|
Dyschronometria
Dyschronometria is a condition of cerebellum, cerebellar dysfunction in which an individual cannot accurately estimate the amount of time that has passed (i.e., distorted time perception). It is associated with cerebellar ataxia, when the cerebellum has been damaged and does not function to its fullest ability. Lesions to the cerebellum can cause dyssynergia, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, dysarthria, and ataxia of stance and gait. Dyschronometria can result from autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (ADCA). Signs and symptoms Common signs of dyschronometria are often generic to cerebellar ataxia, including a lack of spatial awareness, poor short term memory, and inability to keep track of time. The defining symptoms, while not completely understood, involve time perception. For example, when asked to wait for thirty seconds, or tap every second that has gone by, those affected will be able to perform the task for a short time and then become derailed. This can result from a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Perception
The study of time perception or chronoception is a field within psychology, cognitive linguistics and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience, or sense, of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Though directly experiencing or understanding another person's perception of time is not possible, perception can be objectively studied and inference, inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Some temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception. Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Theories Time perception is typically categorized in three distinct ranges, because different ranges of duration are processed in different areas of the brain: * Sub-second timing or millisecond timing * Interval timing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
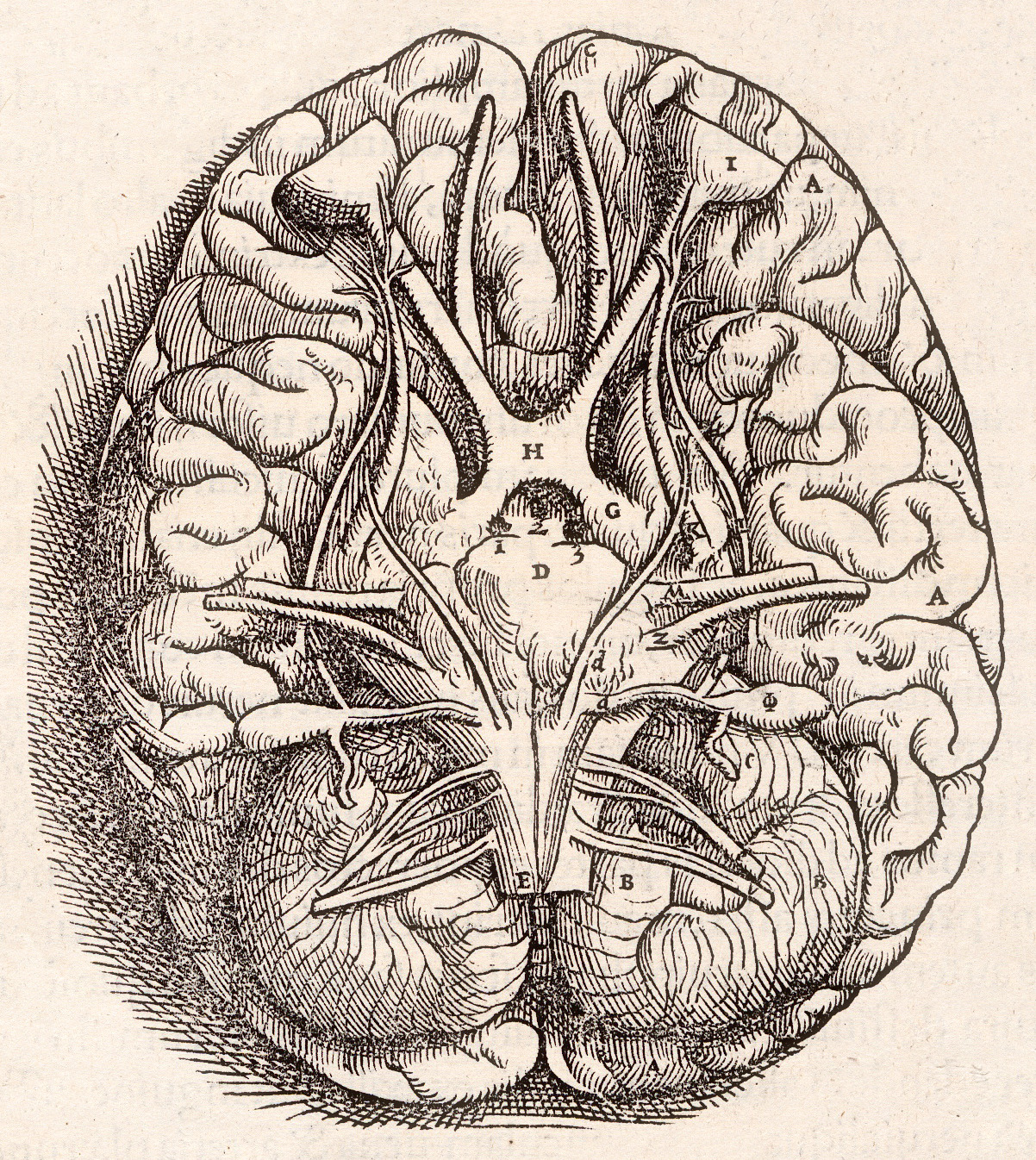
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Term Memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recited. The duration of short-term memory (absent rehearsal or active maintenance) is estimated to be on the order of seconds. The commonly cited capacity of 7 items, found in Miller's Law, has been superseded by 4±1 items. In contrast, long-term memory holds information indefinitely. Short-term memory is not the same as working memory, which refers to structures and processes used for temporarily storing and manipulating information. Stores The idea of separate memories for short-term and long-term storage originated in the 19th century. A model of memory developed in the 1960s assumed that all memories are formed in one store and transfer to others store after a small period of time. This model is referred to as the "modal model", most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of Neural circuit, neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that differs from how it previously functioned. These changes range from individual neuron pathways making new connections, to systematic adjustments like cortical remapping. Examples of neuroplasticity include circuit and network changes that result from learning a new ability, environmental influences, practice, and psychological stress. Neuroplasticity was once thought by neuroscientists to manifest only during childhood, but research in the latter half of the 20th century showed that many aspects of the brain can be altered (or are "plastic") even through adulthood. However, the developing brain exhibits a higher degree of plasticity than the adult brain. Activity-dependent plasticity can have significant implications for healthy development, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (biology)
Stress, either physiological, biological or psychological, is an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition. Stress is the body's method of reacting to a condition such as a threat, challenge or physical and psychological barrier. There are two hormones that an individual produces during a stressful situation, these are well known as adrenaline and cortisol. There are two kinds of stress hormone levels. Resting (basal) cortisol levels are normal everyday quantities that are essential for standard functioning. Reactive cortisol levels are increases in cortisol in response to stressors. Stimuli that alter an organism's environment are responded to by multiple systems in the body. In humans and most mammals, the autonomic nervous system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis are the two major systems that respond to stress. The sympathoadrenal medullary (SAM) axis may activate the fight-or-flight response through the sympathetic nervous system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyslexia
Dyslexia, also known until the 1960s as word blindness, is a disorder characterized by reading below the expected level for one's age. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers. Dyslexia is believed to be caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Some cases run in families. Dyslexia that develops due to a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or dementia is sometimes called "acquired dyslexia" or alexia. The underlying mechanisms of dyslexia result from differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellar Activation
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to the bottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |