|
Embryo Profiling
Embryo quality is the ability of an embryo to perform successfully in terms of conferring a high pregnancy rate and/or resulting in a healthy person. Embryo profiling is the estimation of embryo quality by qualification and/or quantification of various parameters. Estimations of embryo quality guides the choice in embryo selection in ''in vitro'' fertilization. In general, embryo profiling for prediction of pregnancy rates focuses mainly on visual profiles and short-term biomarkers including expression of RNA and proteins, preferably in the surroundings of embryos to avoid any damage to them. On the other hand, embryo profiling for health prediction puts more focus on the genome, and where there is a risk of a genetic disorder it more often involves cell sampling from the embryo for preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Prediction of pregnancy rates Microscopy Embryo quality is mainly evaluated by microscopy at certain time points using a morphological scoring system. This has shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulosa Cell
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete (called an oocyte or egg) in the ovary of mammals. Structure and function In the primordial ovarian follicle, and later in follicle development (folliculogenesis), granulosa cells advance to form a multilayered cumulus oophorus surrounding the oocyte in the preovulatory or antral (or Graafian) follicle. The major functions of granulosa cells include the production of sex steroids, as well as myriad growth factors thought to interact with the oocyte during its development. The sex steroid production begins with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary, stimulating granulosa cells to convert androgens (coming from the thecal cells) to estradiol by aromatase during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. However, after ovulation the granulosa cells turn into granulosa lutein cells that produce progesterone. The progestero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a '' euploid'' cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of some genetic disorders. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells ( nondisjunction). Most cases of aneuploidy in the autosomes result in miscarriage, and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18 and 13. Chromosome abnormalities are detected in 1 of 160 live human births. Autosomal aneuploidy is more dangerous than sex chromosome aneuploidy, as autosomal aneuploidy is almost always lethal to embryos that cease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic (genetics)
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Genetic mosaics may often be confused with chimerism, in which two or more genotypes arise in one individual similarly to mosaicism. In chimerism, though, the two genotypes arise from the fusion of more than one fertilized zygote in the early stages of embryonic development, rather than from a mutation or chromosome loss. Genetic mosaicism can result from many different mechanisms including chromosome nondisjunction, anaphase lag, and endoreplication. Anaphase lagging is the most common way by which mosaicism arises in the preimplantation embryo. Mosaicism can also result from a mutation in one cell during development, in which case the mutation will be passed on only to its daughter cells (and will be present only in certain adu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Birth Rate
Pregnancy rate is the success rate for getting pregnant. It is the percentage of all attempts that leads to pregnancy, with attempts generally referring to menstrual cycles where insemination or any artificial equivalent is used, which may be simple artificial insemination (AI) or AI with additional in vitro fertilization (IVF). Definitions There is no universally accepted definition of the term. Thus in IVF pregnancy rates may be based on initiated treatment cycles, cycles that underwent oocyte retrieval, or cycles where an embryo transfer was performed. In terms of outcome, "pregnancy" may refer to a positive pregnancy test, evidence of a pregnancy with a "viable" fetus or implantation. Furthermore, pregnancy rates can be influenced in IVF by transferring multiple embryos that may result in multiple births. A strict definition in the IVF setting would refer to the singleton pregnancy rate that determines how many live singletons are born in relation to initiated IVF cycles. Relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing standard of care; these are then termed the 'experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annexin A2
Annexin A2 also known as annexin II is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANXA2'' gene. Annexin 2 is involved in diverse cellular processes such as cell motility (especially that of the epithelial cells), linkage of membrane-associated protein complexes to the actin cytoskeleton, endocytosis, fibrinolysis, ion channel formation, and cell matrix interactions. It is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein whose function is to help organize exocytosis of intracellular proteins to the extracellular domain. Annexin II is a pleiotropic protein meaning that its function is dependent on place and time in the body. Gene The ANXA2 gene, located at 15q22.2, has three pseudogenes located on chromosomes 4, 9 and 10, respectively. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function This protein is a member of the annexin family. Members of this calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein family pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stathmin
Stathmin, also known as metablastin and oncoprotein 18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STMN1'' gene. Stathmin is a highly conserved 17 kDa protein that is crucial for the regulation of the cell cytoskeleton. Changes in the cytoskeleton are important because the cytoskeleton is a scaffold required for many cellular processes, such as cytoplasmic organization, cell division and cell motility. More specifically, stathmin is crucial in regulating the cell cycle. It is found solely in eukaryotes. Its function as an important regulatory protein of microtubule dynamics has been well-characterized. Eukaryotic microtubules are one of three major components of the cell's cytoskeleton. They are highly dynamic structures that continuously alternate between assembly and disassembly. Stathmin performs an important function in regulating rapid microtubule remodeling of the cytoskeleton in response to the cell's needs. Microtubules are cylindrical polymers of α,β-tubulin. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
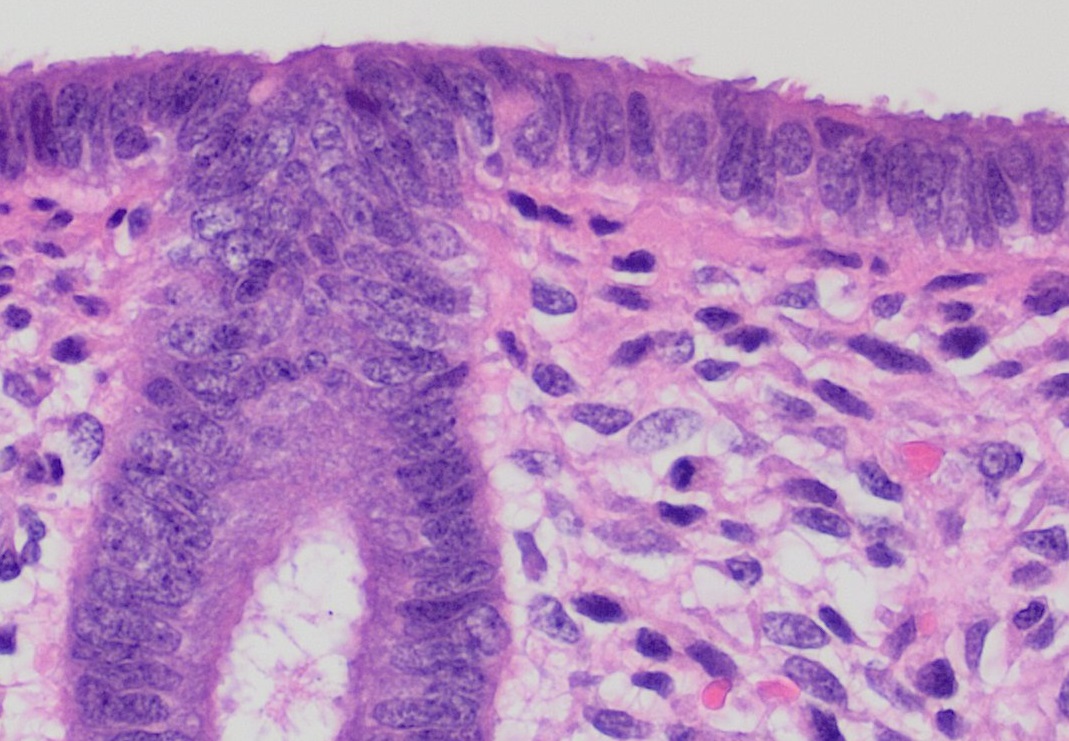
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-G
HLA-G histocompatibility antigen, class I, G, also known as human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HLA-G'' gene. HLA-G belongs to the HLA nonclassical class I heavy chain paralogues. Classical HLA I proteins are found on all nucleated cells and express peptides in their peptide binding groove. They can express "self" peptides when the cell is healthy as well as foreign peptides when the cell is infected by a parasite or cancer. HLA-G is a nonclassical protein and serves a different function from classical HLA class I molecules, but it still expresses a nine amino acid peptide in its peptide binding groove. The third and ninth amino acid in the peptide sequence serve as anchor residues, and are thus conserved in all the peptides HLA-G bind to. Structure This class I molecule is a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain and a light chain ( beta-2 microglobulin). The heavy chain is anchored in the membrane. HLA-G is coded for by 88 al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein secreted by macrophages, T cells, mast cells, natural killer cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts that functions as a cytokine. The pharmaceutical analogs of naturally occurring GM-CSF are called sargramostim and molgramostim. Unlike granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which specifically promotes neutrophil proliferation and maturation, GM-CSF affects more cell types, especially macrophages and eosinophils. Function GM-CSF is a monomeric glycoprotein that functions as a cytokine—it is a white blood cell growth factor. GM-CSF stimulates stem cells to produce granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and monocytes. Monocytes exit the circulation and migrate into tissue, whereupon they mature into macrophages and dendritic cells. Thus, it is part of the immune/ inflammatory cascade, by which activation of a small n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CXCL13
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (CXCL13), also known as B lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC) or B cell-attracting chemokine 1 (BCA-1), is a protein ligand that in humans is encoded by the ''CXCL13'' gene. Function CXCL13 is a small chemokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. As its other names suggest, this chemokine is selectively chemotactic for B cells belonging to both the B-1 and B-2 subsets, and elicits its effects by interacting with chemokine receptor CXCR5. CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5 control the organization of B cells within follicles of lymphoid tissues and is expressed highly in the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and gut of humans. The gene for CXCL13 is located on human chromosome 4 Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 186 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the to ... in a cluster of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |