|
Emerald Shiner
The emerald shiner (''Notropis atherinoides'') is one of hundreds of small, silvery, slender fish species known as shiners. The identifying characteristic of the emerald shiner is the silvery emerald color on its sides. It can grow to 3.5 inches in length and is found across North America from Canada to the Gulf of Mexico, commonly in large, deep lakes and rivers, though sometimes in smaller bodies of water as well. It feeds on small organisms such as zooplankton and insects, congregating in large groups near the surface of the water. It is a quite common fish and is often used as a bait fish. Distribution Emerald shiners are native to North America; they are widely distributed throughout Canada, and south to Virginia and Texas. They range to the gulf coast from Texas to Alabama, and are especially prevalent in the Mississippi Basin. Emerald shiners are most likely the most abundant fish in the Mississippi. Physical description Length Maximum size is 89–127 mm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz (; October 22, 1783September 18, 1840) was a French 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ultimately settling in Ohio in 1815, where he made notable contributions to botany, zoology, and the study of prehistoric earthworks in North America. He also contributed to the study of ancient Mesoamerican linguistics, in addition to work he had already completed in Europe. Rafinesque was an eccentric and erratic genius. He was an autodidact, who excelled in various fields of knowledge, as a zoologist, botanist, writer and polyglot. He wrote prolifically on such diverse topics as anthropology, biology, geology, and linguistics, but was honored in none of these fields during his lifetime. Indeed, he was an outcast in the American scientific community whose submissions were rejected automatically by leading journals. Among his theories were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both area (after Alaska) and population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the most populous city in Texas and the fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most populous in the state and seventh-largest in the U.S. Dallas–Fort Worth and Greater Houston are, respectively, the fourth- and fifth-largest metropolitan statistical areas in the country. Other major cities include Austin, the second most populous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
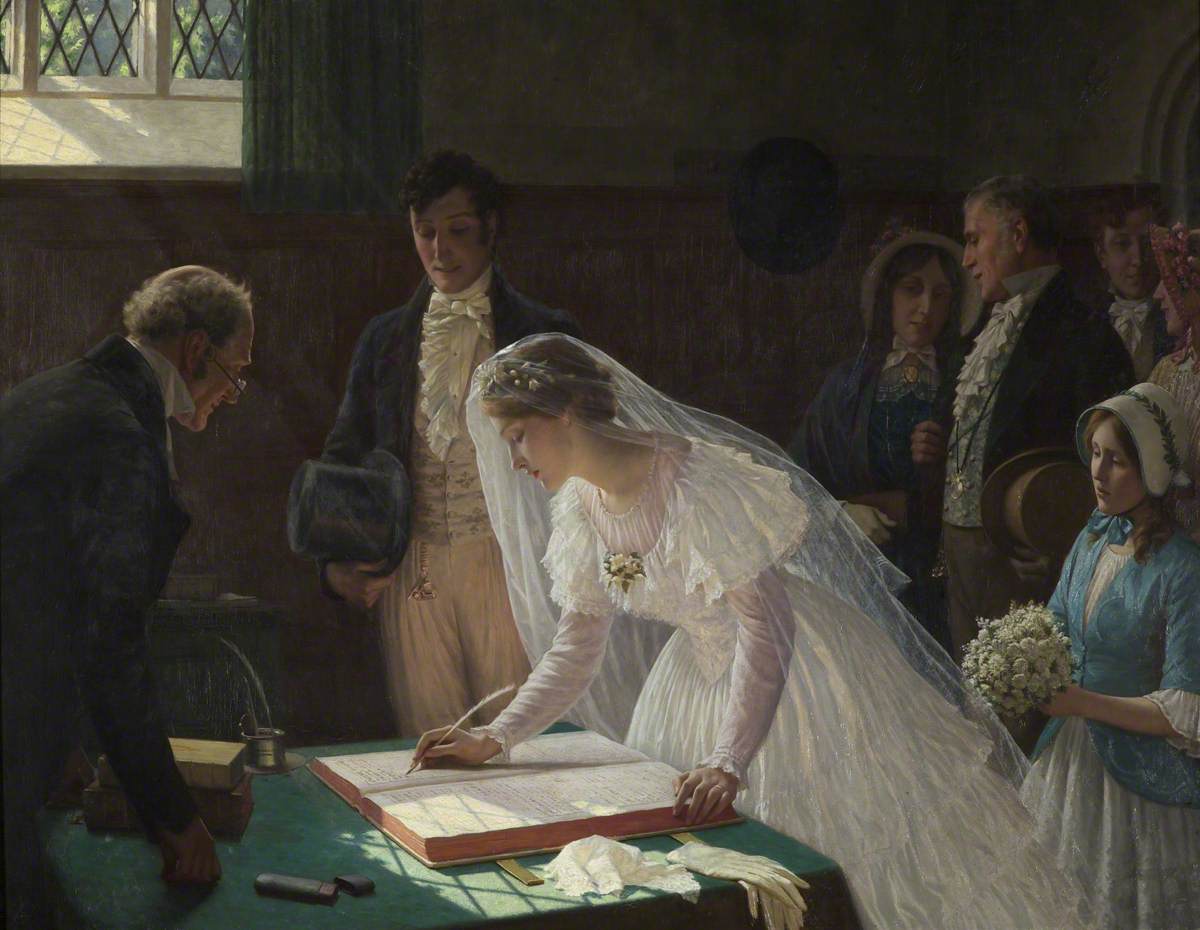
Nuptial
A wedding is a ceremony where two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriage vows by a couple, presentation of a gift (offering, rings, symbolic item, flowers, money, dress), and a public proclamation of marriage by an authority figure or celebrant. Special wedding garments are often worn, and the ceremony is sometimes followed by a wedding reception. Music, poetry, prayers, or readings from religious texts or literature are also commonly incorporated into the ceremony, as well as superstitious customs. Common elements across cultures Some cultures have adopted the traditional Western custom of the white wedding, in which a bride wears a white wedding dress and veil. This tradition was popularized through the marriage of Queen Victoria. Some say Victoria's choice of a white gown may have simply been a sign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opercle
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organisms canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fishy and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray (fish Fin Anatomy)
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim. Fins located in different places on the fish serve different purposes such as moving forward, turning, keeping an upright position or stopping. Most fish use fins when swimming, flying fish use pectoral fins for gliding, and frogfish use them for crawling. Fins can also be used for other purposes; male sharks and mosquitofish use a modified fin to deliver sperm, thresher sharks use their caudal fin to stun prey, reef stonefish have spines in their dorsal fins that inject venom, anglerfish use the first spine of their dorsal fin like a fishing rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through convergent evolution they have independently evolved external superficial fish-like body plans adapted to their marine environments, including most numerously fish, but also mammals such as cetaceans ( whales, dolphins, and porpoises), and even extinct ancient marine reptiles such as various known species of ichthyosaurs. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of large cetaceans to identify individuals in the field. The bony or cartilaginous bones that support the base of the dorsal fin in fish are called ''pterygiophores''. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is to stabilize the animal against ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerald Shiner 150506-A-IF251-936
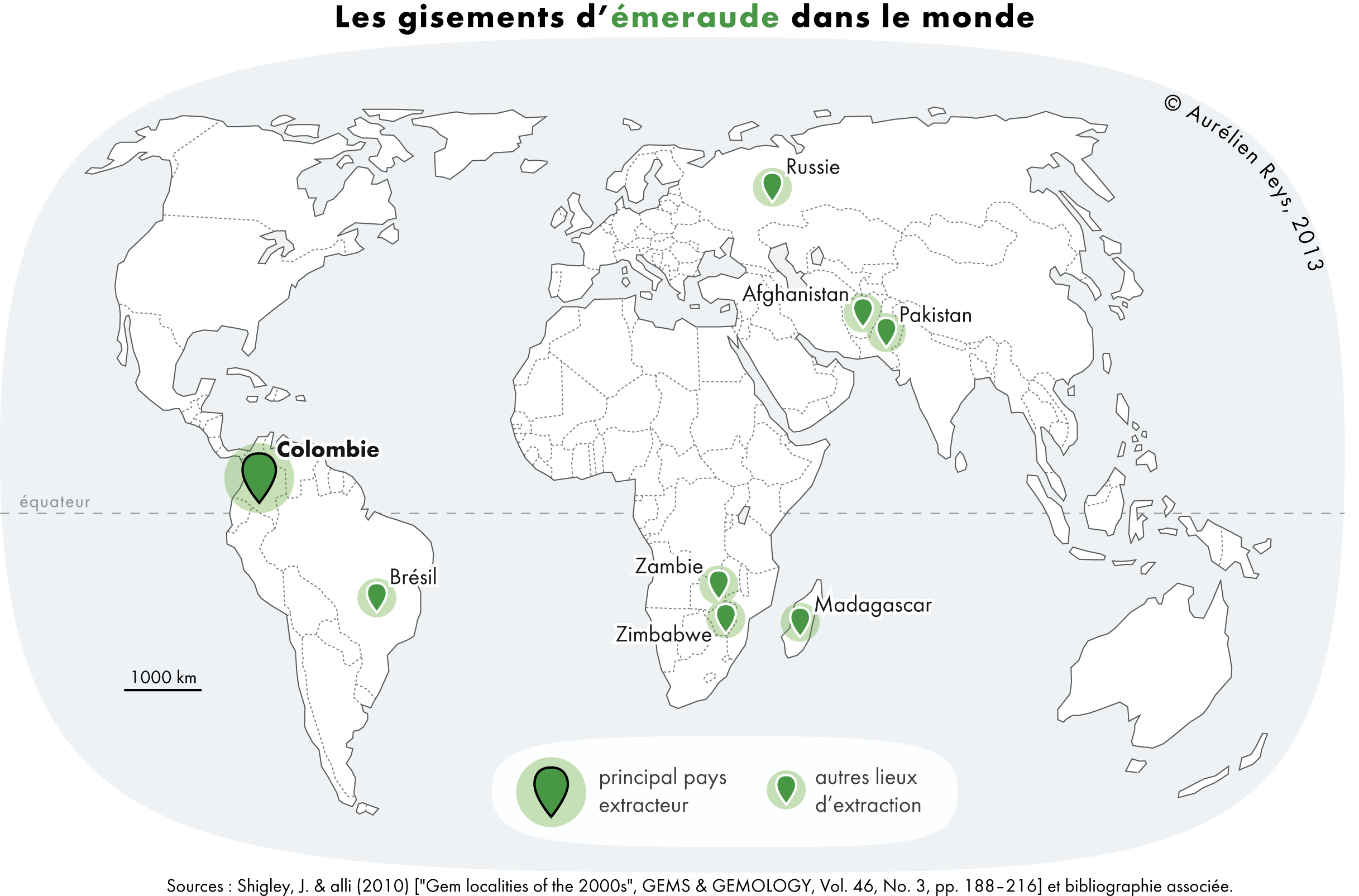
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds are highly included, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via fro, esmeraude and enm, emeraude), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda''/''esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was a via grc, σμάραγδος (smáragdos; "green gem") from a Semitic language. According to Webster's Dictionary the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters–the four ''C''s of connoisseurship: ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)