|
Divisionism
Divisionism, also called chromoluminarism, was the characteristic style in Neo-Impressionist painting defined by the separation of colors into individual dots or patches which interacted optically..Homer, William I. ''Seurat and the Science of Painting.'' Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 1964. By requiring the viewer to combine the colors optically instead of physically mixing pigments, Divisionists believed they were achieving the maximum luminosity scientifically possible. Georges Seurat founded the style around 1884 as chromoluminarism, drawing from his understanding of the scientific theories of Michel Eugène Chevreul, Ogden Rood and Charles Blanc, among others. Divisionism developed along with another style, Pointillism, which is defined specifically by the use of dots of paint and does not necessarily focus on the separation of colors.Ratliff, Floyd. ''Paul Signac and Color in Neo-Impressionism.'' New York: Rockefeller UP, 1992. . Theoretical foundations and development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-impressionism
Neo-Impressionism is a term coined by French art critic Félix Fénéon in 1886 to describe an art movement founded by Georges Seurat. Seurat's most renowned masterpiece, ''A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte'', marked the beginning of this movement when it first made its appearance at an exhibition of the Société des Artistes Indépendants (Salon des Indépendants) in Paris. Around this time, the peak of France's modern era emerged and many painters were in search of new methods. Followers of Neo-Impressionism, in particular, were drawn to modern urban scenes as well as landscapes and seashores. Science-based interpretation of lines and colors influenced Neo-Impressionists' characterization of their own contemporary art. The Pointillism, Pointillist and Divisionism, Divisionist techniques are often mentioned in this context, because they were the dominant techniques in the beginning of the Neo-impressionist movement. Some argue that Neo-Impressionism became the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Metzinger
Jean Dominique Antony Metzinger (; 24 June 1883 – 3 November 1956) was a major 20th-century French painter, theorist, writer, critic and poet, who along with Albert Gleizes wrote the first theoretical work on Cubism. His earliest works, from 1900 to 1904, were influenced by the neo-Impressionism of Georges Seurat and Henri-Edmond Cross. Between 1904 and 1907 Metzinger worked in the Divisionist and Fauvist styles with a strong Paul Cézanne, Cézannian component, leading to some of the first Proto-Cubism, proto-Cubist works. From 1908 Metzinger experimented with the faceting of form, a style that would soon become known as Cubism. His early involvement in Cubism saw him both as an influential artist and an important theorist of the movement. The idea of moving around an object in order to see it from different view-points is treated, for the first time, in Metzinger's ''Note sur la Peinture'', published in 1910.Jean Metzinger, October–November 1910, "Note sur la peinture" Pan: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pointillism
Pointillism (, ) is a technique of painting in which small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an image. Georges Seurat and Paul Signac developed the technique in 1886, branching from Impressionism. The term "Pointillism" was coined by art critics in the late 1880s to ridicule the works of these artists, but is now used without its earlier pejorative connotation. The movement Seurat began with this technique is known as Neo-impressionism. The Divisionism, Divisionists used a similar technique of patterns to form images, though with larger cube-like brushstrokes. Technique The technique relies on the ability of the eye and mind of the viewer to blend the color spots into a fuller range of tones. It is related to Divisionism, a more technical variant of the method. Divisionism is concerned with color theory, whereas pointillism is more focused on the specific style of brushwork used to apply the paint. It is a technique with few serious practitioners today an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Danse, Bacchante
''La danse'' (also known as ''Bacchante'') is an oil painting created circa 1906 by the French artist and theorist Jean Metzinger (1883–1956). ''Bacchante'' is a pre-Cubist or Proto-Cubist work executed in a highly personal Divisionist style during the height of the Fauve period. ''Bacchante'' was painted in Paris at a time when Metzinger and Robert Delaunay painted portraits of one another, exhibiting together at the Salon d'Automne and the Berthe Weill gallery. ''Bacchante'' was exhibited in Paris during the spring of 1907 at the Salon des Indépendants (No. 3460), along with '' Coucher de soleil'' and four other works by Metzinger. The painting was purchased by the art historian and collector Wilhelm Uhde and formed part of his collection until it was sequestered by the French government just before World War I. By 30 May 1921 ''Bacchante'' was owned by the French painter André Lhote. The painting appeared at the auction house Hôtel Drouot where it was presumably purchas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Signac
Paul Victor Jules Signac ( , ; 11 November 1863 – 15 August 1935) was a French Neo-Impressionist painter who, working with Georges Seurat, helped develop the Pointillist style. Biography Paul Signac was born in Paris on 11 November 1863. He followed a course of training in architecture before, at the age of 18, deciding to pursue a career as a painter, after attending an exhibit of Monet's work. He sailed on the Mediterranean Sea, visiting the coasts of Europe and painting the landscapes he encountered. In later years, he also painted a series of watercolors of French harbor cities. In 1884 he met Claude Monet and Georges Seurat. He was struck by the systematic working methods of Seurat and by his theory of colors and he became Seurat's faithful supporter, friend, and heir with his description of Neo-Impressionism and Divisionism method. Under Seurat's influence he abandoned the short brushstrokes of Impressionism to experiment with scientifically-juxtaposed small dots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
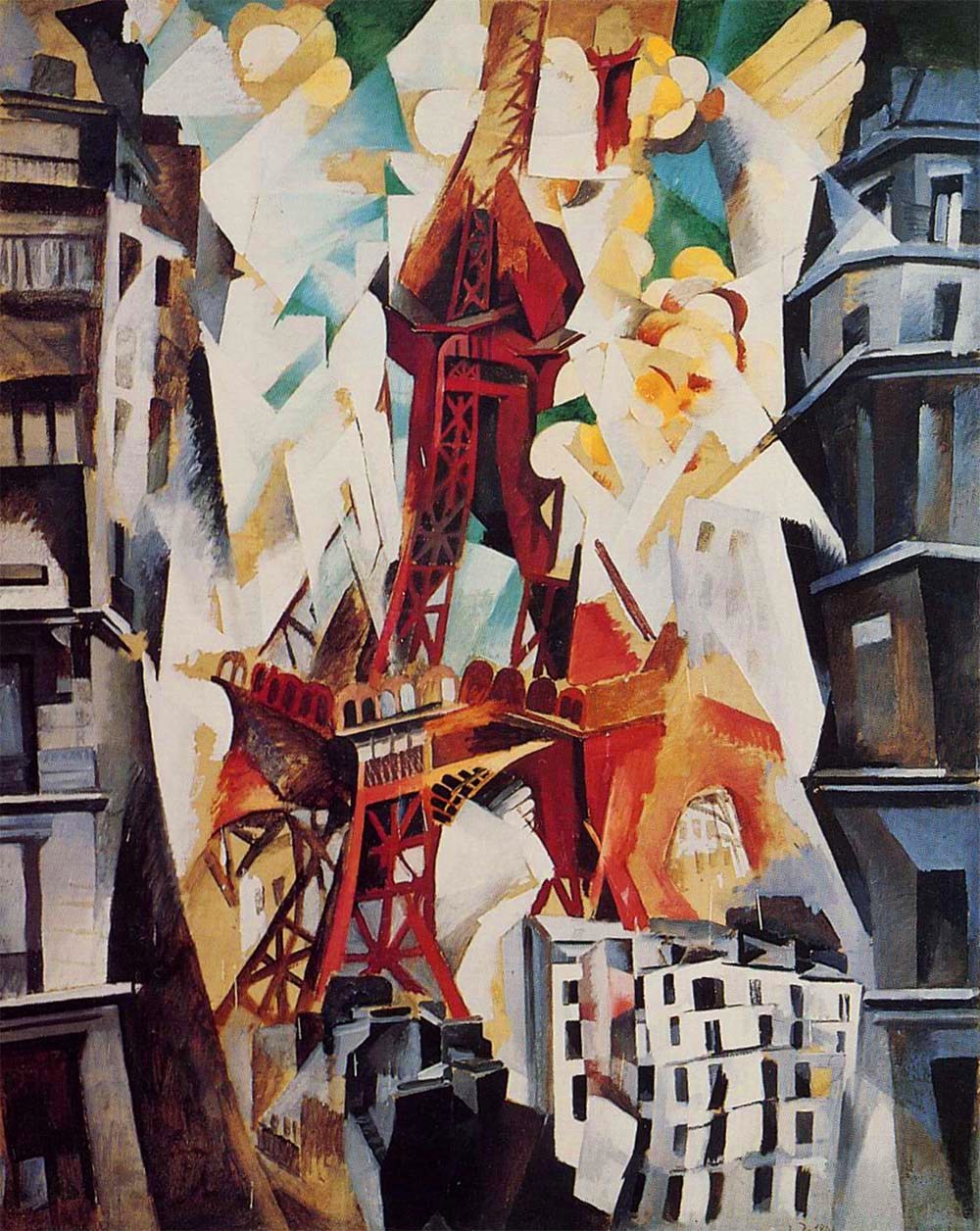
Robert Delaunay
Robert Delaunay (12 April 1885 – 25 October 1941) was a French artist who, with his wife Sonia Delaunay and others, co-founded the Orphism art movement, noted for its use of strong colours and geometric shapes. His later works were more abstract. His key influence related to bold use of colour and a clear love of experimentation with both depth and tone. Overview Delaunay is most closely identified with Orphism. From 1912 to 1914, he painted nonfigurative paintings based on the optical characteristics of brilliant colors that were so dynamic they would function as the form. His theories are mostly concerned with color and light and influenced many, including Stanton Macdonald-Wright, Morgan Russell, Patrick Henry Bruce, Der Blaue Reiter, August Macke, Franz Marc, Paul Klee, and Lyonel Feininger. Art Critic Guillaume Apollinaire was strongly influenced by Delaunay's theories of color and often quoted from them to explain Orphism, which he had named. Delaunay's fixations w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Sunday Afternoon On The Island Of La Grande Jatte
''A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte'' (french: Un dimanche après-midi à l'Île de la Grande Jatte) was painted from 1884 to 1886 and is Georges Seurat's most famous work. A leading example of pointillist technique, executed on a large canvas, it is a founding work of the neo-impressionist movement. Seurat's composition includes a number of Parisians at a park on the banks of the River Seine. It is in the collection of the Art Institute of Chicago. Background In 1879, Georges Seurat enlisted as a soldier in the French army and arrived back home in 1880. Later, he ran a small painter's studio in Paris, and in 1883 showed his work publicly for the first time. The following year, Seurat began to work on ''La Grande Jatte'' and exhibited the painting in the spring of 1886 with the Impressionists. With ''La Grande Jatte'', Seurat was immediately acknowledged as the leader of a new and rebellious form of Impressionism called Neo-Impressionism. Seurat painted ''A Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Seurat
Georges Pierre Seurat ( , , ; 2 December 1859 – 29 March 1891) was a French post-Impressionist artist. He devised the painting techniques known as chromoluminarism and pointillism and used conté crayon for drawings on paper with a rough surface. Seurat's artistic personality combined qualities that are usually thought of as opposed and incompatible: on the one hand, his extreme and delicate sensibility, on the other, a passion for logical abstraction and an almost mathematical precision of mind. His large-scale work ''A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte'' (1884–1886) altered the direction of modern art by initiating Neo-Impressionism, and is one of the icons of late 19th-century painting. Biography Family and education Seurat was born on 2 December 1859 in Paris, at 60 rue de Bondy (now rue René Boulanger). The Seurat family moved to 136 boulevard de Magenta (now 110 boulevard de Magenta) in 1862 or 1863.Seurat: p. 16 His father, Antoine Chrysostome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Pierre Giottino Humbert De Superville
David Pierre Giottino Humbert de Superville (The Hague, 18 July 1770 – Leiden, 9 January 1849) was a Dutch artist and art scholar. He was a draughtsman, lithographer, etcher, and portrait painter, and also wrote treatises on art, including the influential work ''Essai sur les signes inconditionnels dans l'art'' (Leiden, 1827). His 1815 painting of the jurist and statesman Johan Melchior Kemper is now part of the collection of the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. His 1801 etching ''Allegory'' may have been a direct visual inspiration for Paul Gauguin's ''Spirit of the Dead Watching''. Although no direct connection has been made, de Superville was cited by Albert Aurier as one of the forerunners of Symbolist painting and de Superville's book ''Unconditional Signs in Art'' (1827–32) was widely known to that group.Gamboni (2003) A portrait of Humbert de Superville uit 1848, painted by Jacobus Ludovicus Cornet, is now in the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. The biography ''David Pierre Gio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Gogh Museum
The Van Gogh Museum () is a Dutch art museum dedicated to the works of Vincent van Gogh and his contemporaries in the Museum Square in Amsterdam South, close to the Stedelijk Museum, the Rijksmuseum, and the Concertgebouw. The museum opened on 2 June 1973, Ronald de Leeuw,Introduction: the Van Gogh Museum as a National Museum, 1973–1994, ''Van Gogh Museum Journal'', 1995. Retrieved 9 July 2014. and its buildings were designed by Gerrit Rietveld and Kisho Kurokawa. The museum contains the largest collection of Van Gogh's paintings and drawings in the world. In 2017, the museum had 2.3 million visitors and was the most-visited museum in the Netherlands, and the 23rd-most-visited art museum in the world. In 2019, the Van Gogh Museum launched the ''Meet Vincent Van Gogh Experience'', a technology-driven "immersive exhibition" on Van Gogh's life and works, which has toured globally. History Unsold works Upon Vincent van Gogh's death in 1890, his work not sold fell into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Henry (librarian)
Charles Henry (1859–1926) was a French librarian and editor. He was born at Bollwiller, Haut-Rhin, and was educated in Paris, where in 1881 he became assistant and afterward librarian in the Sorbonne. As a specialist in the history of mathematics, he was sent to Italy to seek some manuscripts of that nature which the government wished to publish. He edited several works upon kindred subjects, as well as memoirs, letters, and other volumes, and wrote critiques upon the musical theories of Rameau and Wronski. He is also credited with the invention of several ingenious devices and instruments used in psychophysiological laboratories. He published C. Huet's correspondence under the title ''Un érudit, homme du monde, homme d'église, homme de cour'' (1880), and he issued also ''Problèmes de géométrie pratique'' (1884) and ''Lettres inédites de Mlle. de Lespinasse à Condorcet et à D'Alembert'' (1887). Charles Henry, a mathematician, inventor, esthetician, and intimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |