|
Ejecta
Ejecta (from the Latin: "things thrown out", singular ejectum) are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic materials ( tephra) that came out of a volcanic explosion and magma eruption volcanic vent, or crater, has traveled through the air or under water, and fell back on the ground surface or on the ocean floor. Volcanology Typically in volcanology, ejecta is a result of explosive eruptions. In an explosive eruption, large amounts of gas are dissolved in extremely viscous lava; this lava froths to the surface until the material is expelled rapidly due to the trapped pressure. Sometimes in such an event a lava plug or volcanic neck forms from lava that solidifies inside a volcano's vent, causing heat and pressure to build up to an extreme with no way to escape. When the blockage breaks and cannot sustain itself any longer, a more violent eruption occurs, which allows materials to be ejected out of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejecta Blanket
An ejecta blanket is a generally symmetrical apron of ejecta that surrounds an impact crater; it is layered thickly at the crater's rim and thin to discontinuous at the blanket's outer edge. The impact cratering is one of the basic surface formation mechanisms of the solar system bodies (including the Earth) and the formation and emplacement of ejecta blankets are the fundamental characteristics associated with impact cratering event. The ejecta materials are considered as the transported materials beyond the transient cavity formed during impact cratering regardless of the state of the target materials. Formation A blanket of ejecta is formed during the formation of meteor impact cratering and is composed usually of the materials of that are ejected from the cratering process. Ejecta materials are deposited on the preexisting layer of target materials and therefore it form an inverted stratigraphy than the underlying bedrock. In some cases, the excavated fragment of ejects ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Bomb
A volcanic bomb or lava bomb is a mass of partially molten rock (tephra) larger than 64 mm (2.5 inches) in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption. Because volcanic bombs cool after they leave the volcano, they are extrusive igneous rocks. Volcanic bombs can be thrown many kilometres from an erupting vent, and often acquire aerodynamic shapes during their flight. Bombs can be extremely large; the 1935 eruption of Mount Asama in Japan expelled bombs measuring 5–6 m (16-20 ft) in diameter up to from the vent. Volcanic bombs are a significant volcanic hazard, and can cause severe injuries and death to people in an eruption zone. One such incident occurred at Galeras volcano in Colombia in 1993; six people near the summit were killed and several seriously injured by lava bombs when the volcano erupted unexpectedly. On July 16, 2018, 23 people were injured on a tour boat near the Kilauea volcano as a result of a bask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Rock
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and sedimentary rocks. For these reasons, in geology, volcanics and shallow hypabyssal rocks are not always treated as distinct. In the context of Precambrian shield geology, the term "volcanic" is often applied to what are strictly metavolcanic rocks. Volcanic rocks and sediment that form from magma erupted into the air are called "volcaniclastics," and these are technically sedimentary rocks. Volcanic rocks are among the most common rock types on Earth's surface, particularly in the oceans. On land, they are very common at plate boundaries and in flood basalt provinces. It has been est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Neck
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eden Patera
Eden Patera is a feature located in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle on the planet Mars. In October 2013 the feature gained some attention when it was speculated it may be a supervolcano rather than an impact crater, according to research from the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson , "(at the) base of the black ill , nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town" , image_map = , mapsize = 260px , map_caption = Interactive map ..., led by Joseph R. Michalski. NASA, Oct. 22, 2013 The research postulated the crater was formed by the volcano's [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', and Latin ', mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
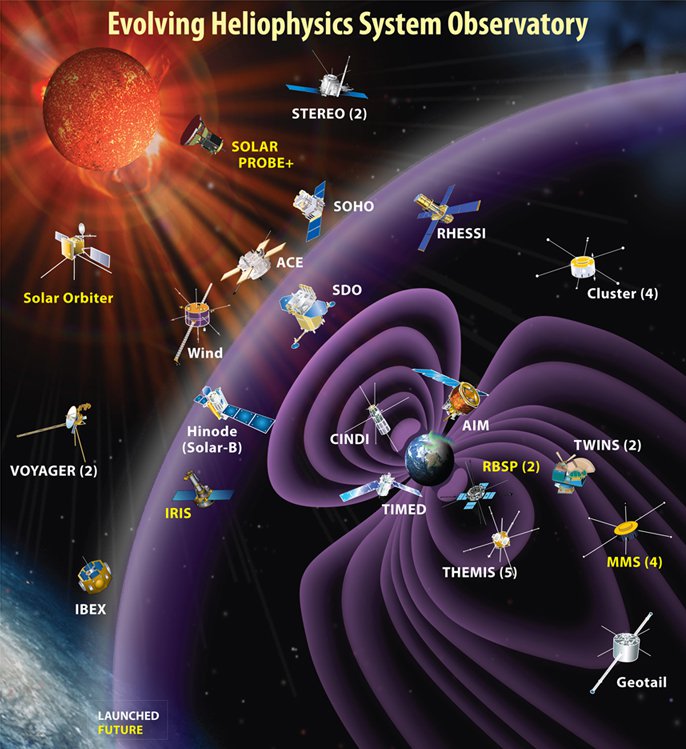
Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA defines heliophysics as "(1) the comprehensive new term for the science of the Sun - Solar System Connection, (2) the exploration, discovery, and understanding of Earth's space environment, and (3) the system science that unites all of the linked phenomena in the region of the cosmos influenced by a star like our Sun." Heliophysics concentrates on the Sun's effects on Earth and other bodies within the Solar System, as well as the changing conditions in space. It is primarily concerned with the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, and upper atmosphere of the Earth and other planets. Heliophysics combines the science of the Sun, corona, heliosphere and geospace, and encompasses a wide variety of astronomical phenomena, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |