|
Engineering Psychology
Engineering psychology, also known as Human Factors Engineering, is the science of human behavior and capability, applied to the design and operation of systems and technology. As an applied field of psychology and an interdisciplinary part of ergonomics, it aims to improve the relationships between people and machines by redesigning equipment, interactions, or the environment in which they take place. The work of an engineering psychologist is often described as making the relationship more "user-friendly." History Engineering psychology was created from within experimental psychology. Engineering psychology started during World War I (1914). The reason why this subject was developed during this time was because many of America's weapons were failing; bombs not falling in the right place to weapons attacking normal marine life. The fault was traced back to human errors. One of the first designs to be built to restrain human error was the use of psychoacoustics by S.S. Stevens an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Behavior
Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity ( mentally, physically, and socially) of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external stimuli throughout their life. Kagan, Jerome, Marc H. Bornstein, and Richard M. Lerner.Human Behaviour." ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020. Behavior is driven by genetic and environmental factors that affect an individual. Behavior is also driven, in part, by thoughts and feelings, which provide insight into individual psyche, revealing such things as attitudes and values. Human behavior is shaped by psychological traits, as personality types vary from person to person, producing different actions and behavior. Social behavior accounts for actions directed at others. It is concerned with the considerable influence of social interaction and culture, as well as ethics, interpersonal relationships, politics, and conflict. Some behaviors are common while others are unusual. The acceptab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Fatigue Research Board
Industrial may refer to: Industry * Industrial archaeology, the study of the history of the industry * Industrial engineering, engineering dealing with the optimization of complex industrial processes or systems * Industrial city, a city dominated by one or more industries * Industrial loan company, a financial institution in the United States that lends money, and may be owned by non-financial institutions * Industrial organization, a field that builds on the theory of the firm by examining the structure and boundaries between firms and markets * Industrial Revolution, the development of industry in the 18th and 19th centuries * Industrial society, a society that has undergone industrialization * Industrial technology, a broad field that includes designing, building, optimizing, managing and operating industrial equipment, and predesignated as acceptable for industrial uses, like factories * Industrial video, a video that targets “industry” as its primary audience * Industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
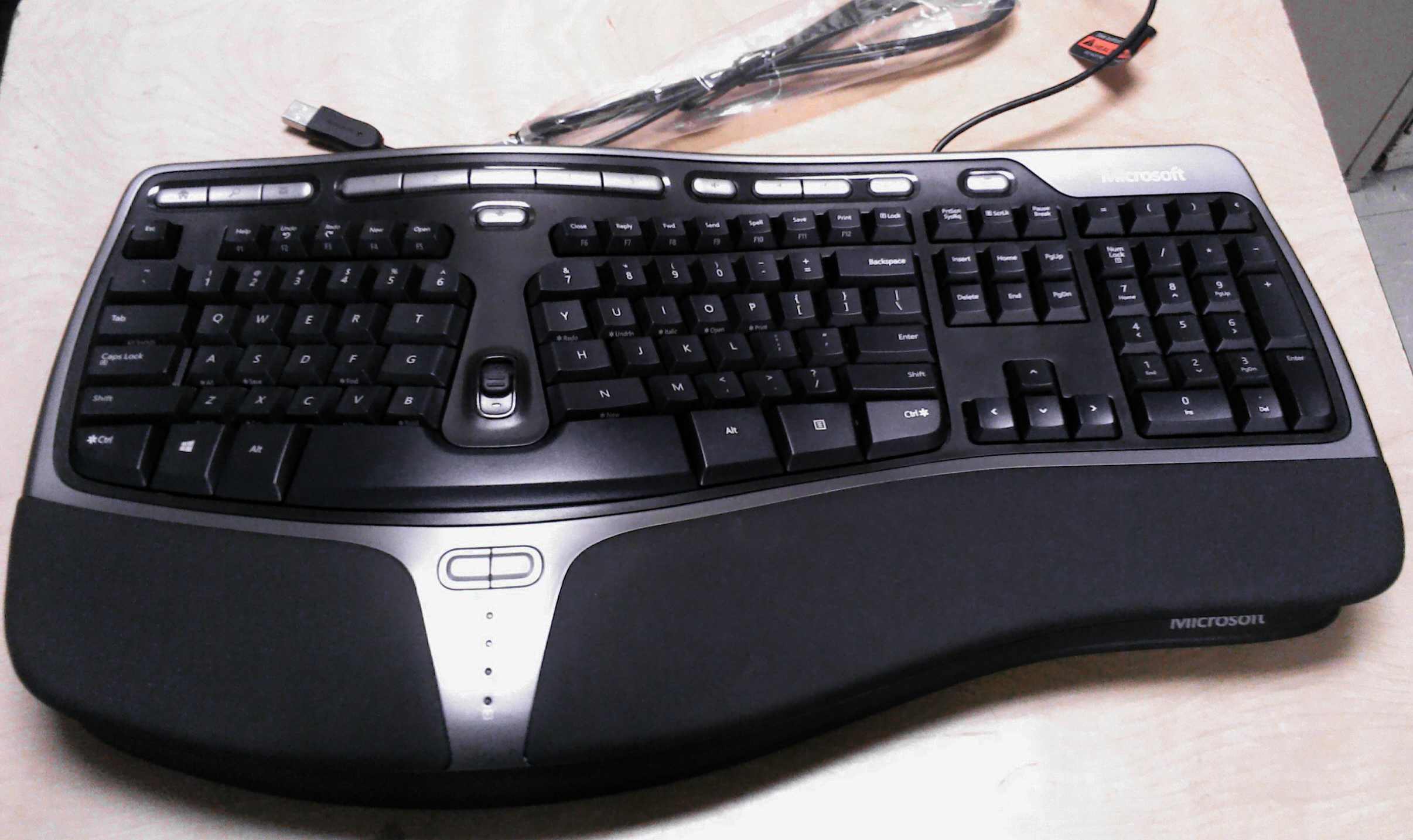
Ergonomics
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learning are to reduce human error, increase productivity, and enhance safety, system availability, and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and the engineered system. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to the four primary goals above. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculoskeletal Injury
Musculoskeletal injury refers to damage of muscular or skeletal systems, which is usually due to a strenuous activity and includes damage to skeletal muscles, bones, tendons, joints, ligaments, and other affected soft tissues. In one study, roughly 25% of approximately 6300 adults received a musculoskeletal injury of some sort within 12 months—of which 83% were activity-related. Musculoskeletal injury spans into a large variety of medical specialties including orthopedic surgery (with diseases such as arthritis requiring surgery), sports medicine, emergency medicine ( acute presentations of joint and muscular pain) and rheumatology (in rheumatological diseases that affect joints such as rheumatoid arthritis). Musculoskeletal injuries can affect any part of the human body including; bones, joints, cartilages, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and other soft tissues. Symptoms include mild to severe aches, low back pain, numbness, tingling, atrophy and weakness. These injuries are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Factors
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learning are to reduce human error, increase productivity, and enhance safety, system availability, and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and the engineered system. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to the four primary goals above. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Factors
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learning are to reduce human error, increase productivity, and enhance safety, system availability, and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and the engineered system. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to the four primary goals above. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Engineering
Cognitive engineering is a method of study using cognitive psychology to design and develop engineering systems to support the cognitive processes of users. History It was an engineering method used in the 1970s at Bell Labs, focused on how people form a cognitive model of a system based upon common metaphors. As explained, by Joseph Henry Condon: According to Condon, the ideas of cognitive engineering were developed later than, and independent from, the early work on the Unix operating system. Don Norman cited principles of cognitive engineering in his 1981 article, "The truth about Unix: The user interface is horrid." Norman criticized the user interface of Unix as being "a disaster for the casual user." However the "casual user" is not the target audience for UNIX and as the Condon quote above indicates, a high level of user interface abstraction leads to cognitive models that may be "totally erroneous." See also * History of Unix The history of Unix dates back to the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Ergonomics
Cognitive ergonomics is a scientific discipline that studies, evaluates, and designs tasks, jobs, products, environments and systems and how they interact with humans and their cognitive abilities. It is defined by the International Ergonomics Association as "concerned with mental processes, such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, as they affect interactions among humans and other elements of a system. Cognitive ergonomics is responsible for how work is done in the mind, meaning, the quality of work is dependent on the persons understanding of situations. Situations could include the goals, means, and constraints of work. The relevant topics include mental workload, decision-making, skilled performance, human-computer interaction, human reliability, work stress and training as these may relate to human-system design." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit For Research In Applied Psychology
The Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit is a branch of the UK Medical Research Council, based in Cambridge, England. The CBSU is a centre for cognitive neuroscience, with a mission to improve human health by understanding and enhancing cognition and behaviour in health, disease and disorder. It is one of the largest and most long-lasting contributors to the development of psychological theory and practice. The CBSU has its own magnetic resonance imaging (MRI, 3T) scanner on-site, as well as a 306-channel magnetoencephalography (MEG) system and a 128-channel electroencephalography (EEG) laboratory. The CBSU has close links to clinical neuroscience research in the University of Cambridge Medical School. Over 140 scientists, students, and support staff work in research areas such as Memory, Attention, Emotion, Speech and Language, Development and Aging, Computational Modelling and Neuroscience Methods. With dedicated facilities available on site, the Unit has particular strengths i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Craik
Kenneth James William Craik (; 1914 – 1945) was a Scottish philosopher and psychologist. Life He was born in Edinburgh on 29 March 1914, the son of James Craik, a solicitor. The family lived at 13 Abercromby Place in Edinburgh's Second New Town (previously the home of William Trotter). He was educated at Edinburgh Academy then studied philosophy at the University of Edinburgh. He received his doctorate from Cambridge University in 1940. He then had a fellowship to St John's College, Cambridge in 1941, where he worked with Magdalen Dorothea Vernon and published papers with her about dark adaptation in 1941 and 1943. He was appointed to be the first director of the Medical Research Council's Cambridge-based Applied Psychology Unit in 1944. During the Second World War he served in the fire-fighting sections of the Civil Defence. Together with Gordon Butler Iles he made major advances on flight simulators for the RAF and did major studies on the effects of fatigue on pilot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederic Bartlett
Sir Frederic Charles Bartlett FRS (20 October 1886 – 30 September 1969) was a British psychologist and the first professor of experimental psychology at the University of Cambridge. He was one of the forerunners of cognitive psychology as well as cultural psychology.Wagoner, B. (2017). The Constructive Mind: Bartlett's Psychology in Reconstruction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Bartlett considered most of his own work on cognitive psychology to be a study in social psychology, but he was also interested in anthropology, moral science, philosophy, and sociology. Bartlett proudly referred to himself as "a Cambridge psychologist" because while he was at the University of Cambridge, settling for one type of psychology was not an option. Biography Frederic Bartlett was born on 20 October 1886 into a middle-class family and raised in Gloucestershire, England. Childhood was not easy for Bartlett. He suffered from pleurisy at a young age, causing him to be homeschooled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |