|
Diphosphane
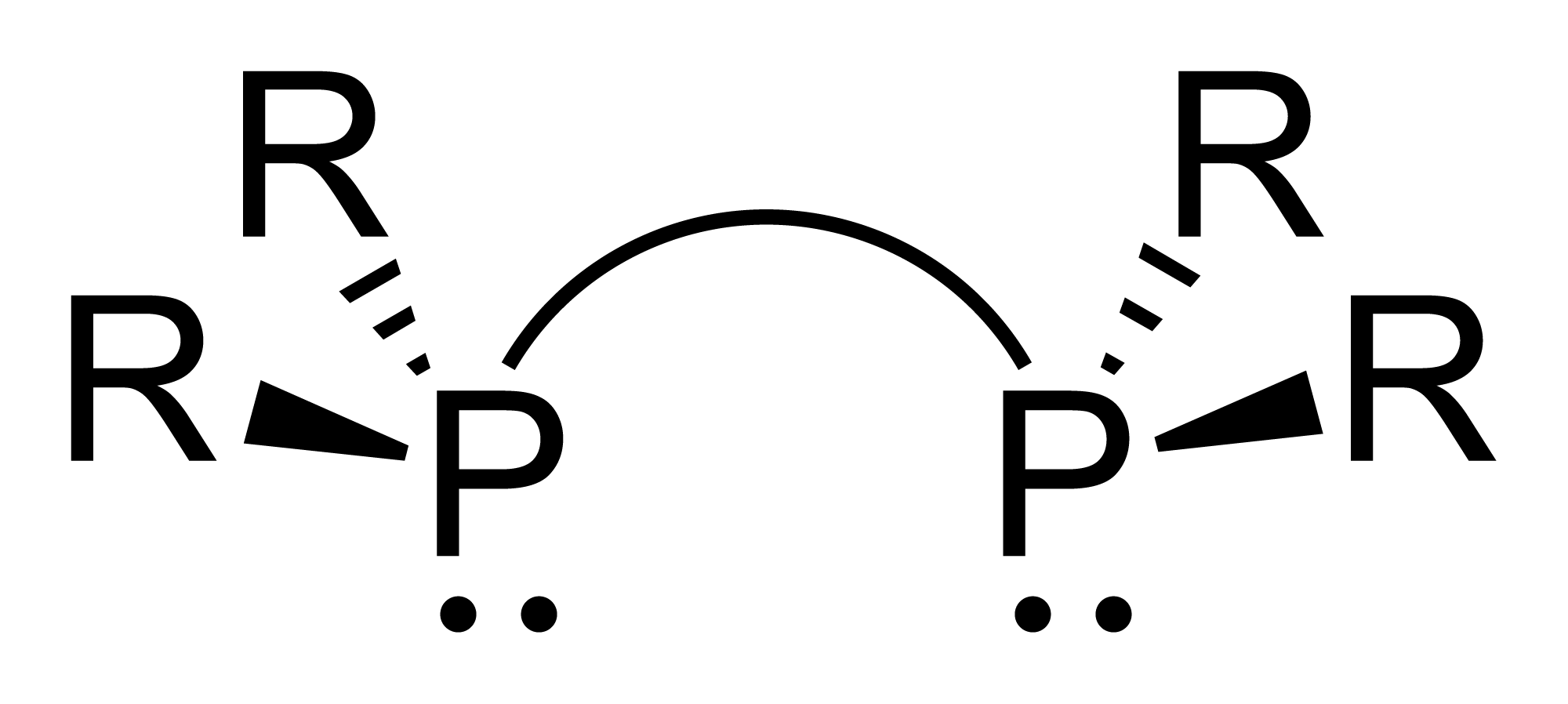
Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air. Properties, preparation, reactions Diphosphane adopts the gauche conformation (like hydrazine, less symmetrical than shown in the image) with a P−P distance of 2.219 angstroms. It is nonbasic, unstable at room temperature, and spontaneously flammable in air. It is only poorly soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents. Its 1H NMR spectrum consists of 32 lines resulting from an A2XX'A'2 splitting system. Diphosphane is produced by the hydrolysis of calcium monophosphide, which can be described as the Ca2+ derivative of . According to an optimized procedure, hydrolysis of 400 g of CaP at −30 °C gives about 20 g of product, slightly contaminated with phosphine. Reaction of diphosphane with butyllithium affords a variety of condense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphorus Tetraiodide
Diphosphorus tetraiodide is an orange crystalline solid with the formula P2I4. It has been used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry. It is a rare example of a compound with phosphorus in the +2 oxidation state, and can be classified as a subhalide of phosphorus. It is the most stable of the diphosphorus tetrahalides. Synthesis and structure Diphosphorus tetraiodide is easily generated by the disproportionation of phosphorus triiodide in dry ether: :2 PI3 → P2I4 + I2 It can also be obtained by treating phosphorus trichloride and potassium iodide in anhydrous conditions. The compound adopts a centrosymmetric structure with a P-P bond of 2.230 Å. Reactions Inorganic chemistry Diphosphorus tetraiodide reacts with bromine to form mixtures PI3−xBrx. With sulfur, it is oxidized to P2S2I4, retaining the P-P bond. It reacts with elemental phosphorus and water to make phosphonium iodide, which is collected via sublimation at 80 °C. Organic chemistry Diphosphorus tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen Hydride
Pnictogen hydrides or hydrogen pnictides are binary compounds of hydrogen with pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") atoms (elements of group 15: nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth) covalently bonded to hydrogen. Pnictogen trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3 (less commonly H3X), with X representing any of the pnictogens. They take on the pyramidal structure (as opposed to the trigonal planar arrangement of the group 13 hydrides), and therefore are polar. These pnictogen trihydrides are generally increasingly unstable and poisonous with heavier elements. Like the simple hydrogen halides and chalcogenides, the pnictogen hydrides are water- soluble. Unlike other hydrides such as hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen fluoride, which form acidic aqueous solutions, ammonia dissolves in water to make ammonium hydroxide which is basic (by forming a hydroxide ion as opposed to hydronium). Phosphine is also water-sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphorus Tetrafluoride
Diphosphorus tetrafluoride is a gaseous compound of phosphorus and fluorine with formula P2F4. Two fluorine atoms are connected to each phosphorus atom, and there is a bond between the two phosphorus atoms. Phosphorus can be considered to have oxidation state +2, as indicated by the name phosphorus difluoride. Production Diphosphorus tetrafluoride was discovered in 1966 by Max Lustig, John K. Ruff and Charles B. Colburn at the Redstone Research Laboratories. The initial synthesis reacted phosphorus iododifluoride with mercury at room temperature. 2PF2I +2Hg → P2F4 + Hg2I2 Properties The P-P bond in diphosphorus tetrafluoride is much stronger than the corresponding N-N bond in dinitrogen tetrafluoride which easily breaks into nitrogen difluoride. The infrared spectrum has absorption at 842 cm−1, 830 cm−1, 820 cm−1, and weaker at 408 cm−1 and 356 cm−1. The molecule has C2h symmetry. Reactions Under ultraviolet light diphosphorus tetraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraphenyldiphosphine
Tetraphenyldiphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2sub>2, where Ph = phenyl (C6H5). It is a white, air-sensitive solid that dissolves in nonpolar solvents. It is a centrosymmetric molecule with a P-P bond of 2.2592 Å. Tetraphenyldiphosphine is produced by reductive coupling of chlorodiphenylphosphine Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is u ...: :2 Ph2PCl + 2 Na → Ph2P-PPh2 + 2 NaCl The compound is used as a source of the Ph2P− group.{{cite journal, title=Zur Kenntnis der Organophosphorverbindungen, III. Umsetzungen mit Diphenylphosphin‐natrium , first1=Wilhelm , last1=Kuchen, first2=Hans, last2=Buchwald, journal=Chem. Ber., volume=92, pages=227–231 , year=1959, doi=10.1002/cber.19590920126 :Ph2P-PPh2 + 2 Na → + 2 NaPPh2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphorus Tetrabromide
Diphosphorus is an inorganic chemical with the chemical formula . Unlike nitrogen, its lighter pnictogen neighbor which forms a stable N2 molecule with a nitrogen to nitrogen triple bond, phosphorus prefers a tetrahedral form P4 because P-P pi-bonds are high in energy. Diphosphorus is, therefore, very reactive with a bond-dissociation energy (117 kcal/ mol or 490 kJ/mol) half that of dinitrogen. The bond distance has been measured at 1.8934 Å. Synthesis Diphosphorus has been generated by heating white phosphorus at 1100 kelvins (827 °C). Nevertheless, some advancements have been obtained in generating the diatomic molecule in homogeneous solution under normal conditions with the use of some transition metal complexes (based on, for example, tungsten and niobium). Methods for dissociation of bonds in P4 molecules via photoexcitation were also proposed. The molecule attracted attention in 2006, when a new method for its synthesis at milder temperatures emerged. This method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphane
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air (pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavoisier, fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphosphane
Triphosphane (IUPAC systematic name) or triphosphine is an inorganic compound having the chemical formula . It can be generated from diphosphine but is highly unstable at room temperature: : Samples have been isolated by gas chromatography. The compound rapidly converts to and the cyclophosphine Cyclopentaphosphine is the inorganic compound with the formula (PH)5. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of cyclo- SiMe3sub>4 (Me = methyl). Although only of theoretical interest, (PH)5 is parent of many related cyclic polyphosphines that are th ... ''cyclo''-. References External linksIUPAC {{Hydrides by group Phosphines Phosphorus hydrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphenes
Diphosphene is a type of organophosphorus compound that has a phosphorus–phosphorus double bond, denoted by R-P=P-R'. These compounds are not common but are of theoretical interest. Normally, compounds with the empirical formula RP exist as rings. However, like other multiple bonds between heavy main-group elements, P=P double bonds can be stabilized by a large steric hindrance from the substitutions. The first isolated diphosphene bis(2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl)diphosphene was exemplified by Masaaki Yoshifuji and his coworkers in 1981, in which diphosphene is stabilized by two bulky phenyl group. Synthesis Synthesis of aryl-substituted diphosphene In 1877, Köhler and Michaelis claimed that they synthesized the first isolated diphosphene (PhP=PPh). However, the molecular weight determination and X-ray crystallographic analysis later proved that this "diphosphene" only had a P-P single bond. Then the research to diphosphenes kept silent over almost 20 years until Masaaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrophoricity
A substance is pyrophoric (from grc-gre, πυροφόρος, , 'fire-bearing') if it ignites spontaneously in air at or below (for gases) or within 5 minutes after coming into contact with air (for liquids and solids). Examples are organolithium compounds and triethylborane. Pyrophoric materials are often water-reactive as well and will ignite when they contact water or humid air. They can be handled safely in atmospheres of argon or (with a few exceptions) nitrogen. Class D fire extinguishers are designated for use in fires involving pyrophoric materials. A related concept is hypergolicity, in which two compounds spontaneously ignite when mixed. Uses The creation of sparks from metals is based on the pyrophoricity of small metal particles, and pyrophoric alloys are made for this purpose. The sparking mechanisms in lighters and various toys, using ferrocerium; starting fires without matches, using a firesteel; the flintlock mechanism in firearms; and spark testing ferrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophosphoryl Chloride
Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula PSCl3.Spilling, C. D. "Thiophosphoryl Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim, 2001. . Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides. Synthesis Thiophosphoryl chloride can be generated by several reactions starting from phosphorus trichloride. The most common and practical synthesis, hence used in industrial manufacturing, is directly reacting phosphorus trichloride with excess sulfur at 180 °C.. :PCl3 + S → PSCl3 Using this method, yields can be very high after purification by distillation. Catalysts facilitate the reaction at lower temperatures, but are not usually necessary. Alternatively, it is obtained by combining phosphorus pentasulfide and phosphorus pentachloride.Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |