|
Dimictic
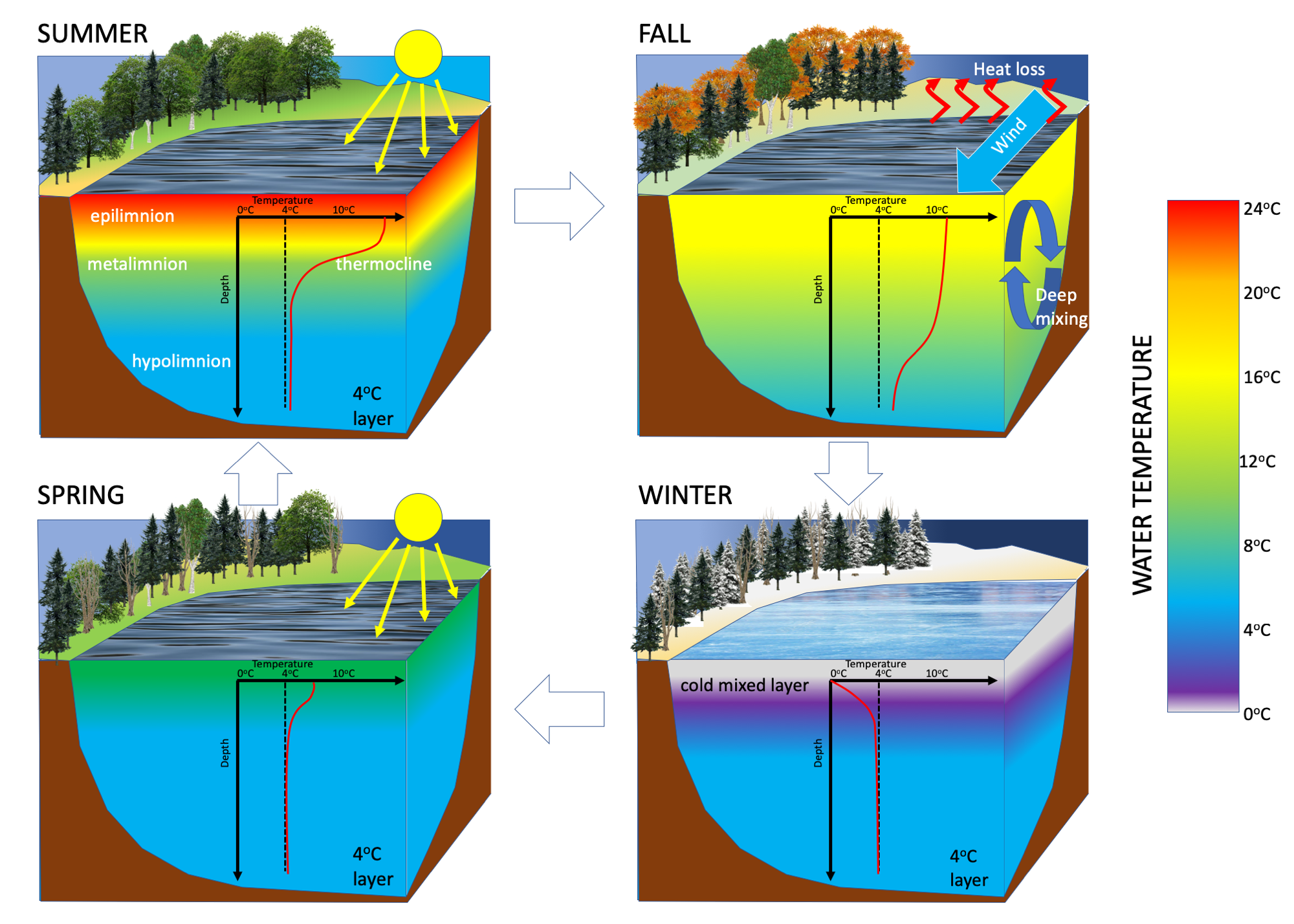
A dimictic lake is a body of freshwater whose difference in temperature between surface and bottom layers becomes negligible twice per year, allowing all strata of the lake's water to circulate vertically. All dimictic lakes are also considered holomictic, a category which includes all lakes which mix one or more times per year. During winter, dimictic lakes are covered by a layer of ice, creating a cold layer at the surface, a slightly warmer layer beneath the ice, and a still-warmer unfrozen bottom layer, while during summer, the same temperature-derived density differences separate the warm surface waters (the epilimnion), from the colder bottom waters (the hypolimnion). In the spring and fall, these temperature differences briefly disappear, and the body of water overturns and circulates from top to bottom. Such lakes are common in mid-latitude regions with temperate climates. Examples of dimictic lakes * Lake Mendota * Lake Superior * Lake Simcoe * Lake Opeongo * Loch Lomon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holomictic
Holomictic lakes are lakes that have a uniform temperature and density from surface to bottom at a specific time during the year, which allows the lake waters to mix in the absence of Stratification (water), stratification. Details Holomictic lakes mix at least occasionally, in contrast to Meromictic lake, meromictic lakes. Most lakes on Earth are holomictic; meromictic lakes are rare, although they may be less rare than commonly thought. Amictic lake, Amictic lakes are sealed off by ice and never mix. There are four types of holomictic lakes: * polymictic lake, Polymictic (mixing many times annually) * Cold monomictic lake, Monomictic (mixing once annually; exhibiting negative stratification) * Warm Monomictic (mixing once annually; exhibiting positive stratification) * dimictic lake, Dimictic (mixing twice annually) * Oligomictic (mixing less than once annually) See also * Thermocline * References External links"Circulation: annual patterns of dimictic lakes" at Encycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymictic
Polymictic lakes are holomictic lakes that are too shallow to develop thermal stratification; thus, their waters can mix from top to bottom throughout the ice-free period. Polymictic lakes can be divided into cold polymictic lakes (i.e., those that are ice-covered in winter), and warm polymictic lakes (i.e., polymictic lakes in regions where ice-cover does not develop in winter). While such lakes are well-mixed on average, during low-wind periods, weak and ephemeral stratification can often develop. See also * Amictic lake * Holomictic lake * Meromictic lake * Monomictic lake * Dimictic lake * Thermocline A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ... * References External links "Circulation: annual patterns of dimictic lakes" at Encyclopædia Britannica Online Lakes by type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomictic
Monomictic lakes are holomictic lakes that mix from top to bottom during one mixing period each year. Monomictic lakes may be subdivided into cold and warm types. Cold monomictic lakes Cold monomictic lakes are lakes that are covered by ice throughout much of the year. During their brief "summer", the surface waters remain at or below 4 °C. The ice prevents these lakes from mixing in winter. During summer, these lakes lack significant thermal stratification, and they mix thoroughly from top to bottom. These lakes are typical of cold-climate regions (e.g. much of the Arctic). An example of a cold monomictic lake is Great Bear Lake in Canada. Warm monomictic lakes Warm monomictic lakes are lakes that never freeze, and are thermally stratified throughout much of the year. The density difference between the warm surface waters (the epilimnion) and the colder bottom waters (the hypolimnion) prevents these lakes from mixing in summer. During winter, the surface waters cool to a te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh water. The northern and westernmost of the Great Lakes of North America, it straddles the Canada–United States border with the province of Ontario to the north and east, and the states of Minnesota to the northwest and Wisconsin and Michigan to the south. It drains into Lake Huron via St. Marys River, then through the lower Great Lakes to the St. Lawrence River and the Atlantic Ocean. Name The Ojibwe name for the lake is ''gichi-gami'' (in syllabics: , pronounced ''gitchi-gami'' or ''kitchi-gami'' in different dialects), meaning "great sea". Henry Wadsworth Longfellow wrote this name as "Gitche Gumee" in the poem ''The Song of Hiawatha'', as did Gordon Lightfoot in his song " The Wreck of the ''Edmund Fitzgerald''". According to oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holomictic
Holomictic lakes are lakes that have a uniform temperature and density from surface to bottom at a specific time during the year, which allows the lake waters to mix in the absence of Stratification (water), stratification. Details Holomictic lakes mix at least occasionally, in contrast to Meromictic lake, meromictic lakes. Most lakes on Earth are holomictic; meromictic lakes are rare, although they may be less rare than commonly thought. Amictic lake, Amictic lakes are sealed off by ice and never mix. There are four types of holomictic lakes: * polymictic lake, Polymictic (mixing many times annually) * Cold monomictic lake, Monomictic (mixing once annually; exhibiting negative stratification) * Warm Monomictic (mixing once annually; exhibiting positive stratification) * dimictic lake, Dimictic (mixing twice annually) * Oligomictic (mixing less than once annually) See also * Thermocline * References External links"Circulation: annual patterns of dimictic lakes" at Encycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amictic
Amictic lakes are "perennially sealed off by ice, from most of the annual seasonal variations in temperature." Amictic lakes exhibit inverse cold water stratification whereby water temperature increases with depth below the ice surface 0 °C (less-dense) up to a theoretical maximum of 4 °C (at which the density of water is highest). Hutchinson–Löffler (1956) classified amictic and other types of lakes based on physical/thermal processes. These processes are influenced by solar radiation and wind. They are strongly tied with seasonality and thus associated with latitude and altitude. Amictic lakes occur in Arctic, Antarctic, and alpine regions and due to permanent ice-cover, these physical/thermal influences have a limited effect on circulation in the water column. For this reason, amictic lakes are commonly referred to as lakes that ''never'' mix. ''"Mixing"'' in this context, however, refers to homogenization of the water column and so the term ''"amictic"'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimictic Lake
A dimictic lake is a body of freshwater whose difference in temperature between surface and bottom layers becomes negligible twice per year, allowing all strata of the lake's water to circulate vertically. All dimictic lakes are also considered holomictic, a category which includes all lakes which mix one or more times per year. During winter, dimictic lakes are covered by a layer of ice, creating a cold layer at the surface, a slightly warmer layer beneath the ice, and a still-warmer unfrozen bottom layer, while during summer, the same temperature-derived density differences separate the warm surface waters (the epilimnion), from the colder bottom waters (the hypolimnion). In the spring and fall, these temperature differences briefly disappear, and the body of water overturns and circulates from top to bottom. Such lakes are common in mid-latitude regions with temperate climates. Examples of dimictic lakes * Lake Mendota * Lake Superior * Lake Simcoe * Opeongo Lake, Lake Opeongo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Stratification
Lake stratification is the tendency of lakes to form separate and distinct thermal layers during warm weather. Typically stratified lakes show three distinct layers, the Epilimnion comprising the top warm layer, the thermocline (or Metalimnion): the middle layer, which may change depth throughout the day, and the colder Hypolimnion extending to the floor of the lake. Definition The thermal stratification of lakes refers to a change in the temperature at different depths in the lake, and is due to the density of water varying with temperature. Cold water is denser than warm water and the epilimnion generally consists of water that is not as dense as the water in the hypolimnion. However, the temperature of maximum density for freshwater is 4 °C. In Temperate climate, temperate regions where lake water warms up and cools through the seasons, a cyclical pattern of overturn occurs that is repeated from year to year as the cold dense water at the top of the lake sinks (see stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coriolis Frequency
The Coriolis frequency ''ƒ'', also called the Coriolis parameter or Coriolis coefficient, is equal to twice the rotation rate ''Ω'' of the Earth multiplied by the sine of the latitude \varphi. :f = 2 \Omega \sin \varphi.\, The rotation rate of the Earth (''Ω'' = 7.2921 × 10−5 rad/s) can be calculated as 2''π'' / ''T'' radians per second, where ''T'' is the rotation period of the Earth which is one ''sidereal'' day (23 h 56 min 4.1 s). In the midlatitudes, the typical value for f is about 10−4 rad/s. Inertial oscillations on the surface of the earth have this frequency. These oscillations are the result of the Coriolis effect. Explanation Consider a body (for example a fixed volume of atmosphere) moving along at a given latitude \varphi at velocity v in the earth's rotating reference frame. In the local reference frame of the body, the vertical direction is parallel to the radial vector pointi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meromictic
A meromictic lake is a lake which has layers of water that do not intermix. In ordinary, holomictic lakes, at least once each year, there is a physical mixing of the surface and the deep waters. The term ''meromictic'' was coined by the Austrian Ingo Findenegg in 1935, apparently based on the older word ''holomictic''. The concepts and terminology used in describing meromictic lakes were essentially complete following some additions by G. Evelyn Hutchinson in 1937. Characteristics Most lakes are ''holomictic''; that is, at least once per year, physical mixing occurs between the surface and the deep waters. In so-called monomictic lakes, the mixing occurs once per year; in dimictic lakes, the mixing occurs twice a year (typically spring and autumn), and in polymictic lakes, the mixing occurs several times a year. In meromictic lakes, however, the layers of the lake water can remain unmixed for years, decades, or centuries. Meromictic lakes can usually be divided into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properties Of Water
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric, meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the phase speed of the wave crests is equal to the group speed of the wave energy for all frequencies. This means that it retains its shape as it moves in the alongshore direction over time. A Kelvin wave (fluid dynamics) is also a long scale perturbation mode of a vortex in superfluid dynamics; in terms of the meteorological or oceanographical derivation, one may assume that the meridional velocity component vanishes (i.e. there is no flow in the north–south direction, thus making the momentum and continuity equations much simpler). This wave is named after the discoverer, Lord Kelvin (1879). Coastal Kelvin wave In a stratified ocean of mean depth ''H'', perturbed by some amount ''η'', free waves propagate along coastal boundaries (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |