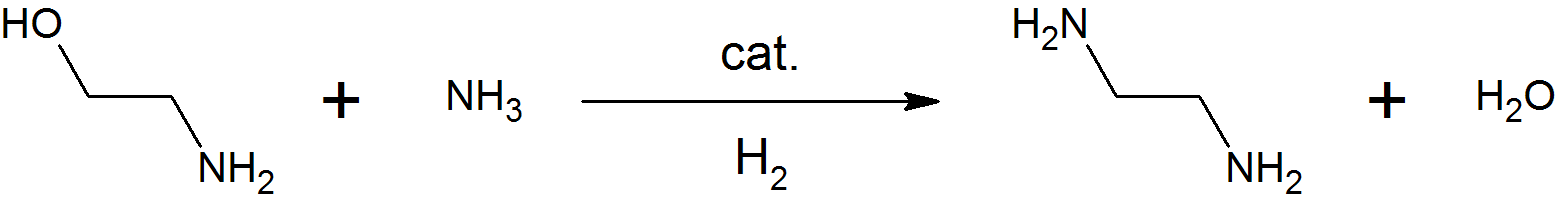|
Diethanolamine
Diethanolamine, often abbreviated as DEA or DEOA, is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2OH)2. Pure diethanolamine is a white solid at room temperature, but its tendencies to absorb water and to supercool meaning that it is often encountered as a colorless, viscous liquid. Diethanolamine is polyfunctional, being a secondary amine and a diol. Like other organic amines, diethanolamine acts as a weak base. Reflecting the hydrophilic character of the secondary amine and hydroxyl groups, DEA is soluble in water. Amides prepared from DEA are often also hydrophilic. In 2013, the chemical was classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as "possibly carcinogenic to humans" ( Group 2B). Production The reaction of ethylene oxide with aqueous ammonia first produces ethanolamine: :C2H4O + NH3 → H2NCH2CH2OH which reacts with a second and third equivalent of ethylene oxide to give DEA and triethanolamine: :C2H4O + H2NCH2CH2OH → HN(CH2CH2OH)2 :C2H4O + H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Diethanolamine
Methyl diethanolamine, also known as ''N''-methyl diethanolamine and more commonly as MDEA, is the organic compound with the formula CH3N(C2H4OH)2. It is a colorless liquid with an ammonia odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and benzene. A tertiary amine, it is widely used as a sweetening agent in chemical, oil refinery, syngas production and natural gas.Matthias Frauenkron, Johann-Peter Melder, Günther Ruider, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Similar compounds are monoethanolamine (MEA), a primary amine, and diethanolamine (DEA), a secondary amine, both of which are also used for amine gas treating. MDEA's defining characteristic when compared to these other amines is its ability to preferentially remove H2S (and strip CO2) from sour gas streams. MDEA's popularity as a solvent for gas treating stems from several advantages it has when compared to other alkanolamin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine, or TEA is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities. Production Triethanolamine is produced from the reaction of ethylene oxide with aqueous ammonia, also produced are ethanolamine and diethanolamine. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry of the reactants. : Applications Triethanolamine is used primarily in making surfactants, such as for emulsifier. It is a common ingredient in formulations used for both industrial and consumer products. The triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids, adjusts and pH buffer, buffers the pH, and solubilizes oils and other ingredients that are not completely Solubility, soluble in water. Triethanolammonium salts in some cases are more soluble than salts of alkali metals that might be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine, or TEA is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities. Production Triethanolamine is produced from the reaction of ethylene oxide with aqueous ammonia, also produced are ethanolamine and diethanolamine. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry of the reactants. : Applications Triethanolamine is used primarily in making surfactants, such as for emulsifier. It is a common ingredient in formulations used for both industrial and consumer products. The triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids, adjusts and pH buffer, buffers the pH, and solubilizes oils and other ingredients that are not completely Solubility, soluble in water. Triethanolammonium salts in some cases are more soluble than salts of alkali metals that might be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethanolamide
Diethanolamides are common ingredients used in cosmetics to act as a foaming agents or as emulsifiers. Chemically, they are amides formed from diethanolamine and carboxylic acids, typically fatty acids. Examples include: * Cocamide diethanolamine * Lauramide diethanolamine * Oleamide diethanolamine Oleamide is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CONH2(. It is the amide derived from the fatty acid oleic acid. It is a colorless waxy solid and occurs in nature. Sometimes labeled as a fatty acid primary amide (FAPA), it is ... References Fatty acid amides {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine (2-aminoethanol, monoethanolamine, ETA, or MEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula or . The molecule is bifunctional, containing both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Ethanolamine is a colorless, viscous liquid with an odor reminiscent of ammonia.. ETA molecules are a component in the formation of cellular membranes and are thus a molecular building block for life. It was thought to exist only on Earth and on certain asteroids, but in 2021 evidence was found that ETA molecules exist in interstellar space. Derivatives of ethanolamine are widespread in nature; e.g., lipids, as precursor of a variety of ''N''-acylethanolamines (NAEs), that modulate several animal and plant physiological processes such as seed germination, plant–pathogen interactions, chloroplast development and flowering, as well as precursor, combined with arachidonic acid 20: 4, ω-6), to form the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA: ; 20:4, ω-6). The ethanolamines comprise a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Methylethanolamine
''N''-Methylethanolamine is an alkanolamine with the formula CH3NHCH2CH2OH. It is flammable, corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid.Matthias Frauenkron, Johann-Peter Melder, Günther Ruider, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of choline. With both an amine and a hydroxyl functional groups, it is a useful intermediate in the chemical synthesis of various products including polymers and pharmaceuticals. It is also used as a solvent, for example in the processing of natural gas, where it is used together with its analogs ethanolamine and dimethylethanolamine. Production ''N''-Methylethanolamine is produced industrially by reacting ethylene oxide with excess methylamine in aqueous solution. This reaction yields a mixture of the 1:1 addition product NMEA (1) and - by a further addition of another ethylene oxide - the 1:2 addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis-tris Methane
Bis-tris methane, also known as BIS-TRIS or BTM, is a buffering agent used in biochemistry. Bis-tris methane is an organic tertiary amine with labile protons having a pKa of 6.46 at 25 °C. It is an effective buffer between the pH 5.8 and 7.2. Bis-tris methane binds strongly to Cu and Pb ions as well as, weakly, to Mg, Ca, Mn, Co, Ni, Zn and Cd. See also *Bis-tris propane *Tris *Tricine Tricine is an organic compound that is used in buffer solutions. The name tricine comes from tris and glycine, from which it was derived.Good, N.E., et al., Biochemistry, v. 5, 467 (1966). It is a white crystalline powder that is moderately solub ... References Polyols Amines Buffer solutions {{amine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylhydroxylamine
Diethylhydroxylamine (DEHA) is an organic compound with the formula (C2H5)2NOH. Strictly, this is ''N'',''N''-diethylhydroxylamine. It has an isomer, ''N'',''O''-diethylhydroxylamine with the formula EtNHOEt. ''N'',''N''-diethylhydroxylamine is a colorless liquid, although it is usually encountered as a solution. It is mainly used as an oxygen scavenger in water treatment. It is a volatile oxygen scavenger and reacts in a ratio of 2.8/1 DEHA/O2. It is employed in high pressure (>70 bar) boiler systems due to a very low rate of reaction at low temperatures and pressures. Due to its volatility, it acts as an oxygen scavenger throughout the entire boiler system due to steam carryover. DEHA also reacts with ferrous metals to form a passivized film of magnetite throughout the boiler system. It has these other uses: #Polymerisation inhibitor #Color stabilizer ( photographics) #Corrosion inhibitor #Discoloration inhibitor ( phenolics) #Antiozonant An antiozonant, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpholine
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O( C H2CH2)2 NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid makes the salt morpholinium chloride. It is a colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine. Production Morpholine is often produced industrially by the dehydration of diethanolamine with sulfuric acid: : Uses Industrial applications Morpholine is a common additive, in parts per million concentrations, for pH adjustment in both fossil fuel and nuclear power plant steam systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N-Diisopropylaminoethanol
''N'',''N''-Diisopropylaminoethanol (DIPA) is a processor for production of various chemicals and also an intermediate in the production of the nerve agent Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that ...s VX and NX. It is a colorless liquid, although aged samples can appear yellow. Health effects Inhalation and skin contact are expected to be the primary ways of occupational exposure to this chemical. Based on single exposure animal tests, it is considered to be slightly toxic if swallowed or inhaled, moderately toxic if absorbed through skin as well as being corrosive to eyes and skin. Vapor may be irritating to the eyes and upper respiratory tract. Temporary and reversible visual disturbances characterized by mildly blurred vision, a blue-gray discolorization of sight (blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylethanolamine
Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE or DMEA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improving skin tone and also taken orally as a nootropic. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine. Industrial uses Dimethylaminoethanol is used as a curing agent for polyurethanes and epoxy resins. It is a precursor to other chemicals, such as the nitrogen mustard 2-dimethylaminoethyl chloride. The acrylate ester is used as a flocculating agent. Related compounds are used in gas purification, e.g. removal of hydrogen sulfide from sour gas streams. Nutraceutical uses The bitartrate salt of DMAE, i.e. 2-dimethylaminoethanol (+)-bitartrate, is sold as a dietary supplement. It is a white powder providing 37% DMAE. Animal tests show possible benefit for improving spatial memory and working memory.Edward D Levin, Jed E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |