|
Deterministic Blockmodeling
Deterministic blockmodeling is an approach in blockmodeling that does not assume a probabilistic model, and instead relies on the exact or approximate algorithms, which are used to find blockmodel(s). This approach typically minimizes some inconsistency that can occur with the ideal block structure. Such analysis is focused on clustering (grouping) of the network (or adjacency matrix) that is obtained with minimizing an objective function, which measures discrepancy from the ideal block structure. However, some indirect approaches (or methods between direct and indirect approaches, such as CONCOR) do not explicitly minimize inconsistencies or optimize some criterion function. This approach was popularized in the 1970s, due to the presence of two computer packages ( CONCOR and STRUCTURE) that were used to "find a permutation In mathematics, a permutation of a set is, loosely speaking, an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockmodeling
Blockmodeling is a set or a coherent framework, that is used for analyzing social structure and also for setting procedure(s) for partitioning (clustering) social network's units (nodes, vertices, actors), based on specific patterns, which form a distinctive structure through interconnectivity.Patrick Doreian, An Intuitive Introduction to Blockmodeling with Examples, ''BMS: Bulletin of Sociological Methodology'' / ''Bulletin de Méthodologie Sociologique'', January, 1999, No. 61 (January, 1999), pp. 5–34. It is primarily used in statistics, machine learning and network science. As an empirical procedure, blockmodeling assumes that all the units in a specific network can be grouped together to such extent to which they are equivalent. Regarding equivalency, it can be structural, regular or generalized.Anuška Ferligoj: Blockmodeling, http://mrvar.fdv.uni-lj.si/sola/info4/nusa/doc/blockmodeling-2.pdf Using blockmodeling, a network can be analyzed using newly created blockmodels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probabilistic Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of sample data (and similar data from a larger population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the data-generating process. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" ( Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth Bollen). All statistical hypothesis tests and all statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. Introduction Informally, a statistical model can be thought of as a statistical assumption (or set of statistical assumptions) with a certain property: that the assumption allows us to calculate the probability of any event. As an example, consider a pair of ordinary six-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockmodel
Blockmodel (sometimes also block model) in blockmodeling (part of network science) is defined as a multitude of structures, which are obtained with: * identification of all vertices (e.g., units, nodes) within a cluster and at the same time representing each cluster as a vertex, from which vertices for another graph can be constructed; * combination of all the links (ties), represented in a block as a single link between positions, while at the same time constructing one tie for each block. In a case, when there are no ties in a block, there will be no ties between the two positions, that define the block. In principle, blockmodeling, as a process, is composed from three steps. In the first step, the number of units is determined. This is followed (in the second step) by selection or determination of permitted blocks, that will occur and perhaps also the locations in the matrix. The last, third step, using computer program, the partitioning of units is done, according to the pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Theory
Network theory is the study of graphs as a representation of either symmetric relations or asymmetric relations between discrete objects. In computer science and network science, network theory is a part of graph theory: a network can be defined as a graph in which nodes and/or edges have attributes (e.g. names). Network theory has applications in many disciplines including statistical physics, particle physics, computer science, electrical engineering, biology, archaeology, economics, finance, operations research, climatology, ecology, public health, sociology, and neuroscience. Applications of network theory include logistical networks, the World Wide Web, Internet, gene regulatory networks, metabolic networks, social networks, epistemological networks, etc.; see List of network theory topics for more examples. Euler's solution of the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem is considered to be the first true proof in the theory of networks. Network optimization Network pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, unle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CONCOR
Concor Holdings (Proprietary) Limited. is a South African construction and mining services company. It is active throughout Southern Africa, involved in mining, civil engineering, building and road projects. Concor returned as an independent brand in late 2016. Company history Origin Dr F. Piccini, the original founder of Construction Corporation, registered the company in Johannesburg on 28 April 1948. The other four founding members were M. Barnabo, B. Chiozzi, U. Mantelli and V. Cini. The original name Construction Corporation was finally shortened to CONCOR. Dr Piccinni was originally a chairman of Ferrocemento, an Italian construction giant and the emerging Concor received its technical support initially from there. File:Original Concor Logo 1948.png, Original Concor Logo 1948 File:Original Concor Logo up to 2006.jpg, Concor Logo up to 2006 File:CONCOR LOGO.jpg, Concor Logo 2017 to current Initial projects The company's first major project was the construction of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleš Žiberna
Aleš Žiberna is a Slovene statistician, whose specialty is network analysis. His specific research interests include blockmodeling, multivariate analysis and computer intensive methods (e.g., computer simulations, resampling methods). Currently, he is employed at the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Ljubljana, specifically at the Chair of Social Informatics and Methodology, and Centre for Methodology and Informatics. Work In 2007, he proposed a solution to the generalized valued blockmodeling by introducing homogeneity blockmodeling with the basic idea "that the inconsistency of an empirical block with its ideal block can be measured by within block variability of appropriate values". The newly-formed ideal blocks, which are appropriate for blockmodeling of valued networks, are then presented together with the definitions of their block inconsistencies. He also (in 2007/08) developed an implicit blockmodeling approach, based on previous work of Batagel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STRUCTURE
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set is, loosely speaking, an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is already ordered, a rearrangement of its elements. The word "permutation" also refers to the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set. Permutations differ from combinations, which are selections of some members of a set regardless of order. For example, written as tuples, there are six permutations of the set , namely (1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), and (3, 2, 1). These are all the possible orderings of this three-element set. Anagrams of words whose letters are different are also permutations: the letters are already ordered in the original word, and the anagram is a reordering of the letters. The study of permutations of finite sets is an important topic in the fields of combinatorics and group theory. Permutations are used in almost every branch of mathematics, and in many other fields of scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
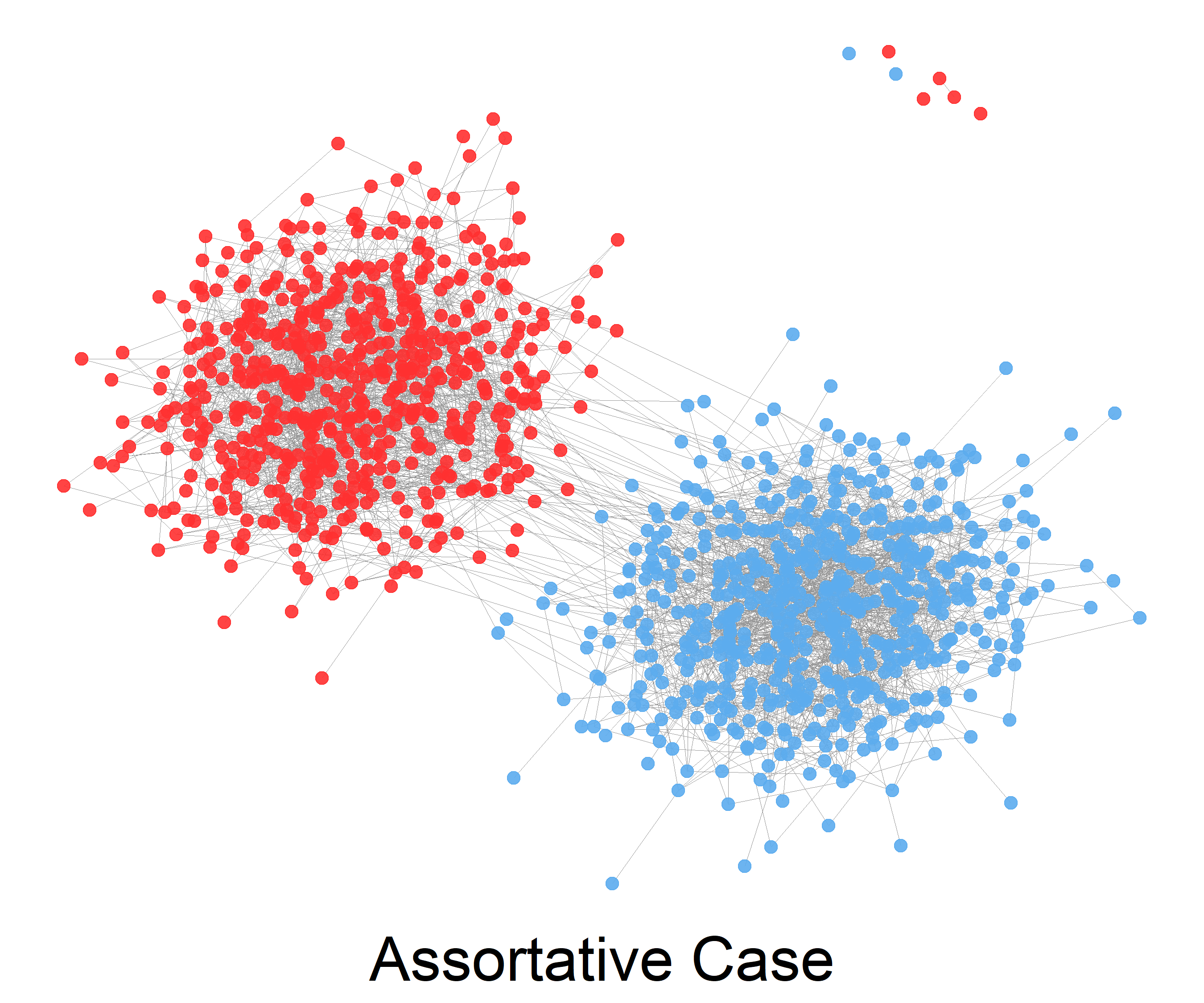
Stochastic Blockmodeling
The stochastic block model is a generative model for random graphs. This model tends to produce graphs containing ''communities'', subsets of nodes characterized by being connected with one another with particular edge densities. For example, edges may be more common within communities than between communities. Its mathematical formulation has been firstly introduced in 1983 in the field of social network by Holland et al. The stochastic block model is important in statistics Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ..., machine learning, and network science, where it serves as a useful benchmark for the task of recovering community structure in graph data. Definition The stochastic block model takes the following parameters: * The number n of vertices; * a partition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |