|
Dystrophin-associated Protein Complex
The dystrophin-associated protein complex, also known as the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex is a multiprotein complex that includes dystrophin and the dystrophin-associated proteins. It is one of the two protein complexes that make up the costamere in striated muscle cells. The other complex is the ''integrin-vinculin-talin complex''. Structure The dystrophin-associated protein complex includes dystrophin. Dystrophin binds to actin of the cytoskeleton, and also to proteins in the extracellular matrix. The dystrophin-associated protein complex also contains dystrophin-associated proteins. This includes a four subunit sarcoglycan complex, which is fixed to dystrophin in muscle cells. In the epithelia of the kidney, dystrophin may be replaced with utrophin. Aquaporin 4 may be connected to the dystrophin-associated protein complex. Function The dystrophin-associated protein complex is important for cell structure and cell signalling. It is one of two protein comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprotein Complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining the components of a complex. Examples of protein complexes include the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms. The disorder is X-linked recessive. About two thirds of cases are inherited from a person's mother, while one third of cases are due to a new mutation. It is caused by a mutation in the gene for the protein dystrophin. Dystrophin is important to maintain the muscle fiber's cell membrane. Genetic testing can often make the diagnosis at birth. Those affected also have a high level of creatine kinase in their blood. Although there is no know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually ultrarare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making muscle proteins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
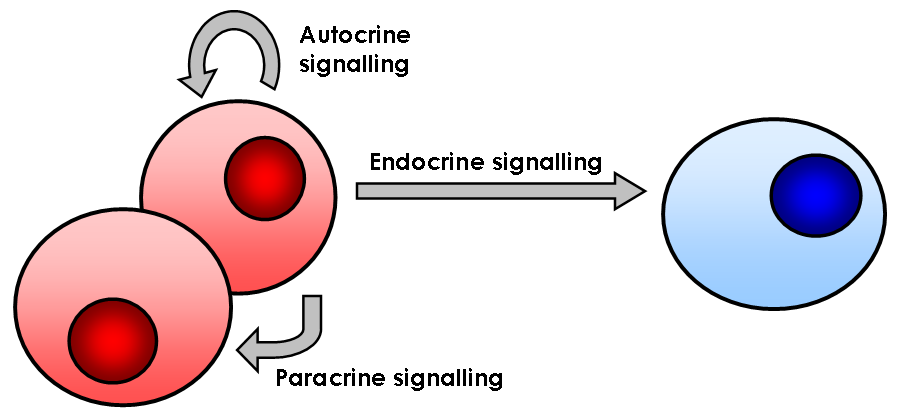
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaporin 4
Aquaporin-4, also known as AQP-4, is a water channel protein encoded by the ''AQP4'' gene in humans. AQP-4 belongs to the aquaporin family of integral membrane proteins that conduct water through the cell membrane. A limited number of aquaporins are found within the central nervous system (CNS): AQP1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, and 11, but more exclusive representation of AQP1, 4, and 9 are found in the brain and spinal cord. AQP4 shows the largest presence in the cerebellum and spinal cord grey matter. In the CNS, AQP4 is the most prevalent aquaporin channel, specifically located at the perimicrovessel astrocyte foot processes, glia limitans, and ependyma. In addition, this channel is commonly found facilitating water movement near cerebrospinal fluid and vasculature. Aquaporin-4 was first identified in 1986. It was the first evidence of the existence of water transport channels. The method that was used to discover the existence of the transport channels was through knockout experiments. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utrophin
Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UTRN'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the cytoskeleton. Utrophin was found during research into Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. The name is a contraction for ''ubiquitous dystrophin''. The 900 kb gene for utrophin is found on the long arm of human chromosome 6. Utrophin was discovered due to its homology with dystrophin. It was found by screening a peptide containing the C-terminal domain of dystrophin against cDNA libraries. The homology varies over its full length from less than 30% in regions of the central rod structural domain to 85% (identity 73%) for the actin binding domain. The tertiary structure of utrophin contains a C-terminus that consists of protein–protein interaction motifs that interact with dystroglycan, a central rod region consisting of a triple coiled-coil repeat, and an actin-binding N-terminus. In normal muscle cells, utrophin is located at the neuromuscular synapse and my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Cell
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stomach. Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystrophin
Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the costamere or the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC). Many muscle proteins, such as α-dystrobrevin, syncoilin, synemin, sarcoglycan, dystroglycan, and sarcospan, colocalize with dystrophin at the costamere. It has a molecular weight of 427 kDa Dystrophin is coded for by the ''DMD'' gene – the largest known human gene, covering 2.4 megabases (0.08% of the human genome) at locus Xp21. The primary transcript in muscle measures about 2,100 kilobases and takes 16 hours to transcribe; the mature mRNA measures 14.0 kilobases. The 79-exon muscle transcript codes for a protein of 3685 amino acid residues. Spontaneous or inherited mutations in the dystrophin gene can cause different forms of muscular dystrophy, a disease characterized by p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoglycan Complex
The sarcoglycans are a family of transmembrane proteins (α, β, γ, δ or ε) involved in the protein complex responsible for connecting the muscle fibre cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix, preventing damage to the muscle fibre sarcolemma through shearing forces. The dystrophin glycoprotein complex (DGC) is a membrane-spanning complex that links the interior cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix in muscle. The sarcoglycan complex is a subcomplex within the DGC and is composed of six muscle-specific, transmembrane proteins (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta-, epsilon-,and zeta-sarcoglycan). The sarcoglycans are asparagine-linked glycosylated proteins with single transmembrane domains. The disorders caused by the mutations of the sarcoglycans are called sarcoglycanopathies. Mutations in the α, β, γ or δ genes (not ε) encoding these proteins can lead to the associated limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Genes * SGCA * SGCB * SGCD * SGCE * SGCG Gamma-sarcoglycan is a prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |