|
Doublesex
''Doublesex'' (''dsx'') is a gene that is involved in the sex determination system of many insects including the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Sex determination The gene is expressed in both male and female flies and is subject to alternative splicing, producing the protein isoforms ''dsxf'' in females and the longer ''dsxm'' in males. The production of ''dsxf'' is caused by the presence of the female-specific version of the ''transformer'' (''tra'') gene. In a sense, the isoform of ''dsx'' informs a cell about the organism's sex; for instance, female genitals only develop if ''dsxf'' is present. In conjunction with the gene ''fruitless'', ''dsx'' also causes differences in the brain structure and behavior of males and females. Lay summary: Although the details of sex determination differ in the various species, there is a gene related to ''dsx'' in vertebrates (DMRT1) and in nematodes ( MAB-3). All of these are transcription factor In molecular biology, a tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMRT1
Doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1, also known as DMRT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DMRT1'' gene. Function DMRT1 is a dose sensitive transcription factor protein that regulates Sertoli cells and germ cells. The DMRT1 gene is located at the end of the 9th chromosome. This gene is found in a cluster with two other members of the gene family, having in common a zinc finger-like DNA-binding motif (DM domain). The DM domain is an ancient, conserved component of the vertebrate sex-determining pathway that is also a key regulator of male development in flies and nematodes, and is found to be the key sex-determining factor in chickens. The majority of DMRT1 protein is located in the testicular cord and Sertoli cells, with a small amount in the germ cells. This gene exhibits a gonad-specific and sexually dimorphic expression pattern, just like the related ''doublesex'' gene in fruit flies. Defective testicular development and XY feminization occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
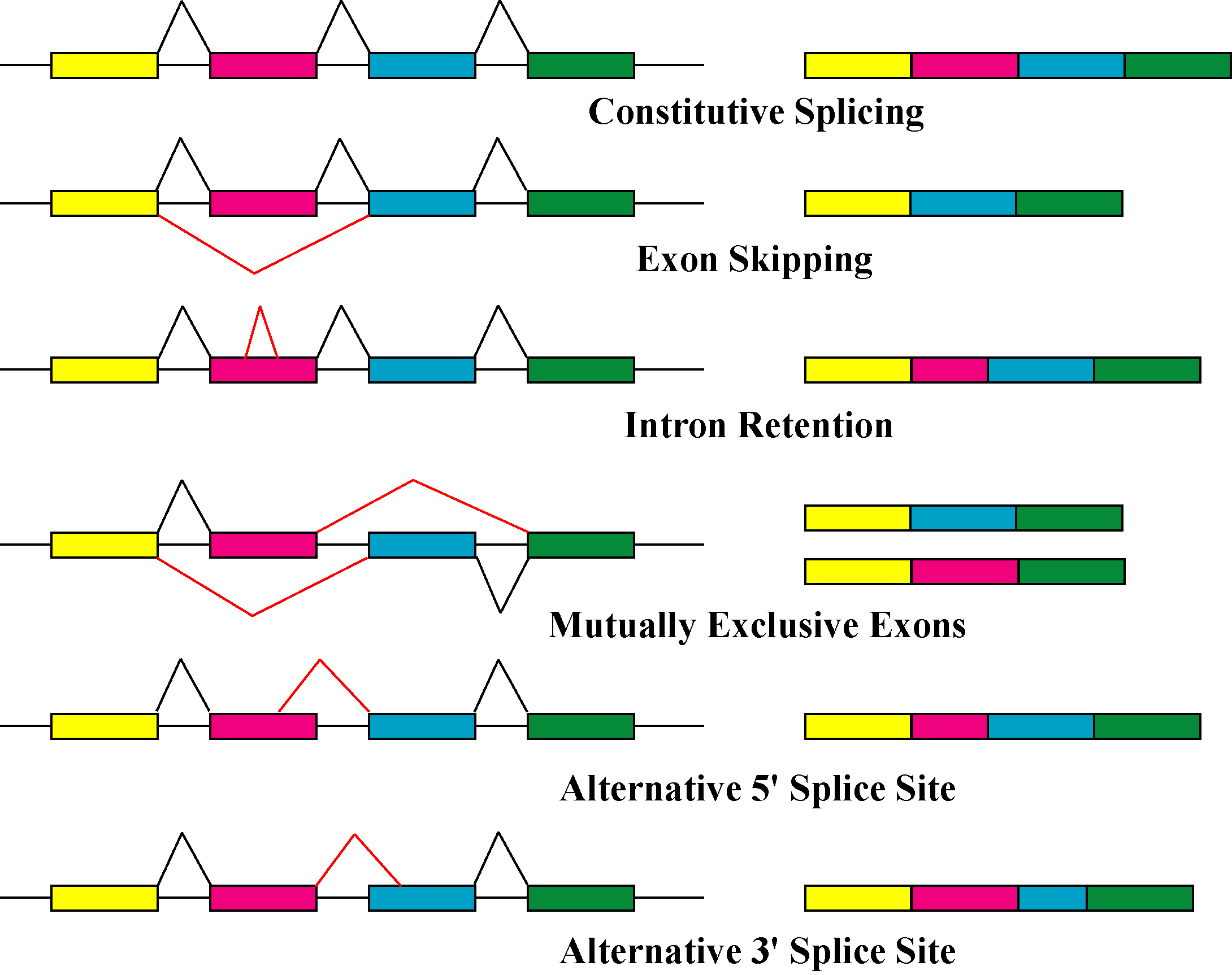
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster Genes
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appearance, beh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
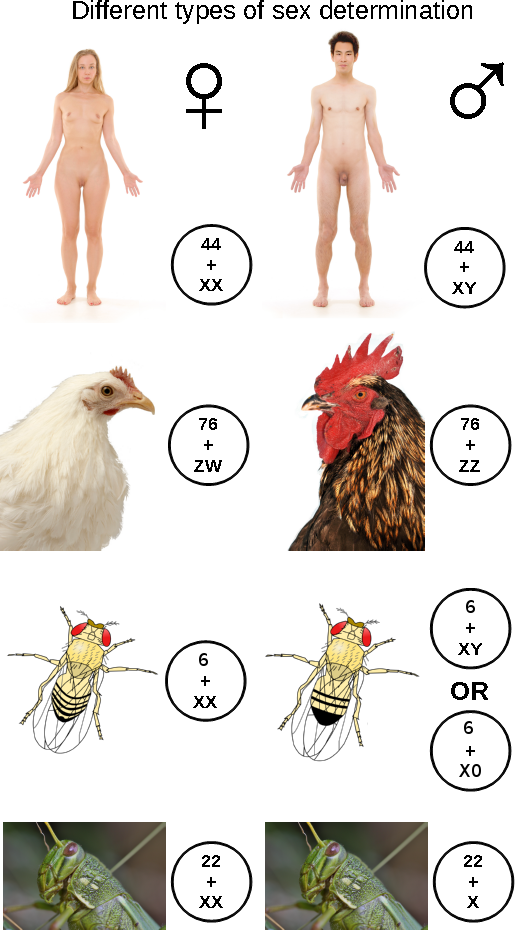
Sex-determination Systems
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two sexes. In some species there are hermaphrodites. There are also some species that are only one sex due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual differentiation is generally triggered by a main gene (a "sex locus"), with a multitude of other genes following in a domino effect. In other cases, sex of a fetus is determined by environmental variables (such as temperature). The details of some sex-determination systems are not yet fully understo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two sexes. In some species there are hermaphrodites. There are also some species that are only one sex due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual differentiation is generally triggered by a main gene (a "sex locus"), with a multitude of other genes following in a domino effect. In other cases, sex of a fetus is determined by environmental variables (such as temperature). The details of some sex-determination systems are not yet fully understo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruitless (gene)
The ''fruitless'' gene (''fru'') is a ''Drosophila melanogaster'' gene that encodes several variants of a putative transcription factor protein. Normal ''fruitless'' function is required for proper development of several anatomical structures necessary for courtship, including motor neurons which innervate muscles needed for fly sexual behaviors. The gene does not have an obvious mammalian homolog, but appears to function in sex determination in species as distant as the mosquito ''Anopheles gambiae''. ''fruitless'' serves as an example of how a gene or a group of genes may regulate the development and/or function of neurons involved in innate behavior. Research on ''fruitless'' has received attention in the popular press, since it provokes discussion on genetics of human sexual orientation, and behaviors such as gender-specific aggression. Function Male flies with mutations in the ''fruitless'' gene display altered sexual behavior. Fruitfly courtship, which involves a comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ScienceDaily
''Science Daily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. As of 2010, the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast Quantcast is an American technology company, founded in 2006, that specializes in AI-driven real-time advertising, audience insights and measurement. It has offices in the United States, Canada, Australia, Singapore, United Kingdom, Ireland, Fran ... ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |