|
Dichotomous
A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are complements. In logic, the partitions are opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multicategorical variables as binary variables is called dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichotomization is temporarily ignored for modeling purposes. Etymology The term ''di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Complement
In set theory, the complement of a set , often denoted by (or ), is the set of elements not in . When all sets in the universe, i.e. all sets under consideration, are considered to be members of a given set , the absolute complement of is the set of elements in that are not in . The relative complement of with respect to a set , also termed the set difference of and , written B \setminus A, is the set of elements in that are not in . Absolute complement Definition If is a set, then the absolute complement of (or simply the complement of ) is the set of elements not in (within a larger set that is implicitly defined). In other words, let be a set that contains all the elements under study; if there is no need to mention , either because it has been previously specified, or it is obvious and unique, then the absolute complement of is the relative complement of in : A^\complement = U \setminus A. Or formally: A^\complement = \. The absolute complement of is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undistributed Middle
The fallacy of the undistributed middle () is a formal fallacy that is committed when the middle term in a categorical syllogism is not distributed in either the minor premise or the major premise. It is thus a syllogistic fallacy. Classical formulation In classical syllogisms, all statements consist of two terms and are in the form of "A" (all), "E" (none), "I" (some), or "O" (some not). The first term is distributed in A statements; the second is distributed in O statements; both are distributed in "E" statements, and none are distributed in I statements. The fallacy of the undistributed middle occurs when the term that links the two premises is never distributed. In this example, distribution is marked in boldface: # All Z is B # All Y is B # Therefore, all Y is Z B is the common term between the two premises (the middle term) but is never distributed, so this syllogism is invalid. B would be distributed by introducing a premise which states either All B is Z, or Some B is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
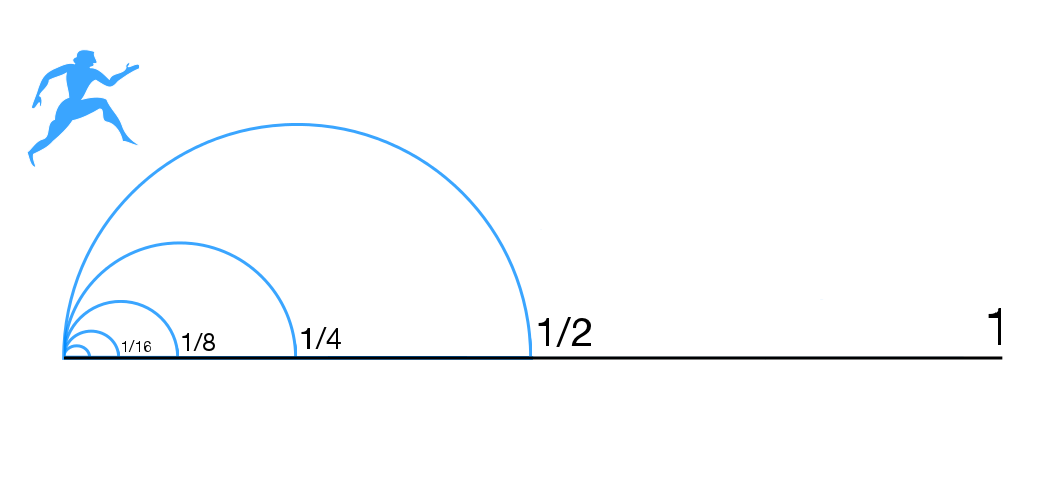
Dichotomy Paradox
Zeno's paradoxes are a set of philosophical problems generally thought to have been devised by Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea (c. 490–430 BC) to support Parmenides' doctrine that contrary to the evidence of one's senses, the belief in plurality and change is mistaken, and in particular that motion is nothing but an illusion. It is usually assumed, based on Plato's ''Parmenides'' (128a–d), that Zeno took on the project of creating these paradoxes because other philosophers had created paradoxes against Parmenides' view. Thus Plato has Zeno say the purpose of the paradoxes "is to show that their hypothesis that existences are many, if properly followed up, leads to still more absurd results than the hypothesis that they are one." Plato has Socrates claim that Zeno and Parmenides were essentially arguing exactly the same point. Some of Zeno's nine surviving paradoxes (preserved in Aristotle's ''Physics'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (set Theory)
In set theory and its applications throughout mathematics, a class is a collection of sets (or sometimes other mathematical objects) that can be unambiguously defined by a property that all its members share. Classes act as a way to have set-like collections while differing from sets so as to avoid Russell's paradox (see ). The precise definition of "class" depends on foundational context. In work on Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, the notion of class is informal, whereas other set theories, such as von Neumann–Bernays–Gödel set theory, axiomatize the notion of "proper class", e.g., as entities that are not members of another entity. A class that is not a set (informally in Zermelo–Fraenkel) is called a proper class, and a class that is a set is sometimes called a small class. For instance, the class of all ordinal numbers, and the class of all sets, are proper classes in many formal systems. In Quine's set-theoretical writing, the phrase "ultimate class" is often used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipartite (other)
{{disambig ...
Bipartite may refer to: * 2 (number) * Bipartite (theology), a philosophical term describing the human duality of body and soul * Bipartite graph, in mathematics, a graph in which the vertices are partitioned into two sets and every edge has an endpoint in each set * Bipartite uterus, a type of uterus found in deer and moose, etc. * Bipartite treaty, a treaty between two parties See also * Dichotomy A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Opposition
A binary opposition (also binary system) is a pair of related terms or concepts that are opposite in meaning. Binary opposition is the system of language and/or thought by which two theoretical opposites are strictly defined and set off against one another. It is the contrast between two mutually exclusive terms, such as on and off, up and down, left and right. Binary opposition is an important concept of structuralism, which sees such distinctions as fundamental to all language and thought.Baldick, C 2004. The concise Oxford Dictionary of literary terms, viewed 8 March 2011, http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1056-binaryopposition.html In structuralism, a binary opposition is seen as a fundamental organizer of human philosophy, culture, and language. Binary opposition originated in Saussurean structuralist theory.Fogarty, S 2005, The literary encyclopedia, viewed 6 March 2011, http://www.litencyc.com/php/stopics.php?pec=true&UID=122 According to Ferdinand de Saussure, the binary opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature (astronomy)
In spherical astronomy, quadrature is the configuration of a celestial object in which its elongation is perpendicular to the direction of the Sun. It is applied especially to the position of a superior planet or the Moon at its first and last quarter phases. This is not to be confused with the Moon at dichotomy (exactly half-lit) as viewed from Earth, which occurs at 89.85 degrees and 270.15 degrees. As shown in the diagram, a planet (or other object) can be at the western quadrature (when it is to the west of the Sun when viewed from the Earth) or at the eastern quadrature (when it is to the east of the Sun when viewed from the Earth). Note that an inferior planet can never be at quadrature to the reference planet. At quadrature, the shadow that a planet casts on its planetary rings appears most offset from the planet (e.g., Saturn's rings); the dark side of a planet (e.g., Mars) is maximally visible. See also * Astrological aspect In astrology, an aspect is an angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to Applied science, practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Computer programming, software). Computer science is generally considered an area of research, academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing Vulnerability (computing), security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dummy Variable (statistics)
In regression analysis, a dummy variable (also known as indicator variable or just dummy) is one that takes the values 0 or 1 to indicate the absence or presence of some categorical effect that may be expected to shift the outcome. For example, if we were studying the relationship between gender and income, we could use a dummy variable to represent the gender of each individual in the study. The variable would take on a value of 1 for males and 0 for females. Dummy variables are commonly used in regression analysis to represent categorical variables that have more than two levels, such as education level or occupation. In this case, multiple dummy variables would be created to represent each level of the variable, and only one dummy variable would take on a value of 1 for each observation. Dummy variables are useful because they allow us to include categorical variables in our analysis, which would otherwise be difficult to include due to their non-numeric nature. They can also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Scale
Ordinal data is a categorical, statistical data type where the variables have natural, ordered categories and the distances between the categories are not known. These data exist on an ordinal scale, one of four levels of measurement described by S. S. Stevens in 1946. The ordinal scale is distinguished from the nominal scale by having a ''ranking''. It also differs from the interval scale and ratio scale by not having category widths that represent equal increments of the underlying attribute. Examples of ordinal data A well-known example of ordinal data is the Likert scale. An example of a Likert scale is: Examples of ordinal data are often found in questionnaires: for example, the survey question "Is your general health poor, reasonable, good, or excellent?" may have those answers coded respectively as 1, 2, 3, and 4. Sometimes data on an interval scale or ratio scale are grouped onto an ordinal scale: for example, individuals whose income is known might be grouped into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)