|
Eigendecomposition
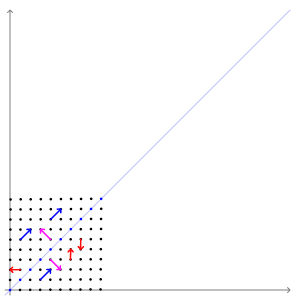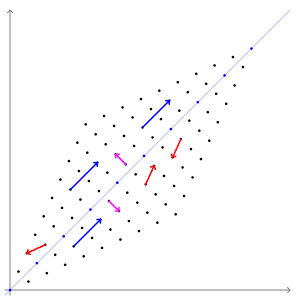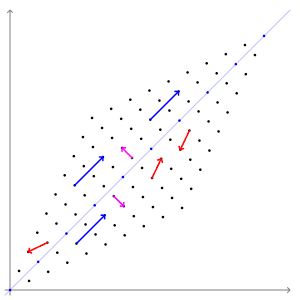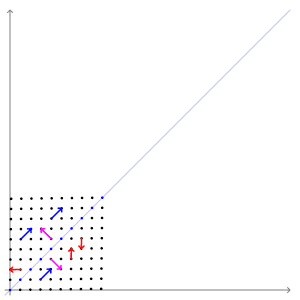
In linear algebra, eigendecomposition is the factorization of a matrix into a canonical form, whereby the matrix is represented in terms of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Only diagonalizable matrices can be factorized in this way. When the matrix being factorized is a normal or real symmetric matrix, the decomposition is called "spectral decomposition", derived from the spectral theorem. Fundamental theory of matrix eigenvectors and eigenvalues A (nonzero) vector of dimension is an eigenvector of a square matrix if it satisfies a linear equation of the form :\mathbf \mathbf = \lambda \mathbf for some scalar . Then is called the eigenvalue corresponding to . Geometrically speaking, the eigenvectors of are the vectors that merely elongates or shrinks, and the amount that they elongate/shrink by is the eigenvalue. The above equation is called the eigenvalue equation or the eigenvalue problem. This yields an equation for the eigenvalues : p\left(\lambda\right) = \det\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Decomposition
In the mathematical discipline of linear algebra, a matrix decomposition or matrix factorization is a factorization of a matrix into a product of matrices. There are many different matrix decompositions; each finds use among a particular class of problems. Example In numerical analysis, different decompositions are used to implement efficient matrix algorithms. For instance, when solving a system of linear equations A \mathbf = \mathbf, the matrix ''A'' can be decomposed via the LU decomposition. The LU decomposition factorizes a matrix into a lower triangular matrix ''L'' and an upper triangular matrix ''U''. The systems L(U \mathbf) = \mathbf and U \mathbf = L^ \mathbf require fewer additions and multiplications to solve, compared with the original system A \mathbf = \mathbf, though one might require significantly more digits in inexact arithmetic such as floating point. Similarly, the QR decomposition expresses ''A'' as ''QR'' with ''Q'' an orthogonal matrix and ''R'' an u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Factorization
In the mathematics, mathematical discipline of linear algebra, a matrix decomposition or matrix factorization is a factorization of a Matrix (mathematics), matrix into a product of matrices. There are many different matrix decompositions; each finds use among a particular class of problems. Example In numerical analysis, different decompositions are used to implement efficient matrix algorithms. For instance, when solving a system of linear equations A \mathbf = \mathbf, the matrix ''A'' can be decomposed via the LU decomposition. The LU decomposition factorizes a matrix into a lower triangular matrix ''L'' and an upper triangular matrix ''U''. The systems L(U \mathbf) = \mathbf and U \mathbf = L^ \mathbf require fewer additions and multiplications to solve, compared with the original system A \mathbf = \mathbf, though one might require significantly more digits in inexact arithmetic such as floating point. Similarly, the QR decomposition expresses ''A'' as ''QR'' with ''Q'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Multiplicity
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Multiplicity
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalue
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Theorem
In mathematics, particularly linear algebra and functional analysis, a spectral theorem is a result about when a linear operator or matrix can be diagonalized (that is, represented as a diagonal matrix in some basis). This is extremely useful because computations involving a diagonalizable matrix can often be reduced to much simpler computations involving the corresponding diagonal matrix. The concept of diagonalization is relatively straightforward for operators on finite-dimensional vector spaces but requires some modification for operators on infinite-dimensional spaces. In general, the spectral theorem identifies a class of linear operators that can be modeled by multiplication operators, which are as simple as one can hope to find. In more abstract language, the spectral theorem is a statement about commutative C*-algebras. See also spectral theory for a historical perspective. Examples of operators to which the spectral theorem applies are self-adjoint operators or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum Of A Matrix
In mathematics, the spectrum of a matrix is the set of its eigenvalues. More generally, if T\colon V \to V is a linear operator on any finite-dimensional vector space, its spectrum is the set of scalars \lambda such that T-\lambda I is not invertible. The determinant of the matrix equals the product of its eigenvalues. Similarly, the trace of the matrix equals the sum of its eigenvalues. From this point of view, we can define the pseudo-determinant for a singular matrix to be the product of its nonzero eigenvalues (the density of multivariate normal distribution will need this quantity). In many applications, such as PageRank, one is interested in the dominant eigenvalue, i.e. that which is largest in absolute value. In other applications, the smallest eigenvalue is important, but in general, the whole spectrum provides valuable information about a matrix. Definition Let ''V'' be a finite-dimensional vector space over some field ''K'' and suppose ''T'' : ''V'' → ''V'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Transformation
In linear algebra, linear transformations can be represented by matrices. If T is a linear transformation mapping \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m and \mathbf x is a column vector with n entries, then T( \mathbf x ) = A \mathbf x for some m \times n matrix A, called the transformation matrix of T. Note that A has m rows and n columns, whereas the transformation T is from \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m. There are alternative expressions of transformation matrices involving row vectors that are preferred by some authors. Uses Matrices allow arbitrary linear transformations to be displayed in a consistent format, suitable for computation. This also allows transformations to be composed easily (by multiplying their matrices). Linear transformations are not the only ones that can be represented by matrices. Some transformations that are non-linear on an n-dimensional Euclidean space R''n'' can be represented as linear transformations on the ''n''+1-dimensional space R''n''+1. These include both af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column Space
In linear algebra, the column space (also called the range or image) of a matrix ''A'' is the span (set of all possible linear combinations) of its column vectors. The column space of a matrix is the image or range of the corresponding matrix transformation. Let \mathbb be a field. The column space of an matrix with components from \mathbb is a linear subspace of the ''m''-space \mathbb^m. The dimension of the column space is called the rank of the matrix and is at most .Linear algebra, as discussed in this article, is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. Almost all of the material in this article can be found in Lay 2005, Meyer 2001, and Strang 2005. A definition for matrices over a ring \mathbb is also possible. The row space is defined similarly. The row space and the column space of a matrix are sometimes denoted as and respectively. This article considers matrices of real numbers. The row and column spaces ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Equation
In mathematics, a set of simultaneous equations, also known as a system of equations or an equation system, is a finite set of equations for which common solutions are sought. An equation system is usually classified in the same manner as single equations, namely as a: * System of linear equations, * System of nonlinear equations, * System of bilinear equations, * System of polynomial equations, * System of differential equations, or a * System of difference equations See also * Simultaneous equations model, a statistical model in the form of simultaneous linear equations * Elementary algebra Elementary algebra encompasses the basic concepts of algebra. It is often contrasted with arithmetic: arithmetic deals with specified numbers, whilst algebra introduces variables (quantities without fixed values). This use of variables enta ..., for elementary methods {{set index article Equations Broad-concept articles de:Gleichung#Gleichungssysteme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |