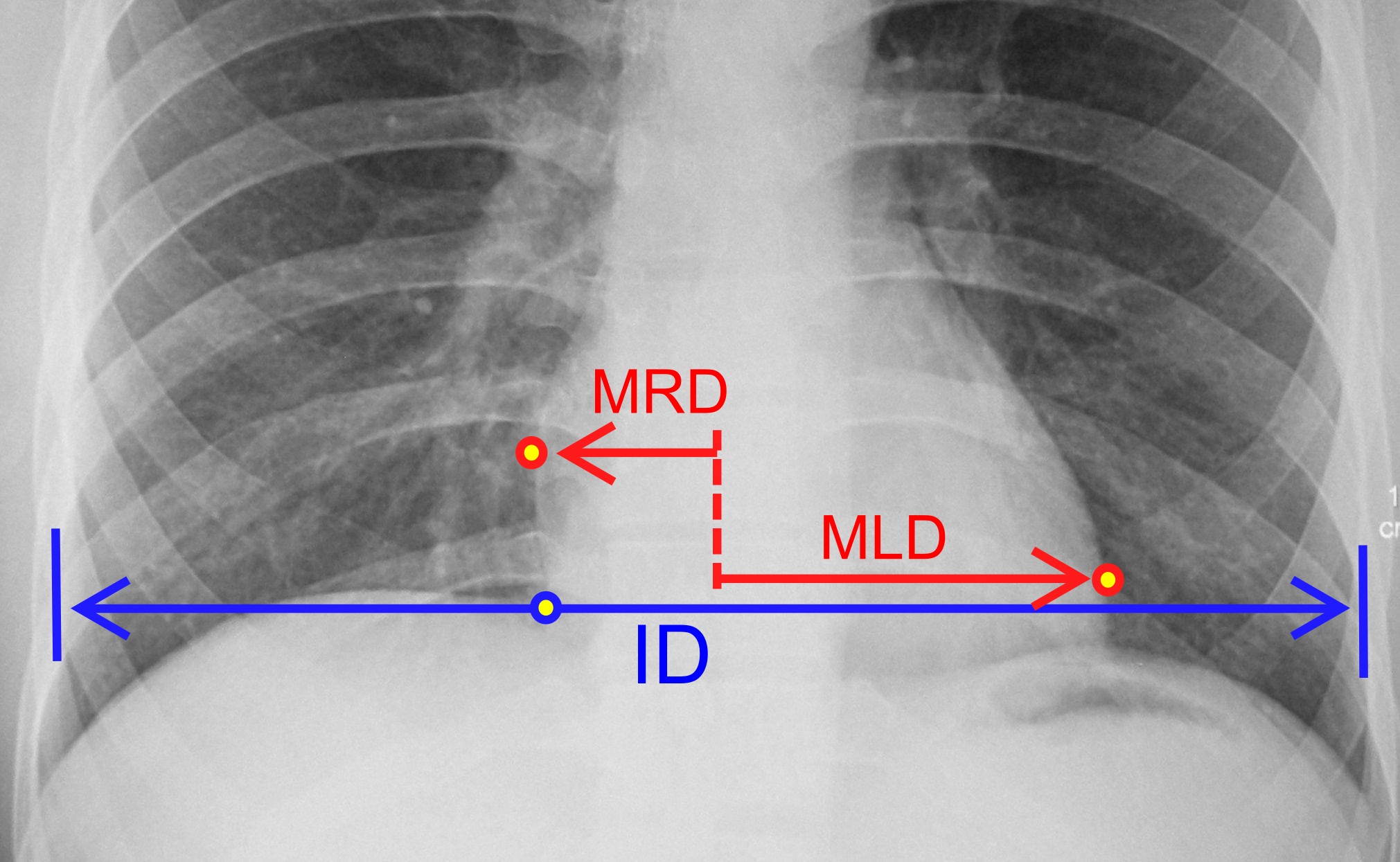
Enlarged Heart
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the heart is enlarged. As such, it is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity, heart valve disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly can be serious depending on what part of the heart is enlarged, and can result in congestive heart failure. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death. Cardiomegaly may improve over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong treatment with medication. Having an immediate family member who has or had cardiomegaly may indicate that a person is more susceptible to getting this condition. Signs and symptoms For many people, cardiomegaly is asymptomatic. For ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
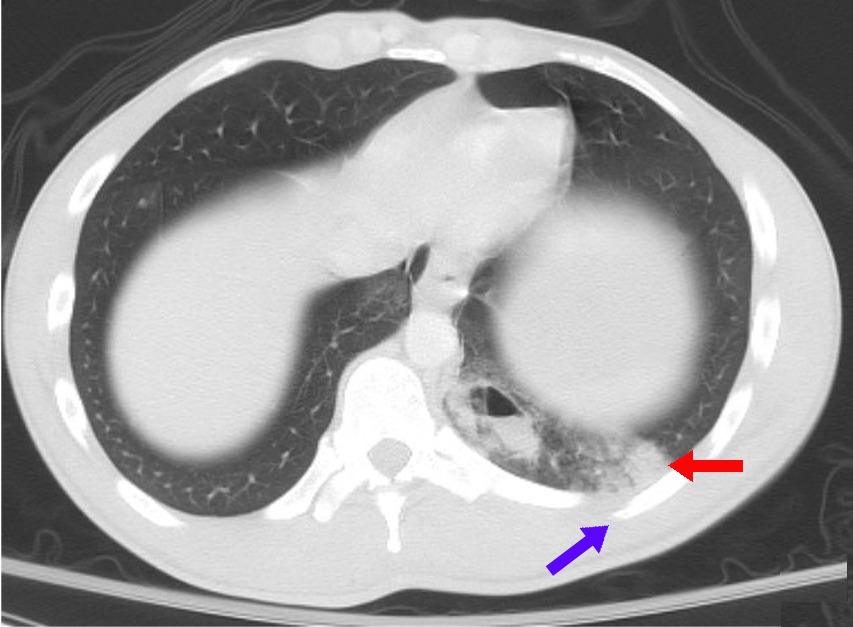
Effusion
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Such a hole is often described as a ''pinhole'' and the escape of the gas is due to the pressure difference between the container and the exterior. Under these conditions, essentially all molecules which arrive at the hole continue and pass through the hole, since collisions between molecules in the region of the hole are negligible. Conversely, when the diameter is larger than the mean free path of the gas, flow obeys the Sampson flow law. In medical terminology, an effusion refers to accumulation of fluid in an anatomic space, usually without loculation. Specific examples include subdural, mastoid, pericardial and pleural effusions. Etymology The word effusion derives from the Latin word, effundo, which means "shed, pour forth, pour out, utter, lavish, waste." Effusion into vacuum Effusion from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and one on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocardiograms
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia). Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvular Heart Disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging,Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano. Lancet. 2006 Sep;368(9540):1005-11. but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy. Anatomically, the valves are part of the dense connective tissue of the heart known as the cardiac skeleton and are responsible for the regulation of blood flow through the heart and great vessels. Valve failure or dysfunction can result in diminished heart functionality, though the particular consequences are dependent on the type and severity of valvular disease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerotic
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, electrocardiogram, and exercise stress test, am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

