|
Ego Defenses
In psychoanalytic theory, a defence mechanism (American English: defense mechanism), is an Unconscious mind, unconscious psychological operation that functions to protect a person from anxiety-producing thoughts and feelings related to internal conflicts and outer stressors. The idea of defence mechanisms comes from psychoanalytic theory, a psychological perspective of personality that sees personality as the interaction between three components: id, ego, and super-ego. These psychological strategies may help people put distance between themselves and threats or unwanted feelings, such as guilt or shame. Defence mechanisms may result in healthy or unhealthy consequences depending on the circumstances and frequency with which the mechanism is used.Utah Psych. "Defense Mechanisms" 2010. Retrieved on 05 October 2013. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalytic Theory
Psychoanalytic theory is the theory of personality organization and the dynamics of personality development that guides psychoanalysis, a clinical method for treating psychopathology. First laid out by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th century, psychoanalytic theory has undergone many refinements since his work. The psychoanalytic theory came to full prominence in the last third of the twentieth century as part of the flow of critical discourse regarding psychological treatments after the 1960s, long after Freud's death in 1939. Freud had ceased his analysis of the brain and his physiological studies and shifted his focus to the study of the mind and the related psychological attributes making up the mind, and on treatment using free association and the phenomena of transference. His study emphasized the recognition of childhood events that could influence the mental functioning of adults. His examination of the genetic and then the developmental aspects gave the psychoanalytic theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Formation
In psychoanalytic theory, reaction formation (german: Reaktionsbildung) is a defense mechanism in which emotions and impulses which are anxiety-producing or perceived to be unacceptable are mastered by exaggeration of the directly opposing tendency. Charles Rycroft, ''A Critical Dictionary of Psychoanalysis'' (London, 2nd Edn, 1995) The reaction formations belong to Level 3 of neurotic defense mechanisms, which also include dissociation, displacement, intellectualization, and repression. Theory Reaction formation depends on the hypothesis that " e instincts and their derivatives may be arranged as pairs of opposites: life versus death, construction versus destruction, action versus passivity, dominance versus submission, and so forth. When one of the instincts produces anxiety by exerting pressure on the ego either directly or by way of the superego, the ego may try to sidetrack the offending impulse by concentrating upon its opposite. For example, if feelings of hate towards a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Plutchik
Robert Plutchik (21 October 1927 – 29 April 2006) was a professor emeritus at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine and adjunct professor at the University of South Florida. He received his Ph.D. from Columbia University and he was also a psychologist. He authored or coauthored more than 260 articles, 45 chapters and eight books and edited seven books. His research interests included the study of emotions, the study of suicide and violence, and the study of the psychotherapy process. Theory of emotion Plutchik proposed a psychoevolutionary classification approach for general emotional responses.Plutchik, R. (1980). A general psychoevolutionary theory of emotion. In R. Plutchik & H. Kellerman (eds.), Emotion: Theory, research and experience, Theories of emotion (Vol. 1, pp. 3–33). New York: Academic Press.Plutchik R. (1982) A psychoevolutionary theory of emotions Social Science Information. 21: 529–53. He considered there to be eight primary emotions—anger, fear, sadness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Stage Theories
In psychology, developmental stage theories are theories that divide psychological development into distinct stages which are characterized by qualitative differences in behavior. Developmental stage theories are one type of structural stage theory. There are several different views about psychological and physical development and how they proceed throughout the life span. The two main psychological developmental theories include continuous and discontinuous development. In addition to individual differences in development, developmental psychologists generally agree that development occurs in an orderly way and in different areas simultaneously. Stage theories The development of the human mind is complex and a debated subject, and may take place in a continuous or discontinuous fashion. Continuous development, like the height of a child, is measurable and quantitative, while discontinuous development is qualitative, like hair or skin color, where those traits fall only under a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Eman Vaillant
George Eman Vaillant (; born June 16, 1934) is an American psychiatrist and Professor at Harvard Medical School and Director of Research for the Department of Psychiatry, Brigham and Women's Hospital. Vaillant has spent his research career charting adult development and the recovery process of schizophrenia, heroin addiction, alcoholism, and personality disorder. Through 2003, he spent 30 years as Director of the Study of Adult Development at the Harvard University Health Service. The study has prospectively charted the lives of 724 men and women for over 60 years. Biography George Eman Vaillant's father, George Clapp Vaillant, committed suicide in 1945. George Eman was traumatized by his father's death and thus had deep emotional reasons for being interested in psychiatry. He graduated from Harvard College and Harvard Medical School, did his psychiatric residency at the Massachusetts Mental Health Center and completed his psychoanalytic training at the Boston Psychoanalytic Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Relations Theory
Object relations theory is a school of thought in psychoanalytic theory centered around theories of stages of ego development. Its concerns include the relation of the psyche to others in childhood and the exploration of relationships between external people, as well as internal images and the relations found in them. Thinkers of the school maintain that the infant's relationship with the mother primarily determines the formation of its personality in adult life. Particularly, attachment is the bedrock of the development of the self or the psychic organization that creates the sense of identity. Theory While its groundwork derives from theories of development of the ego in Freudian psychodynamics, object relations theory does not place emphasis on the role of biological drives in the formation of personality in adulthood. Thinkers of the school instead suggest that the way people relate to others and situations in their adult lives is shaped by family experiences during inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD), also known as emotionally unstable personality disorder (EUPD), is a personality disorder characterized by a long-term pattern of unstable interpersonal relationships, distorted sense of self, and strong emotional reactions. Those affected often engage in self-harm and other dangerous behaviors, often due to their difficulty with returning their emotional level to a healthy or normal baseline. They may also struggle with a feeling of emptiness, fear of abandonment, and detachment from reality. Symptoms of BPD may be triggered by events considered normal to others. BPD typically begins by early adulthood and occurs across a variety of situations. Substance use disorders, depression, and eating disorders are commonly associated with BPD. Some 8 to 10% of people affected by the disorder may die by suicide. The disorder is often stigmatized in both the media and the psychiatric field and as a result is often underdiagnosed. The causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto F
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', '' Odo'', '' Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded from the 7th century ( Odo, son of Uro, courtier of Sigebert III). It was the name of three 10th-century German kings, the first of whom was Otto I the Great, the first Holy Roman Emperor, founder of the Ottonian dynasty. The Gothic form of the prefix was ''auda-'' (as in e.g. '' Audaþius''), the Anglo-Saxon form was ''ead-'' (as in e.g. ''Eadmund''), and the Old Norse form was '' auð-''. The given name Otis arose from an English surname, which was in turn derived from ''Ode'', a variant form of ''Odo, Otto''. Due to Otto von Bismarck, the given name ''Otto'' was strongly associated with the German Empire in the later 19th century. It was comparatively frequently given in the United States (presumably in German American families) duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
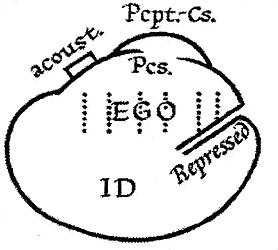
Id (psychology)
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego uses b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (psychology)
In psychology, displacement (german: Verschiebung, lit=shift, move) is an unconscious defence mechanism whereby the mind substitutes either a new aim or a new object for goals felt in their original form to be dangerous or unacceptable. Freud The concept of displacement originated with Sigmund Freud. Initially he saw it as a means of dream-distortion, involving a shift of emphasis from important to unimportant elements, or the replacement of something by a mere illusion. Freud called this “displacement of accent.” Displacement of object: Feelings that are connected with one person are displaced onto another person. A man who has had a bad day at the office, comes home and yells at his wife and children, is displacing his anger from the workplace onto his family. Freud thought that when children have animal phobias, they may be displacing fears of their parents onto an animal. Displacement of attribution: A characteristic that one perceives in oneself but seems unacceptable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-harm
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilation have been used for any self-harming behavior regardless of suicidal intent. It is not the same as masochism, as no sexual or nonsexual pleasure is obtained. The most common form of self-harm is using a sharp object to cut the skin. Other forms include scratching, hitting, or burning body parts. While earlier usage included interfering with wound healing, excessive skin-picking, hair-pulling, and the ingestion of toxins, current usage distinguishes these behaviors from self-harm. Likewise, tissue damage from drug abuse or eating disorders is not considered self-harm because it is ordinarily an unintended side-effect but context may be needed as intent for such acts varies. Although self-harm is by definition non-suicidal, it may still b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introjection
In psychology, introjection is the unconscious adoption of the thoughts or personality traits of others. It occurs as a normal part of development, such as a child taking on parental values and attitudes. It can also be a defense mechanism in situations that arouse anxiety. The tendency is also known as identification or internalization. It has been associated with both normal and pathological development. Theory Introjection is a concept rooted in the psychoanalytic theories of unconscious motivations. Unconscious motivation refers to processes in the mind which occur automatically and bypass conscious examination and considerations. Introjection is the learning process or in some cases a defense mechanism where a person unconsciously absorbs experiences and makes them part their psyche. Introjection in learning In psychoanalysis, introjection (german: Introjektion) refers to an unconscious process wherein one takes components of another person's identity, such as f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |