|
Eel-tailed Catfish
The eel-tailed catfish, ''Tandanus tandanus'', is a species of catfish ( order Siluriformes) of the family Plotosidae. This fish is also known as dewfish, freshwater catfish, jewfish, and tandan. This species is a freshwater fish native to the Murray-Darling river system of eastern Australia. The scientific name for eel-tailed catfish comes from a name for the fish in an unidentified Aboriginal Australian language - ''Tandan'' - which Major Thomas Livingston Mitchell recorded on his 1832 expedition. Description Eel-tailed catfish commonly grow to about 50.0 centimetres (19.7 in) and weigh about 1.8 kilograms (4.0 lb). Fish of this species may grow up to about 90.0 cm (35.4 in) and weigh up to 6.0 kg (13.2 lb). Eel-tailed catfish may live up to about 8 years. Eel-tailed catfish have large head with thick and fleshy lips and tubular nostrils. The skin is tough and smooth. Body coloration in adults vary from olive-green to brown, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Mitchell (explorer)
Sir Thomas Livingstone Mitchell (15 June 1792 – 5 October 1855), surveyor and explorer of Southeastern Australia, was born at Grangemouth in Stirlingshire, Scotland. In 1827 he took up an appointment as Assistant Surveyor General of New South Wales. The following year he became Surveyor General and remained in this position until his death. Mitchell was knighted in 1839 for his contribution to the surveying of Australia. Early life Born in Scotland on 15 June 1792, he was son of John Mitchell of Carron Works and was brought up from childhood by his uncle, Thomas Livingstone of Parkhall, Stirlingshire. Peninsular War On the death of his uncle, he joined the British army in Portugal as a volunteer in the Peninsular War, at the age of sixteen. On 24 June 1811, at the age of nineteen, he received his first commission as 2nd Lieutenant in the 1st Battalion 95th Rifles (later the Rifle Brigade / Royal Green Jackets). Utilising his skills as a draughtsman of outstanding ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet ( Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish Of Oceania
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores (species that eat dead material on the bottom), and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, ''Vandellia cirrhosa''. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus ''Corydoras'', are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandanus
''Tandanus'' is a genus of eeltail catfishes endemic to Australia. Species There are currently 3 recognized species in this genus: * ''Tandanus bostocki'' Whitley, 1944 (Freshwater cobbler) * ''Tandanus tandanus'' Mitchell, 1838 (Tandan catfish) * ''Tandanus tropicanus'' Welsh, Jerry Jerry may refer to: Animals * Jerry (Grand National winner), racehorse, winner of the 1840 Grand National * Jerry (St Leger winner), racehorse, winner of 1824 St Leger Stakes Arts, entertainment, and media * Jerry (film), ''Jerry'' (film), a 200 ... & Burrows, 2014 (Wet Tropics Tandan) References * Catfish genera Freshwater fish genera Taxa named by Thomas Mitchell (explorer) {{catfish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Carp
The Eurasian carp or European carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), widely known as the common carp, is a widespread freshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers in Europe and Asia.Fishbase''Cyprinus carpio'' Linnaeus, 1758/ref>Arkive The native wild populations are considered vulnerable to extinction by the International Union for Conservation of Nature ( IUCN), but the species has also been domesticated and introduced (see aquaculture) into environments worldwide, and is often considered a destructive invasive species, being included in the list of the world's 100 worst invasive species. It gives its name to the carp family, Cyprinidae. Taxonomy The two subspecies are: * '' Cyprinus carpio carpio'', native to much of Europe (notably the Danube and Volga rivers)Jian Feng Zhou, Qing Jiang Wu, Yu Zhen Ye & Jin Gou Tong (2003). Genetic divergence between ''Cyprinus carpio carpio'' and ''Cyprinus carpio haematopterus'' as assessed by mitochondrial DNA analysis, with emph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cestode
Cestoda is a Class (biology), class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitism, parasitic; many have complex Life history theory, life histories, including a stage in a Host (biology)#Definitive and secondary hosts, definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, ''Diphyllob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
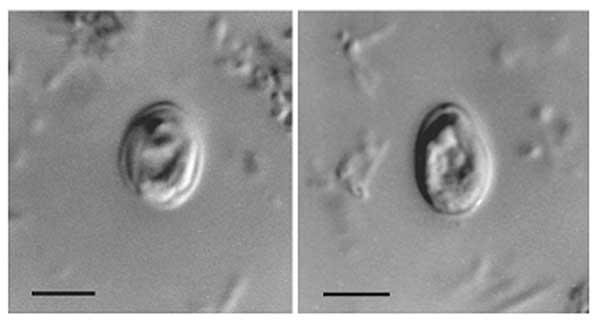
Intestinal Parasite
An intestinal parasite infection is a condition in which a parasite infects the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other animals. Such parasites can live anywhere in the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall. Routes of exposure and infection include ingestion of undercooked meat, drinking infected water, fecal-oral transmission and skin absorption. Some types of helminths and protozoa are classified as intestinal parasites that cause infection—those that reside in the intestines. These infections can damage or sicken the host (humans or other animals). If the intestinal parasite infection is caused by helminths, the infection is called helminthiasis. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms depend on the type of infection. Intestinal parasites produce a variety of symptoms in those affected, most of which manifest themselves in gastrointestinal complications and general weakness. Gastrointestinal conditions include inflammation of the small and/or large intestine, diar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mudbugs, baybugs or yabbies. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some species are found in brooks and streams, where fresh water is running, while others thrive in swamps, ditches, and paddy fields. Most crayfish cannot tolerate polluted water, although some species, such as '' Procambarus clarkii'', are hardier. Crayfish feed on animals and plants, either living or decomposing, and detritus. The term "crayfish" is applied to saltwater species in some countries. Terminology The name "crayfish" comes from the Old French word ' ( Modern French '). The word has been modified to "crayfish" by association with "fish" (folk etymology). The largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
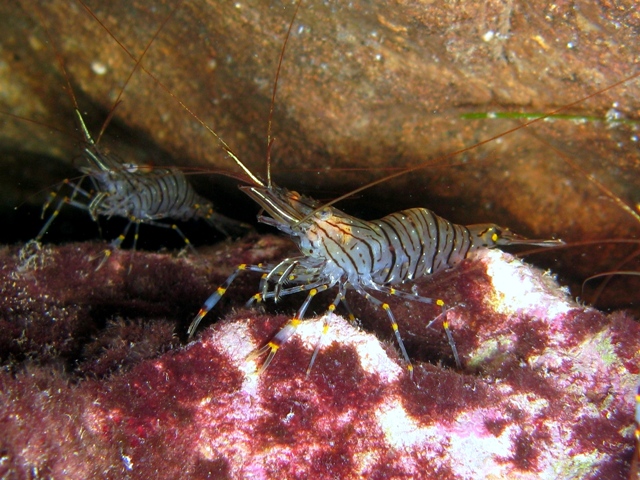
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails ( abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chironomid
The Chironomidae (informally known as chironomids, nonbiting midges, or lake flies) comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species superficially resemble mosquitoes, but they lack the wing scales and elongated mouthparts of the Culicidae. The name Chironomidae stems from the Ancient Greek word ''kheironómos'', "a pantomimist". Common names and biodiversity This is a large taxon of insects; some estimates of the species numbers suggest well over 10,000 world-wide. Males are easily recognized by their plumose antennae. Adults are known by a variety of vague and inconsistent common names, largely by confusion with other insects. For example, chironomids are known as "lake flies" in parts of Canada and Lake Winnebago, Wisconsin, but "bay flies" in the areas near the bay of Green Bay, Wisconsin. They are called "sand flies", "muckleheads", "muffleheads", "Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |