|
Dermatophyte
Dermatophyte (from Greek '' derma'' "skin" ( GEN ''dermatos'') and ''phyton'' "plant") is a common label for a group of fungus of ''Arthrodermataceae'' that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic (asexual or imperfect fungi) mold genera are: '' Microsporum'', '' Epidermophyton'' and ''Trichophyton''. There are about 40 species in these three genera. Species capable of reproducing sexually belong in the teleomorphic genus Arthroderma, of the Ascomycota (see Teleomorph, anamorph and holomorph for more information on this type of fungal life cycle). As of 2019 a total of nine genera are identified and new phylogenetic taxonomy has been proposed. Dermatophytes cause infections of the skin, hair, and nails, obtaining nutrients from keratinized material. The organisms colonize the keratin tissues causing inflammation as the host responds to metabolic byproducts. Colonies of dermatophytes are usually restricted to the nonliving cornified l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot, known medically as ''tinea pedis'', is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as '' tinea''. Athlete's foot is caused by a number of different fungi, including species of '' Trichophyton'', '' Epidermophyton'', and '' Microsporum''. The condition is typically acquired by coming into contact with infected skin, or fungus in the environment. Common places where the fungi can survive are around swimming pools and in locker rooms. They may also be spread from other animals. Usually diagnosis is made based on signs and symptoms; however, it can be confirmed either by culture or seeing hyphae us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringworm
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Pedis Interdigitalis
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringworm On The Arm, Or Tinea Corporis Due To Trichophyton Mentagrophytes PHIL 2938 Lores
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
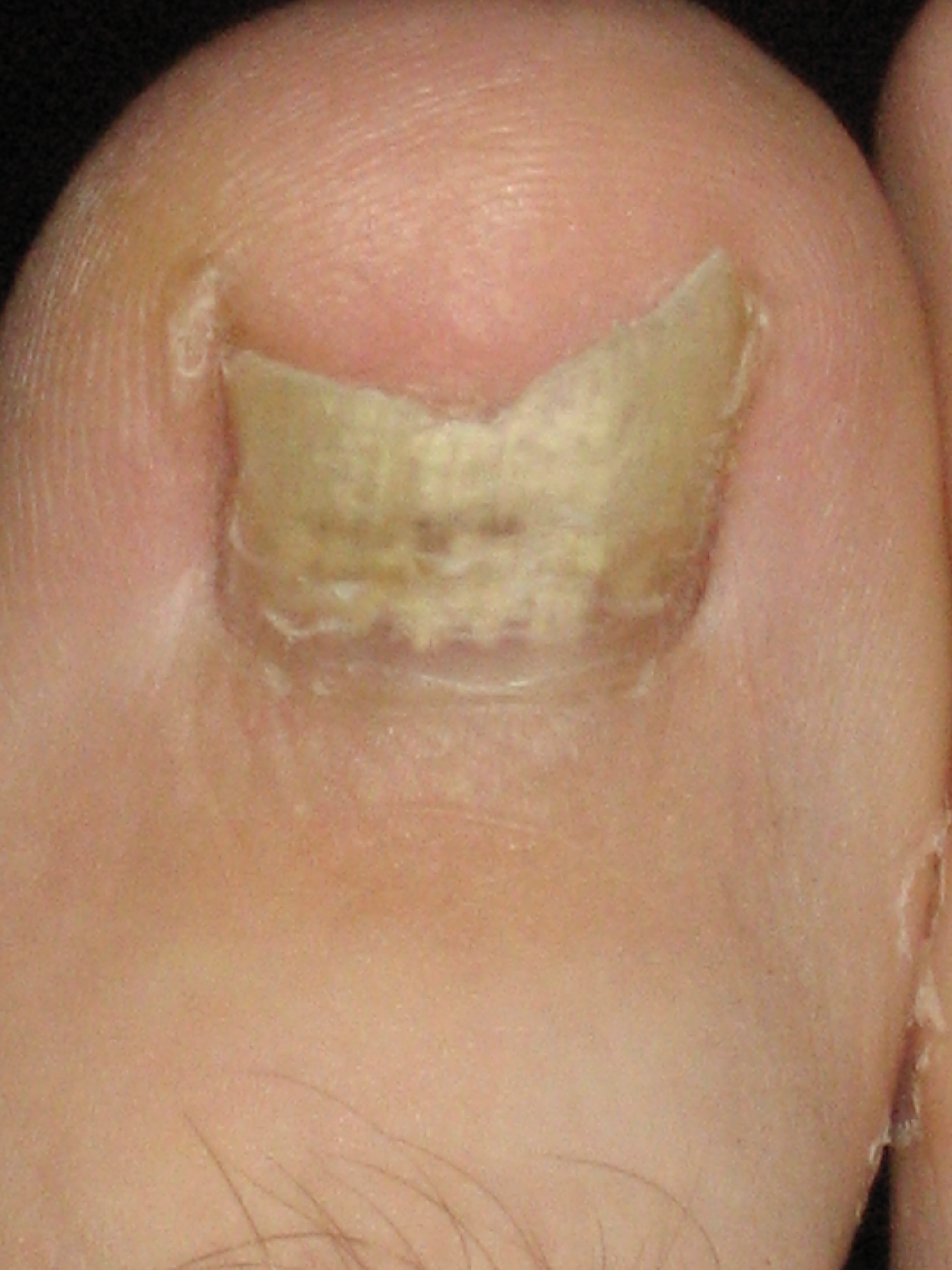
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Toenails or fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and ''Fusarium''. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing. Onychomycosis does not necessarily require treatment. The antifungal medication terbinafine taken by mouth appears to be the most effective but is associated with liver problems. Trimming the affected nails when on treatment also appears useful. There is a ciclopirox-containing nail polish, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichophyton Tonsurans
''Trichophyton tonsurans'' is a fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae that causes ringworm infection of the scalp. It was first recognized by David Gruby in 1844. Isolates are characterized as the "–" or negative mating type of the '' Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii'' complex. This species is thought to be conspecific with '' T. equinum'', although the latter represents the "+" mating strain of the same biological species Despite their biological conspecificity, clones of the two mating types appear to have undergone evolutionary divergence with isolates of the ''T. tonsurans''-type consistently associated with Tinea capitis (particularly in children) whereas the ''T. equinum''-type, as its name implies, is associated with horses as a regular host. Phylogenetic relationships were established in isolates from Northern Brazil, through fingerprinting polymorphic RAPD and M13 markers. There seems to be lower genomic variability in the ''T. tonsurans'' species due to allopatric diverge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichophyton
''Trichophyton'' is a genus of fungi, which includes the parasitic varieties that cause tinea, including athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, and similar infections of the nail, beard, skin and scalp. Trichophyton fungi are molds characterized by the development of both smooth-walled macro- and microconidia. Macroconidia are mostly borne laterally directly on the hyphae or on short pedicels, and are thin- or thick-walled, clavate to fusiform, and range from 4 to 8 by 8 to 50 μm in size. Macroconidia are few or absent in many species. Microconidia are spherical, pyriform to clavate or of irregular shape, and range from 2 to 3 by 2 to 4 μm in size. Species and their habitat preference According to current classification, the genus includes anthropophilic and zoophilic species. Anthropophilic fungi prefer to infect humans. Zoophilic fungi prefer to infect animals other than humans. Humans and animals are natural reservoirs for parasitic or dermatophytic fungi. Other ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichophyton Rubrum
''Trichophyton rubrum'' is a dermatophytic fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is an exclusively clonal, anthropophilic saprotroph that colonizes the upper layers of dead skin, and is the most common cause of athlete's foot, fungal infection of nail, jock itch, and ringworm worldwide. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' was first described by in 1845 and is currently considered to be a complex of species that comprises multiple, geographically patterned morphotypes, several of which have been formally described as distinct taxa, including ''T. raubitschekii'', ''T. gourvilii'', ''T. megninii'' and ''T. soudanense''. Growth and morphology Typical isolates of ''T. rubrum'' are white and cottony on the surface. The colony underside is usually red, although some isolates appear more yellowish and others more brownish. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' grows slowly in culture with sparse production of teardrop or peg-shaped microconidia laterally on fertile hyphae. Macroconidia, when present, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermophyton
''Epidermophyton'' is a genus of fungus causing superficial and cutaneous mycoses, including ''E. floccosum'', and causes tinea corporis (ringworm), tinea cruris (jock itch), tinea pedis Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple ... (athlete's foot), and tinea unguium (fungal infection of the nail bed). References External linksDoctor Fungus Parasitic fungi [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsporum
''Microsporum'' is a genus of fungi that causes tinea capitis, tinea corporis, ringworm, and other dermatophytoses (fungal infections of the skin). ''Microsporum'' forms both macroconidia (large asexual reproductive structures) and microconidia (smaller asexual reproductive structures) on short conidiophores. Macroconidia are hyaline, multiseptate, variable in form, fusiform, spindle-shaped to obovate, 7–20 by 30–160 um in size, with thin or thick echinulate to verrucose cell walls. Their shape, size and cell wall features are important characteristics for species identification. Microconidia are hyaline, single-celled, pyriform to clavate, smooth-walled, 2.5–3.5 by 4–7 um in size and are not diagnostic for any one species. The separation of this genus from ''Trichophyton'' is essentially based on the roughness of the macroconidial cell wall, although in practice this may sometimes be difficult to observe. Seventeen species of ''Microsporum'' have been de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Favus
Favus (Latin for " honeycomb") or tinea favosa is the severe form of tinea capitis, a skin infectious disease caused by the dermatophyte fungus ''Trichophyton schoenleinii.'' Typically the species affects the scalp, but occasionally occurs as onychomycosis, tinea barbae, or tinea corporis. The word ''favid'' is more used than French word ''favus'', which is close to the Latin etymology. Presentation The uncomplicated appearance is that of a number of yellowish, circular, cup-shaped crusts (scutulum or shield) grouped in patches like a honeycomb, each crust about the size of a split pea, with a bundle of hair projecting in the center. These increase in size and become crusted over, so that the characteristic lesion can only be seen round the edge of the scab. A mousy odour is often present. Growth continues to take place for several months, when scab and scutulum go away, leaving a shining bare patch destitute of hair. The disease is essentially chronic, lasting from ten to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Microculture.jpg)