|
Energy Rating Label
In Australia and New Zealand, an energy rating label or energy rating is a label affixed to various appliances prior to retail sale, which allows consumers to compare the Efficient energy use#Appliances, energy efficiency of product and allows consumers to know how much power a particular model will use to run. They allow consumers to compare the energy consumption of similar products, and factor lifetime running cost into their purchasing decision.Labelling Overview [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Rating Label
In Australia and New Zealand, an energy rating label or energy rating is a label affixed to various appliances prior to retail sale, which allows consumers to compare the Efficient energy use#Appliances, energy efficiency of product and allows consumers to know how much power a particular model will use to run. They allow consumers to compare the energy consumption of similar products, and factor lifetime running cost into their purchasing decision.Labelling Overview [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Policy In Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal. Federal policies for energy in Australia continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production. Australia is the 10th most coal-dependent country in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage and the coal industry produces over 30% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. In 2018 Australia was the 8th highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the world. Australia's energy policy features a combination of coal power stations and hydro electricity plants. The Australian government has decided not to build nuclear power plants, although it is one of the world's largest producers of uranium. Electricit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of New Zealand
The environment of New Zealand is characterised by an endemic flora and fauna which has evolved in near isolation from the rest of the world. The main islands of New Zealand span two biomes, temperate and subtropical, complicated by large mountainous areas above the tree line.Walter, H. & Breckle, S-W. (2002). ''Walter's Vegetation of the Earth: The Ecological Systems of the Geo-Biosphere''. New York: Springer-Verlag, p. 86 There are also New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, numerous smaller islands which extend into the subantarctic. The prevailing weather systems bring significantly more rain to the west of the country. New Zealand's territorial waters cover a much larger area than its landmass and extend over the continental shelf and abyssal plateau in the South Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea and Southern ocean. Historically having an isolated and endemic ecosystem far into modernity, the arrival of Polynesians about 1300 AD and then later European settlers began to have significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of Australia
The Australian environment ranges from virtually pristine Antarctic territory and rainforests to degraded industrial areas of major cities. Forty distinct ecoregions have been identified across the Australian mainland and islands. Central Australia has a very dry climate. The interior has a number of deserts while most of the coastal areas are populated. Northern Australia experiences tropical cyclones while much of the country is prone to periodic drought. This dry and warm environment and exposure to cyclones, makes Australia particularly vulnerable to climate change -- with some areas already experiencing increases in wildfires and fragile ecosystems. The island ecology of Australia has led to a number of unique endemic plant and animal species, notably marsupials like the kangaroo and koala. Agriculture and mining are predominant land uses which cause negative impacts on many different ecosystems. The management of the impact on the environment from the mining industry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy In New Zealand
Despite abundant natural resources and a relatively small population, New Zealand is a net importer of energy, in the form of petroleum products. The ratio of non-renewable and renewable energy sources was fairly consistent from 1975 to 2008, with about 70 percent of primary energy supply coming from hydrocarbon fuels. This ratio decreased to about 60 percent in 2018. The proportion of non-renewable energy varies annually, depending on water flows into hydro-electricity lakes and demand for energy. In 2018, approximately 60% of primary energy was from non-renewable hydrocarbon fuels and 40% was from renewable sources. In 2007 energy consumption per capita was 120 gigajoules. Per capita energy consumption had increased 8 per cent since 1998. New Zealand uses more energy per capita than 17 of 30 OECD countries. New Zealand is one of 13 OECD countries that does not operate nuclear power stations. From 1994 to 2018, the energy intensity of the economy per unit of GDP declined by 33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
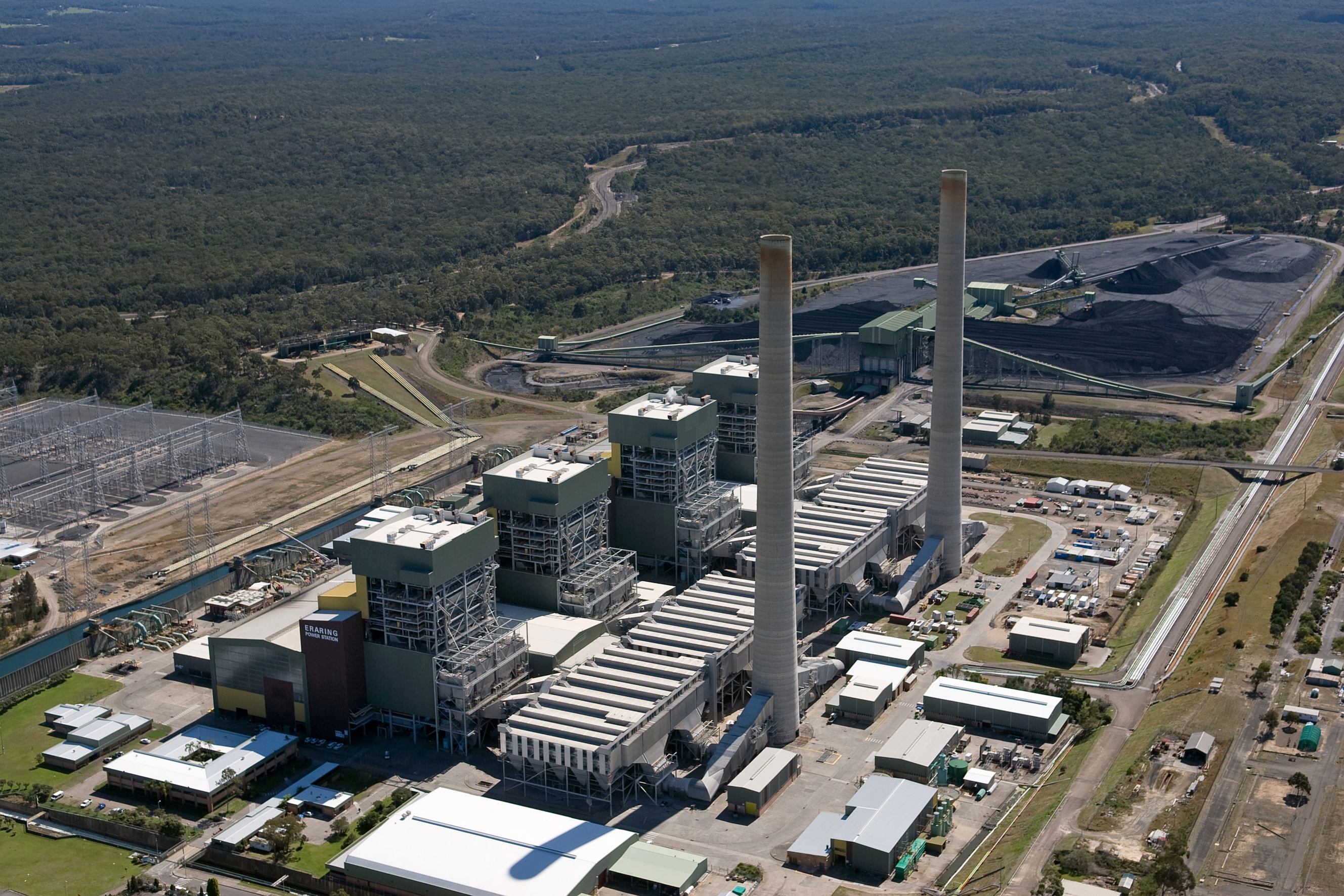
Energy In Australia
Energy in Australia is the production in Australia of energy and electricity, for consumption or export. Energy policy of Australia describes the politics of Australia as it relates to energy. Australia is a net energy exporter, and was the fourth-highest coal producer in the world in 2009. Energy in Australia is sourced largely from coal and natural gas, however, recently, due to the increasing effects of global warming and human-induced climate change on the global environment, there has been a shift towards renewable energy such as solar power and wind power both in Australia and abroad. In 2020, renewable energy accounted for 27.7% of the total amount of electricity generated in Australia. Overview In 2009, Australia had the highest per capita emissions in the world. At that time, Maplecroft's Energy Emissions Index (CEEI) showed that Australia releases 20.58 tons of per person per year, more than any other country. However, emissions have since been reduced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Efficiency And Conservation Authority
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA) is a New Zealand government/Crown agency responsible for promoting energy efficiency and conservation. The EECA was set up by the Fourth National Government of New Zealand in 1992 to encourage, support and promote energy efficiency, energy conservation, and the use of renewable sources of energy. The EECA, by promoting energy efficiency, helps to reduce climate change and GHG emissions through energy efficiency measures. History In 2000 EECA became a Crown entity, established under the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Act 2000. It is subject to the Crown Entities Act 2004. The passing of the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Act meant that for the first time, New Zealand had a legislative basis for promoting energy efficiency, energy conservation, and renewable energy. The Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority is responsible for preparing a national energy efficiency and conservation strategy for approval by the admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WELS Rating
Water Efficiency Labelling and Standard (WELS) is a labeling scheme initiated by the Australian Government to help Australian households conserve water and money. On 1 July 2006, it became mandatory across Australia to carry a (WELS) Water Rating label when selling showers, washing machines, dishwashers, toilet equipment, urinal equipment and tap equipment intended for use over kitchen sinks, bathroom basins, laundry tubs or ablution troughs. See also *Energy rating label *Water efficiency Water efficiency is the practice of reducing water consumption by measuring the amount of water required for a particular purpose and is proportionate to the amount of essential water used.Vickers, Amy. “Water use and conservation." Amherst, MA ... References External links Water Rating scheme 2006 introductions Ecolabelling Water conservation Water supply and sanitation in Australia {{Watersupply-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
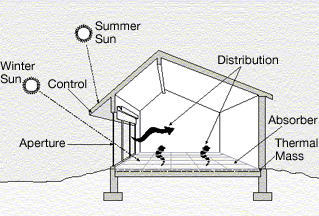
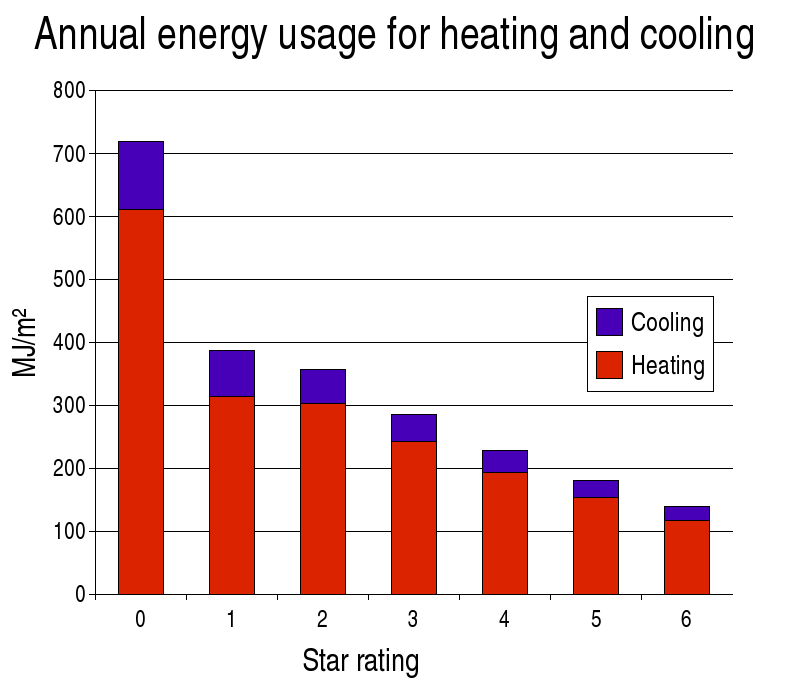
House Energy Rating
The Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme (NatHERS) is a national scheme to measure the energy conservation, energy efficiency of a residential dwelling in Australia. An accredited software tool assesses the home based on a variety of criteria and produces an energy star rating. Background and history The Five Star Design Rating (FSDR) was an award developed in the 1980s for "high efficiency through excellence in design and construction" which assisted builders in marketing energy efficient home designs. The certification was developed by the Glass, Mass and Insulation Council of Australia (GMI Council) together with CSIRO Division of Building Research. The GMI Council was funded by Government of Australia, Federal and state governments (New South Wales Government, New South Wales, Government of South Australia, South Australia, Tasmanian Government, Tasmania, and Victorian Government, Victoria) and by private investors. Under FSDR, the basic elements of glass, mass and insul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union Energy Label
EU Directive 92/75/EC established an energy consumption labelling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites. In an attempt to keep up with advances in energy efficiency, A+, A++ and A+++ grades were later introduced for various products; since 2010, a new type of label exists that makes use of pictograms rather than words, to allow manufacturers to use a single label for products sold in different countries. Directive 92/75/EC was replaced by Direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Sector In New Zealand
The electricity sector in New Zealand uses mainly renewable energy, such as Hydroelectricity, hydropower, geothermal energy, geothermal power and increasingly wind energy. , 82% of electricity is generated from renewable sources, making New Zealand one of the countries with the lowest carbon dioxide emissions from electricity generation. Electricity demand grew by an average of 2.1% per year from 1974 to 2010 but decreased by 1.2% from 2010 to 2013. The New Zealand electricity market, electricity market is regulated by the Electricity Authority (New Zealand), Electricity Authority. Electricity lines businesses, including Transpower New Zealand, Transpower and the distribution lines companies, are regulated by the Commerce Commission. Control is also exerted by the minister of energy in the New Zealand Cabinet, though the minister for state-owned enterprises and the minister for climate change also have some powers by virtue of their positions and policy influence in the governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |