|
Embodied Language Processing
Embodied cognition occurs when an organism's Sensory-motor coupling, sensorimotor capacities (ability of the body to respond to its senses with movement), body and environment play an important role in thinking. The way in which a person's body and their surroundings interacts also allows for specific brain functions to develop and in the future to be able to act.Cowart, M. (2005, Jul. 8 ). Embodied Cognition. http://www.iep.utm.edu/embodcog/ This means that not only does the mind influence the body's movements, but the body also influences the abilities of the mind, also termed the Bi-directional hypothesis of language and action, bi-directional hypothesis. There are three generalizations that are assumed to be true relating to embodied cognition. A person's motor system (that controls movement of the body) is activated when (1) they observe manipulable objects, (2) process action verbs, and (3) observe another individual's movements. Embodied semantics is one of two theorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embodied Cognition
Embodied cognition is the theory that many features of cognition, whether human or otherwise, are shaped by aspects of an organism's entire body. Sensory and motor systems are seen as fundamentally integrated with cognitive processing. The cognitive features include high-level mental constructs (such as concepts and categories) and performance on various cognitive tasks (such as reasoning or judgment). The bodily aspects involve the motor system, the perceptual system, the bodily interactions with the environment ( situatedness), and the assumptions about the world built into the organism's functional structure. The embodied mind thesis challenges other theories, such as cognitivism, computationalism, and Cartesian dualism. It is closely related to the extended mind thesis, situated cognition, and enactivism. The modern version depends on insights drawn from up to date research in psychology, linguistics, cognitive science, dynamical systems, artificial intelligence, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
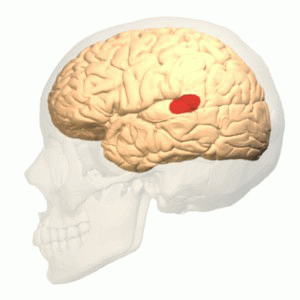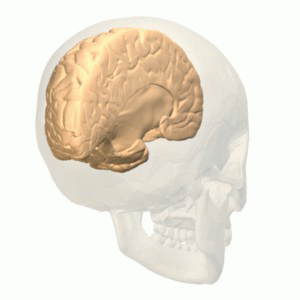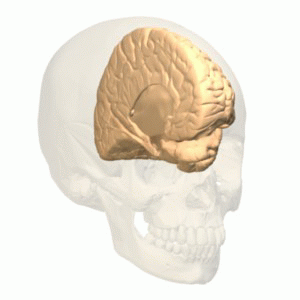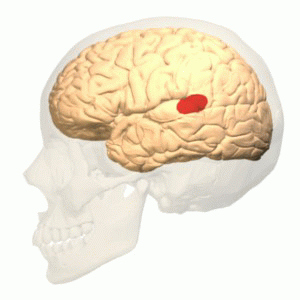
Wernicke's Area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to Broca's area, which is primarily involved in the production of language. It is traditionally thought to reside in Brodmann area 22, which is located in the superior temporal gyrus in the dominant cerebral hemisphere, which is the left hemisphere in about 95% of right-handed individuals and 70% of left-handed individuals. Damage caused to Wernicke's area results in receptive, fluent aphasia. This means that the person with aphasia will be able to fluently connect words, but the phrases will lack meaning. This is unlike non-fluent aphasia, in which the person will use meaningful words, but in a non-fluent, telegraphic manner. Structure Wernicke's area is traditionally viewed as being located in the posterior section of the superior tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experiential Knowledge
Experiential knowledge is knowledge gained through experience, as opposed to a priori (before experience) knowledge: it can also be contrasted both with propositional (textbook) knowledge, and with practical knowledge. Experiential knowledge is cognate to Michael Polanyi's personal knowledge, as well as to Bertrand Russell's contrast of Knowledge by Acquaintance and by Description. A posteriori In the philosophy of mind, the phrase often refers to knowledge that can ''only'' be acquired through experience, such as, for example, the knowledge of what it is like to see colours, which could not be explained to someone born blind: the necessity of experiential knowledge becomes clear if one was asked to explain to a blind person a colour like blue. The question of a posteriori knowledge might be formulated as: can Adam or Eve know what water feels like on their skin prior to touching it for the first time? Religion Zen emphasises the importance of the experiential element in relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
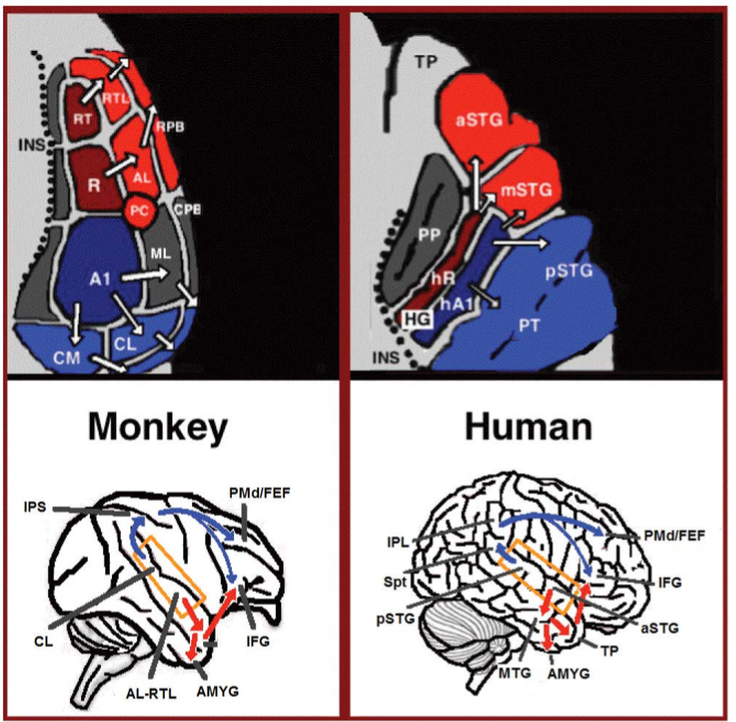
Language Processing In The Brain
Language processing refers to the way humans use words to communicate ideas and feelings, and how such communications are processed and understood. Language processing is considered to be a uniquely human ability that is not produced with the same grammatical understanding or systematicity in even human's closest primate relatives. Throughout the 20th century the dominant model for language processing in the brain was the Geschwind-Lichteim-Wernicke model, which is based primarily on the analysis of brain damaged patients. However, due to improvements in intra-cortical electrophysiological recordings of monkey and human brains, as well non-invasive techniques such as fMRI, PET, MEG and EEG, a dual auditory pathway has been revealed and a two-streams model has been developed. In accordance with this model, there are two pathways that connect the auditory cortex to the frontal lobe, each pathway accounting for different linguistic roles. The auditory ventral stream pathway is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can testable, test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent (logic), antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the :wikt:assumption, assumption in a (possibly Counterfactual conditional, counterfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition And Postposition
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions (or broadly, in traditional grammar, simply prepositions), are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in'', ''under'', ''towards'', ''before'') or mark various semantic roles (''of'', ''for''). A preposition or postposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. A preposition comes before its complement; a postposition comes after its complement. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in'', ''under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as ''in England'', ''under the table'', ''of Jane'' – although there are a few exceptions including "ago" and "notwithstanding", as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead, or have both types. The phrase formed by a preposition or postposition together with its com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called ''chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amodal Perception
Amodal perception is the perception of the whole of a physical structure when only parts of it affect the sensory receptors. For example, a table will be perceived as a complete volumetric structure even if only part of it—the facing surface—projects to the retina; it is perceived as possessing internal volume and hidden rear surfaces despite the fact that only the near surfaces are exposed to view. Similarly, the world around us is perceived as a surrounding plenum, even though only part of it is in view at any time. Another much quoted example is that of the "dog behind a picket fence" in which a long narrow object (the dog) is partially occluded by fence-posts in front of it, but is nevertheless perceived as a single continuous object. Albert Bregman noted an auditory analogue of this phenomenon: when a melody is interrupted by bursts of white noise, it is nonetheless heard as a single melody continuing "behind" the bursts of noise. Formulation of the theory is credited to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Integration
Semantic integration is the process of interrelating information from diverse sources, for example calendars and to do lists, email archives, presence information (physical, psychological, and social), documents of all sorts, contacts (including social graphs), search results, and advertising and marketing relevance derived from them. In this regard, semantics focuses on the organization of and action upon information by acting as an intermediary between heterogeneous data sources, which may conflict not only by structure but also context or value. Applications and methods In enterprise application integration (EAI), semantic integration can facilitate or even automate the communication between computer systems using metadata publishing. Metadata publishing potentially offers the ability to automatically link ontologies. One approach to (semi-)automated ontology mapping requires the definition of a semantic distance or its inverse, semantic similarity and appropriate rules. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Dementia
Semantic dementia (SD), also known as semantic variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA), is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of semantic memory in both the verbal and non-verbal domains. However, the most common presenting symptoms are in the verbal domain (with loss of word meaning). Semantic dementia is a disorder of semantic memory that causes patients to lose the ability to match words or images to their meanings. However, it is fairly rare for patients with semantic dementia to develop category specific impairments, though there have been documented cases of it occurring. Typically, a more generalized semantic impairment results from dimmed semantic representations in the brain. SD is one of the three canonical clinical syndromes associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), with the other two being frontotemporal dementia and progressive nonfluent aphasia. SD is a clinically defined syndrome but is associated with predominantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure The temporal lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative (denotative) or explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding hippocampal region consisting of the perirhinal, parahippocampal, and entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is critical for memory formation, and the surrounding medial temporal cortex is curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supramarginal Gyrus
The supramarginal gyrus is a portion of the parietal lobe. This area of the brain is also known as Brodmann area 40 based on the brain map created by Korbinian Brodmann to define the structures in the cerebral cortex. It is probably involved with language perception and processing, and lesions in it may cause receptive aphasia. Important functions The supramarginal gyrus is part of the somatosensory association cortex, which interprets tactile sensory data and is involved in perception of space and limbs location. It is also involved in identifying postures and gestures of other people and is thus a part of the mirror neuron system. The right-hemisphere supramarginal gyrus appears to play a central role in controlling empathy towards other people. When this structure is not working properly or when individuals have to make very quick judgements, empathy becomes severely limited. Research has shown that disrupting the neurons in the right supramarginal gyrus causes humans to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |