|
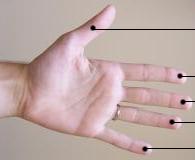
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively "finger" and "toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can be surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as the Ainu, Austroasiatic, Koreanic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), there was a massive influx of Sino-Japanese vocabulary into the language, affecting the phonology of Early Middle Japanese. Late Middle Japanese (1185–1600) saw extensive grammatical changes and the first appearance of European loanwords. The basis of the standard dialect moved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger. Etymology The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''pink'', meaning "little finger". The earliest recorded use of the term "pinkie" is from Scotland in 1808. The term (sometimes spelled "pinky") is common in Scottish English and American English, and is also used extensively in other Commonwealth countries such as New Zealand, Canada, and Australia. Nerves and muscles The little finger is nearly impossible for most people to bend independently (without also bending the ring finger), due to the nerves for each digit being intertwined. There are also nine muscles that control the fifth digit: Three in the hypothenar eminence, two extrinsic flexors, two extrinsic extensors, and two more intrinsic muscles: * Hypothenar eminence: ** Opponens digiti minimi muscle ** Abductor minimi digiti muscle (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Finger
The ring finger, third finger, fourth finger, leech finger, or annulary is the fourth digit of the human hand, located between the middle finger and the little finger. Sometimes the term ring finger only refers to the fourth digit of a left-hand, so named for its traditional association with wedding rings in many societies, although not all use this digit as the ring finger. Traditionally, a wedding ring was worn only by the bride or wife, but in recent times more men also wear a wedding ring. It is also the custom in some societies to wear an engagement ring on the ring finger. In anatomy, the ring finger is called ''digitus medicinalis'', ''the fourth digit'', ''digitus annularis'', ''digitus quartus'', or ''digitus IV''. In Latin, the word ''anulus'' means "ring", ''digitus'' means "digit", and ''quartus'' means "fourth". Etymology The origin of the selection of the fourth digit as the ring finger is not definitively known. According to László A. Magyar, the names of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Finger
The middle finger, long finger, second finger, third finger, toll finger or tall man is the third digit of the human hand, located between the index finger and the ring finger. It is typically the longest digit. In anatomy, it is also called ''the third finger'', ''digitus medius'', ''digitus tertius'' or ''digitus III''. In Western countries, The finger, extending the middle finger (either by itself, or along with the index finger The index finger (also referred to as forefinger, first finger, second finger, pointer finger, trigger finger, digitus secundus, digitus II, and many other terms) is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the mid ... in the United Kingdom: see V sign) is an offensive and obscene gesture, widely recognized as a form of insult, due to its resemblance of an Erection, erect penis, It is known, colloquially, as "flipping the bird", "flipping (someone) off", or "giving (someone) the finger". The middle finger is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Finger
The index finger (also referred to as forefinger, first finger, second finger, pointer finger, trigger finger, digitus secundus, digitus II, and many other terms) is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the middle finger. It is usually the most dextrous and sensitive digit of the hand, though not the longest. It is shorter than the middle finger, and may be shorter or longer than the ring finger (see digit ratio). Anatomy "Index finger" literally means "pointing finger", from the same Latin source as '' indicate;'' its anatomical names are "index finger" and "second digit". The index finger has three phalanges. It does not contain any muscles, but is controlled by muscles in the hand by attachments of tendons to the bones. Uses A lone index finger held vertically is often used to represent the number 1 (but finger counting differs across cultures), or when held up or moved side to side (finger-wagging), it can be an admonitory gesture. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is ''pollex'' (compare ''hallux'' for big toe), and the corresponding adjective for thumb is ''pollical''. Definition Thumb and fingers The English word ''finger'' has two senses, even in the context of appendages of a single typical human hand: # Any of the five terminal members of the hand. # Any of the four terminal members of the hand, other than the thumb Linguistically, it appears that the original sense was the first of these two: (also rendered as ) was, in the inferred Proto-Indo-European language, a suffixed form of (or ), which has given rise to many Indo-European-family words (tens of them defined in English dictionaries) that involve, or stem from, concepts of fiveness. The thumb shares the following with each of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers 1998 p. 603 Oxford Illustrated pp. 311, 380 Land vertebrate fingers The five-rayed anterior limbs of terrestrial vertebrates can be derived phylogenetically from the pectoral fins of fish. Within the taxa of the terrestrial vertebrates, the basic pentadactyl plan, and thus also the fingers and phalanges, undergo many variations. Morphologically the different fingers of terrestrial vertebrates are homolog. The wings of birds and those of bats are not homologous, they are analogue flight organs. However, the phalanges within them are homologous. Chimpanzees have lower limbs that are specialized for manipulation, and (arguably) have fingers on their lower limbs as well. In the case of Primates in general, the digits of the hand a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Tal
Mikhail Nekhemyevich Tal; rus, Михаил Нехемьевич Таль, ''Mikhail Nekhem'yevich Tal' '', ; sometimes transliterated ''Mihails Tals'' or ''Mihail Tal'' (9 November 1936 – 28 June 1992) was a Soviet-Latvian chess player and the eighth World Chess Champion. He is considered a creative genius within the game of chess and one of its best ever players. Tal played in an attacking and daring combinatorial style. His play was known above all for improvisation and unpredictability. It has been said that "Every game for him was as inimitable and invaluable as a poem". His nickname was "Misha", a diminutive for Mikhail, and he earned the nickname "The Magician from Riga". Both ''The Mammoth Book of the World's Greatest Chess Games'' and ''Modern Chess Brilliancies'' include more games by Tal than any other player. He also held the record for the longest unbeaten streak in competitive chess history with 95 games (46 wins, 49 draws) between 23 October 1973 and 16 O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
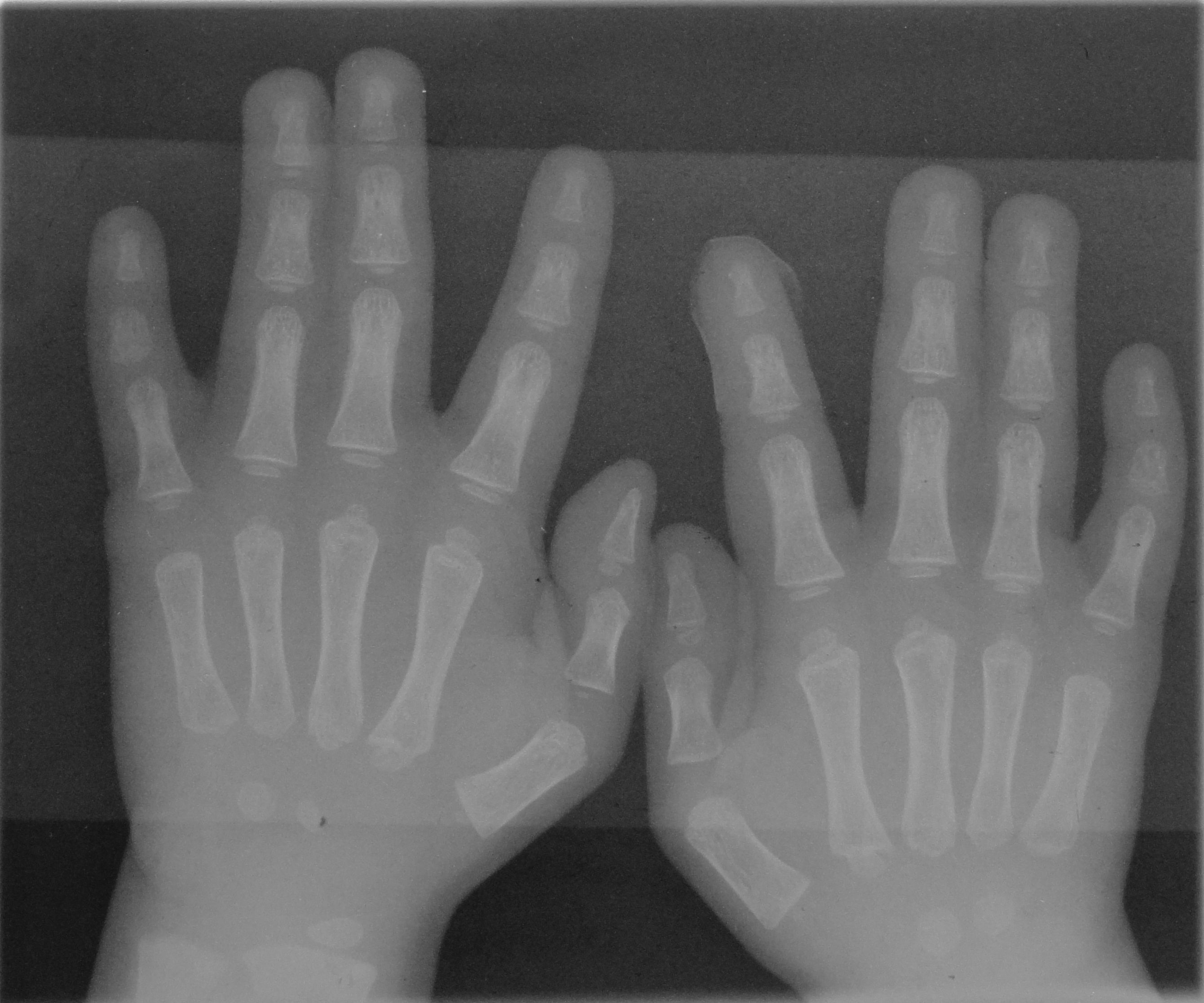
Ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly, split hand, or cleft hand (derived from Greek ''ektroma'' 'abortion' and ''daktylos'' 'finger') involves the deficiency or absence of one or more central digits of the hand or foot and is also known as split hand/split foot malformation (SHFM). The hands and feet of people with ectrodactyly (ectrodactyls) are often described as "claw-like" and may include only the thumb and one finger (usually either the little finger, ring finger, or a syndactyly of the two) with similar abnormalities of the feet. It is a substantial rare form of a congenital disorder in which the development of the hand is disturbed. It is a type I failure of formation – longitudinal arrest. The central ray of the hand is affected and usually appears without proximal deficiencies of nerves, vessels, tendons, muscles and bones in contrast to the radial and ulnar deficiencies. The cleft hand appears as a V-shaped cleft situated in the centre of the hand. The digits at the borders of the cleft might ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes). Signs and symptoms In humans/animals this condition can present itself on one or both hands or feet. The extra digit is usually a small piece of soft tissue that can be removed. Occasionally it contains bone without joints; rarely it may be a complete functioning digit. The extra digit is most common on the ulnar (little finger) side of the hand, less common on the radial (thumb) side, and very rarely within the middle three digits. These are respectively known as postaxial (little finger), preaxial (thumb), and central (ring, middle, index fingers) polydactyly. The extra digit is most commonly an abnormal fork in an existing digit, or it may rarely originate at the wrist as a normal digit does. The incidence of congenital deformities in newborns is approximately 2%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nail (anatomy)
A nail is a claw-like plate found at the tip of the Finger, fingers and Toe, toes on most primates. Nails correspond to the claws found in other animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protective protein called alpha-keratin, which is a polymer. Alpha-keratin is found in the hooves, claws, and horns of vertebrates. Structure The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. Parts of the nail The matrix, sometimes called the ''matrix unguis'', keratogenous membrane, nail matrix, or onychostroma, is the active Tissue (biology), tissue (or Germ layer, germinal Matrix (biology), matrix) that generates cells, which harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate. It is the part of the nail bed that is beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph and blood vessels. The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail plate is determined by the size, length, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |