|
EarFold
EarFold or EarFold method is a surgical method for pinning protruding ears. In contrast to all the other ear-pinning procedures ( otoplasty), metal implants are used instead of sutures. As far as the invasiveness of the surgery is concerned, the Earfold method ranks between the open, invasive conventional ear-pinning procedures (6, 7, 8, 9), and the closed, minimally invasive Stitch method (4, 5) or other variations of minimally invasive procedures (10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18). The ears are cut open and the skin is detached from the cartilage as in conventional ear-pinning operations, but to a lesser extent. Occasionally, the cartilage under the detached skin is also scored or perforated with a needle to weaken it. History The Earfold technique was first described by Norbert V. Kang and Ryan L. Kerstein in 2016 (1). Kang and his colleagues reported on the results and possible complications of the method in 2018 (2). Surgical procedure One or several incisions of approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otoplasty
Otoplasty ( el, οὖς, , "ear" + , , "to shape") denotes the surgical and non-surgical procedures for correcting the deformities and defects of the pinna (external ear), and for reconstructing a defective, or deformed, or absent external ear, consequent to congenital conditions (e.g. microtia, anotia, etc.) and trauma (blunt, penetrating, or blast). The otoplastic surgeon corrects the defect or deformity by creating an external ear that is of natural proportions, contour, and appearance, usually achieved by the reshaping, the moving, and the augmenting of the cartilaginous support framework of the pinna. Moreover, the occurrence of congenital ear deformities occasionally overlaps with other medical conditions (e.g. Treacher Collins syndrome and hemifacial microsomia). History Antiquity Otoplasty (surgery of the ear) was developed in ancient India in the 5th century BC, and described in the medical compendium, the (Sushruta's Compendium, ). The book discussed otoplastic and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
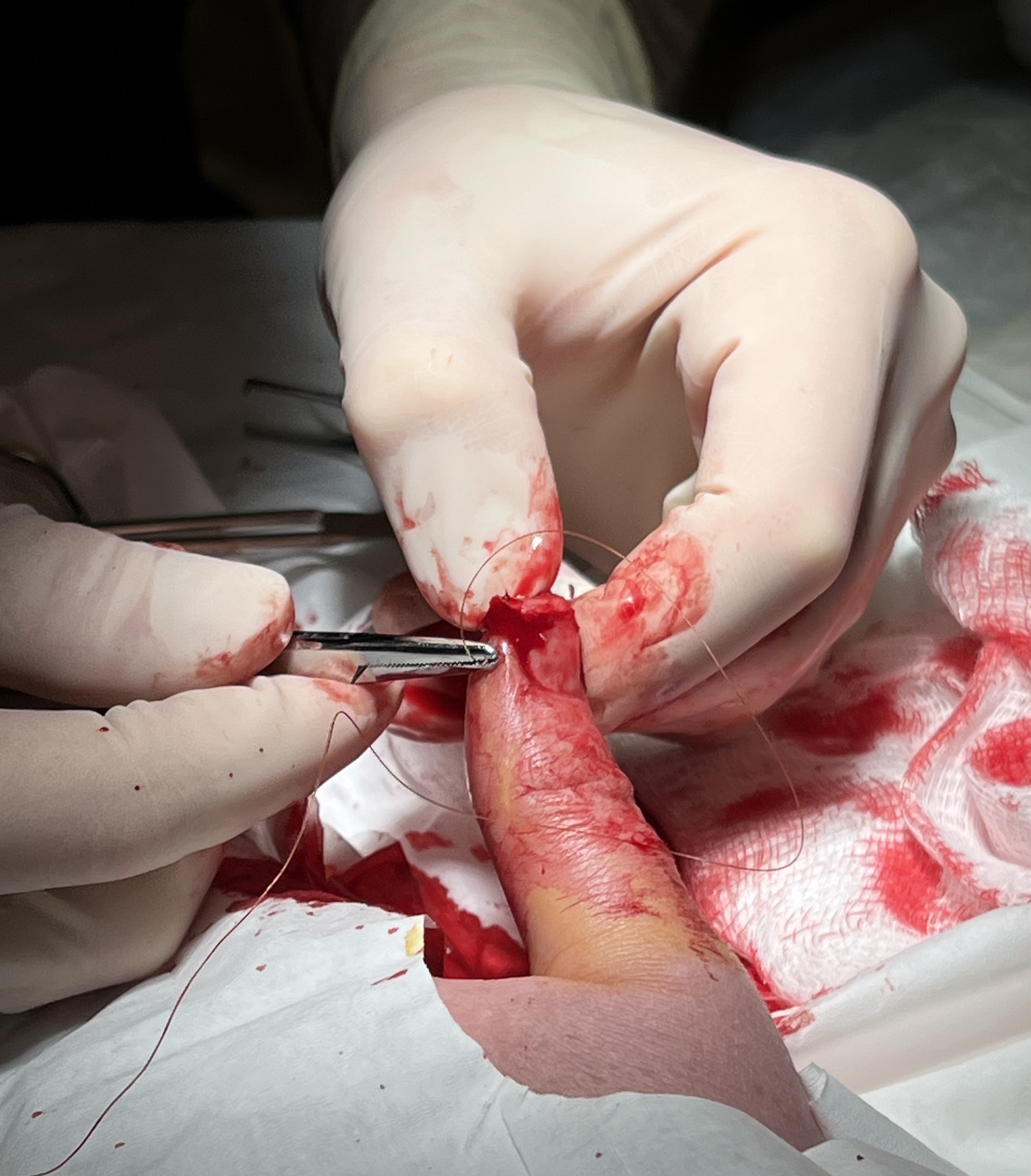
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stitch Method
The Merck stitch method is a minimally invasive procedure for pinning protruding ears, developed by Merck.Merck, W.H. (2013). "Dr Merck’s stitch method. A closed minimally invasive procedure for correction of protruding ears (Die Fadenmethode nach Dr. Merck. Ein geschlossenes, minimal-invasives Verfahren zur Anlegung abstehender Ohren)." ''J Aesthet Chir'', 6, 209-220. The method belongs to the special types of ear pinning surgeries. In contrast to other variations of minimally invasive proceduresTramier, H. ''Personal approach to treatment of prominent ears.'' In: ''Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.'' 99, Number 2,, 562–565, .Vecchione, T.R. 1979 ''Needle scoring of the anterior surface of the cartilage in otoplasty.'' In: ''Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.'' 64, Number 4, 568, . the stitch method does not use additional techniques from the traditional ear pinning surgeries (otoplasty). It belongs to the closed ear pinning surgeries because the ear is not cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitinol
Nickel titanium, also known as Nitinol, is a metal alloy of nickel and titanium, where the two elements are present in roughly equal atomic percentages. Different alloys are named according to the weight percentage of nickel; e.g., Nitinol 55 and Nitinol 60. It exhibits the shape memory effect and superelasticity at different temperatures. Nitinol alloys exhibit two closely related and unique properties: the shape memory effect and superelasticity (also called pseudoelasticity). Shape memory is the ability of Nitinol to undergo deformation at one temperature, stay in its deformed shape when the external force is removed, then recover its original, undeformed shape upon heating above its "transformation temperature". Superelasticity is the ability for the metal to undergo large deformations and immediately return to its undeformed shape upon removal of the external load. Nitinol can deform 10–30 times as much as ordinary metals and return to its original shape. Whether Nitinol be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihelix
The antihelix (anthelix) is a part of the visible ear; the pinna. The antihelix is a curved prominence of cartilage parallel with and in front of the helix on the pinna. The antihelix divides above into two ''legs'' or crura; the ''crura antihelicis'', between which is a triangular depression, the ''fossa triangularis''. Additional images File:Gray906.png, The muscles of the auricula. File:Earcov.JPG, Left human ear An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of ... File:Slide2COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. File:Slide3COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. File:Slide4COR.JPG, External ear. Right auricle. Lateral view. External links * () (#5) Auditory system {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Surgery
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Scars
A hypertrophic scar is a cutaneous condition characterized by deposits of excessive amounts of collagen which gives rise to a raised scar, but not to the degree observed with keloids. Like keloids, they form most often at the sites of pimples, body piercings, cuts and burns. They often contain nerves and blood vessels. They generally develop after thermal or traumatic injury that involves the deep layers of the dermis and express high levels of TGF-β. Cause Mechanical tension on a wound has been identified as a leading cause for hypertrophic scar formation. When a normal wound heals, the body produces new collagen fibers at a rate which balances the breakdown of old collagen. Hypertrophic scars are red and thick and may be itchy or painful. They do not extend beyond the boundary of the original wound, but may continue to thicken for up to six months. Hypertrophic scars usually improve over one or two years, but may cause distress due to their appearance or the intensity of the itc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type 3) at the site of a healed skin injury which is then slowly replaced by collagen type 1. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown in color. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect movement of skin. In the United States keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetry
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in precise terms or in more aesthetic terms. The absence of or violation of symmetry that are either expected or desired can have important consequences for a system. In organisms Due to how cells divide in organisms, asymmetry in organisms is fairly usual in at least one dimension, with biological symmetry also being common in at least one dimension. Louis Pasteur proposed that biological molecules are asymmetric because the cosmic .e. physicalforces that preside over their formation are themselves asymmetric. While at his time, and even now, the symmetry of physical processes are highlighted, it is known that there are fundamental physical asymmetries, starting with time. Asymmetry in biology Asymmetry is an important and widespread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |