|
Dysthanasia
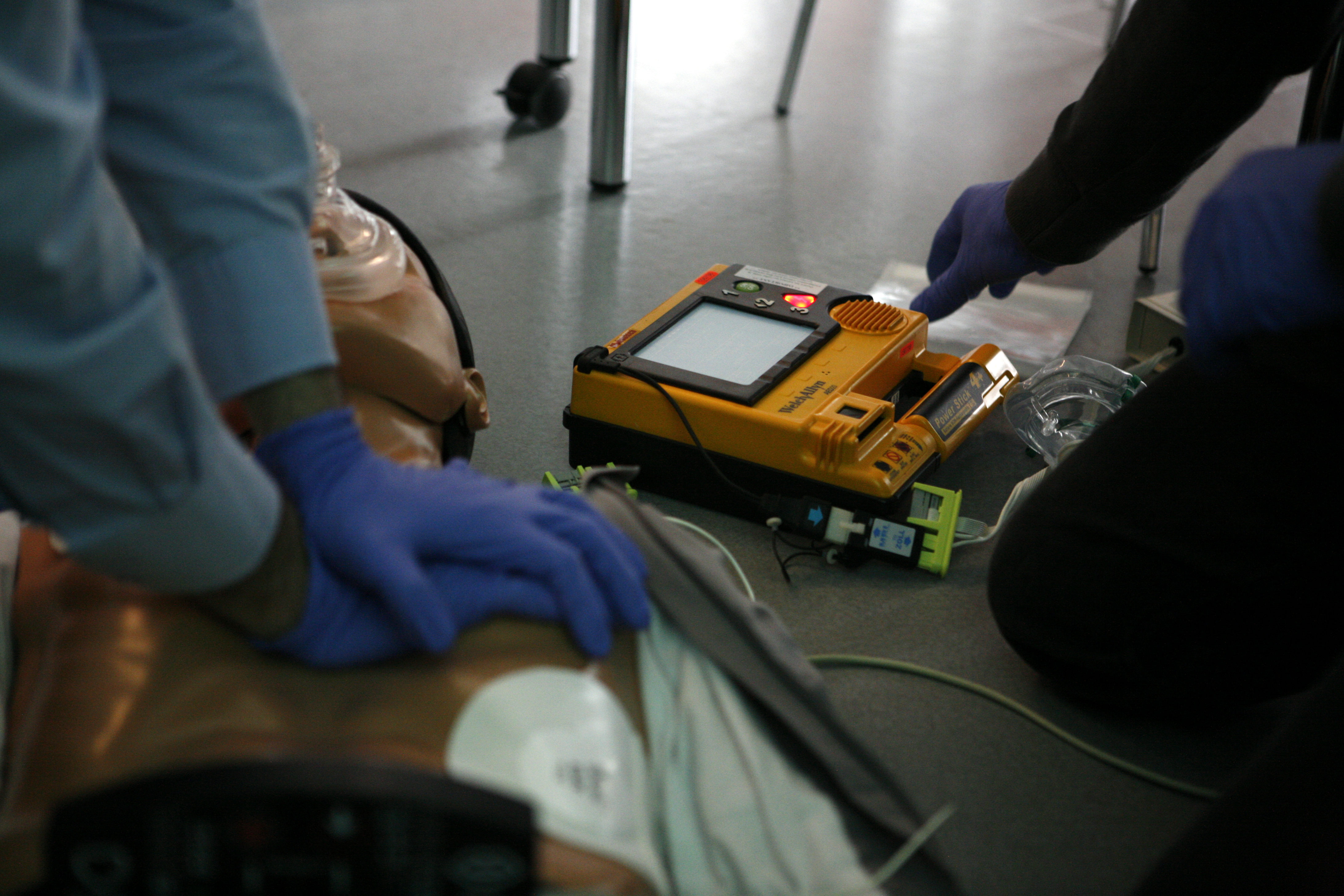
In medicine, dysthanasia means "bad death" and is considered a common fault of modern medicine. Dysthanasia is a term generally used when a person is kept alive artificially, in a condition where otherwise they cannot survive; sometimes for some sort of ulterior motive. Dysthanasia occurs when a person who is dying has their biological life extended through technological means without regard to the person's quality of life. Technologies such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator, artificial ventilation, ventricular assist devices, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation can extend the dying process. In some cases, cardiopulmonary resuscitation can be considered a form of dysthanasia. The term was used frequently in the investigation into the death of Formula One driver Ayrton Senna in 1994. The etymology of the term is from the Greek language: δυσ, ''dus''; "bad, difficult" + θάνατος, ''thanatos''; "death". See also * Brain death *Death with Dignity National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations. CPR involves chest compressions for adults between and deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Of Ayrton Senna
On 1 May 1994, Brazilian Formula One driver Ayrton Senna was killed after his car crashed into a concrete barrier while he was leading the 1994 San Marino Grand Prix at the Autodromo Enzo e Dino Ferrari in Italy. The previous day, Austrian driver Roland Ratzenberger had died when his car crashed during qualification for the race. His and Senna's crashes were the worst of several that took place that weekend (including a serious one involving Rubens Barrichello) and were the first fatal collisions to occur during a Formula One race meeting in 12 years and not repeated until the fatal crash of Jules Bianchi at the 2014 Japanese Grand Prix at Suzuka Circuit. This became a turning point in the safety of Formula One, prompting the implementation of new safety measures in both Formula One and the circuit, as well as the Grand Prix Drivers' Association to be reestablished. The Supreme Court of Cassation of Italy ruled that mechanical failure was the cause of the crash. Background In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliative Care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Within the published literature, many definitions of palliative care exist. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes palliative care as "an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial, and spiritual." In the past, palliative care was a disease specific approach, but today the WHO takes a more broad approach, that the principles of palliative care should be applied as early as possible to any chronic and ultimately fatal illness. Palliative care is appropriate for individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Support
Life support comprises the treatments and techniques performed in an emergency in order to support life after the failure of one or more vital organs. Healthcare providers and emergency medical technicians are generally certified to perform basic and advanced life support procedures; however, basic life support is sometimes provided at the scene of an emergency by family members or bystanders before emergency services arrive. In the case of cardiac injuries, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is initiated by bystanders or family members 25% of the time. Basic life support techniques, such as performing CPR on a victim of cardiac arrest, can double or even triple that patient's chance of survival. Other types of basic life support include relief from choking (which can be done by using the Heimlich maneuver), staunching of bleeding by direct compression and elevation above the heart (and if necessary, pressure on arterial pressure points and the use of a manufactured or improvised tourni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthanasia
Euthanasia (from el, εὐθανασία 'good death': εὖ, ''eu'' 'well, good' + θάνατος, ''thanatos'' 'death') is the practice of intentionally ending life to eliminate pain and suffering. Different countries have different euthanasia laws. The British House of Lords select committee on medical ethics defines euthanasia as "a deliberate intervention undertaken with the express intention of ending a life, to relieve intractable suffering". In the Netherlands and Belgium, euthanasia is understood as "termination of life by a doctor at the request of a patient". The Dutch law, however, does not use the term 'euthanasia' but includes the concept under the broader definition of "assisted suicide and termination of life on request". Euthanasia is categorized in different ways, which include voluntary, non-voluntary, or involuntary. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death With Dignity National Center
Death with Dignity National Center is a 501(c)(3) nonpartisan nonprofit organization, headquartered in Portland, Oregon, that has led the legal defense of and education about Death with Dignity laws throughout the United States for more than 25 years. The Death with Dignity National Center helped write and defend in courts the nation's first successful assisted dying law, the Oregon Death with Dignity Act, protecting the right of persons with terminal illness to control their own death. The Death with Dignity National Center is affiliated with the Death with Dignity Political Fund, a distinct and separately incorporated 501(c)(4) organization responsible for the promotion of death with dignity legislation in other states around the U.S. Mission "The mission of the Death with Dignity National Center is to promote death with dignity laws based on our model legislation, the Oregon Death with Dignity Act, both to provide an option for dying individuals and to stimulate nationwid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Death
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of brain function which may include cessation of involuntary activity necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some autonomic functions remain. It is also distinct from comas as long as some brain and bodily activity and function remain, and it is also not the same as the condition locked-in syndrome. A differential diagnosis can medically distinguish these differing conditions. Brain death is used as an indicator of legal death in many jurisdictions, but it is defined inconsistently and often confused by the public. Various parts of the brain may keep functioning when others do not anymore, and the term "brain death" has been used to refer to various combinations. For example, although one major medical dictionary considers "brain death" to be synonymous with "cerebral death" (death of the cerebrum), the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayrton Senna
Ayrton Senna da Silva (; 21 March 1960 – 1 May 1994) was a Brazilian racing driver who won the Formula One List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, World Drivers' Championship in , , and . Senna is one of three Formula One drivers from Brazil to win the World Championship and won List of Formula One Grand Prix wins by Ayrton Senna, 41 Grands Prix and 65 pole positions, with the latter being the record until 2006. He Death of Ayrton Senna, died in an accident while leading the 1994 San Marino Grand Prix, driving for the Williams Grand Prix Engineering, Williams team. Senna is considered by media, commentators and fans to be one of the greatest F1 drivers in the history of the sport. Senna began his motorsport career in karting, moved up to Open wheel car, open-wheel racing in 1981 and won the 1983 British Formula Three Championship. He made his Formula One debut with Toleman-Hart Racing Engines, Hart in 1984 Formula One season, 1984, before moving to Team Lotus, Lotus-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, which became the FIA Formula One World Championship in 1981, has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The word ''formula'' in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants' cars must conform. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as ''Grands Prix'', which take place worldwide on both purpose-built circuits and closed public roads. A points system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Each driver must hold a valid Super Licence, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA. The races must run on tracks graded "1" (formerly "A"), the highest grade-rating issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Postgraduate Medicine
The ''Journal of Postgraduate Medicine'' is a multidisciplinary quarterly bio medical journal. The journal is the official publication of the Staff Society of Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India. The journal was established in 1955 with N.M. Purandare as its first editor-in-chief. It is published open access. Abstracting and Indexing The journal is indexed and abstracted in Index Medicus, Current Contents, Science Citation Index The Science Citation Index Expanded – previously entitled Science Citation Index – is a citation index originally produced by the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) and created by Eugene Garfield. It was officially launched in 1964 and ..., EMBASE, CAB Abstracts, and AMED. External links * History of the journalThe journal's Golden Jubilee Celebration Open access journals Quarterly journals English-language journals Medknow Publications academic journals Publications establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |