|
Dense Granule
Dense granules (also known as dense bodies or delta granules) are specialized secretory organelles. Dense granules are found only in platelets and are smaller than alpha granules.Michelson, A. D. (2013). ''Platelets'' (Vol. 3rd ed). Amsterdam: Academic Press. The origin of these dense granules is still unknown, however, it is thought that may come from the mechanism involving the endocytotic pathway.Ambrosio, A. L., Boyle, J. A., & Di Pietro, S. M. (2012). Mechanism of platelet dense granule biogenesis: study of cargo transport and function of Rab32 and Rab38 in a model system. ''Blood'', ''120''(19), 4072–4081. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-420745 Dense granules are a sub group of lysosome-related organelles (LRO). There are about three to eight of these in a normal human platelet.McNicol, A., & Israels, S. J. (1999). ''Platelet dense granules: Structure, function and implications for haemostasis'' doi://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(99)00015-8 " In unicellular organisms They are foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
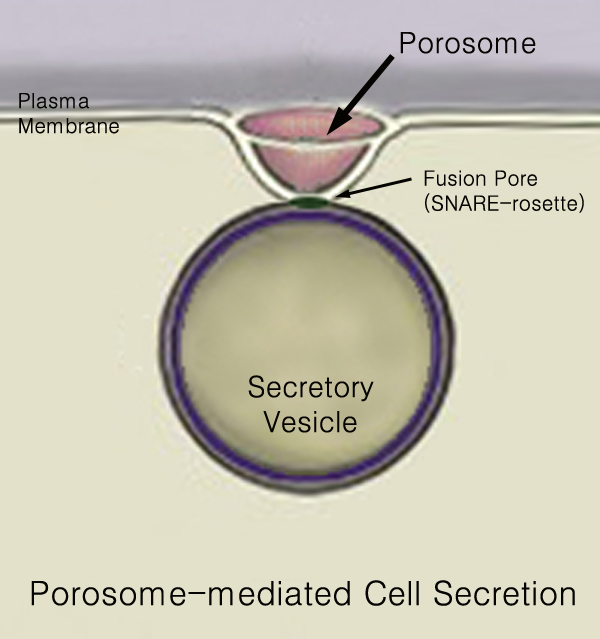 |
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. '' Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + '' cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound secretory vesicles are carried to the cell membrane, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
RALA
Ras-related protein Ral-A (RalA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RALA'' gene on chromosome 7. This protein is one of two paralogs of the Ral protein, the other being RalB, and part of the Ras GTPase family. RalA functions as a molecular switch to activate a number of biological processes, majorly cell division and transport, via signaling pathways. Its biological role thus implicates it in many cancers. Structure The Ral isoforms share an 80% overall match in amino acid sequence and 100% match in their effector-binding region. The two isoforms mainly differ in the C-terminal hypervariable region, which contains multiple sites for post-translational modification, leading to diverging subcellular localization and biological function. For example, phosphorylation of Serine 194 on RalA by the kinase Aurora A results in the relocation of RalA to the inner mitochondrial membrane, where RalA helps carry out mitochondrial fission; whereas phosphorylation of Serine 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at various locations in the interior of the cell. Adenylate cyclase is ''activated'' by a range of signaling molecules through the activation of adenylate cyclase stimulatory G ( Gs)-protein-coupled receptors. Adenylate cyclase is ''inhibited'' by agonists of adenylate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
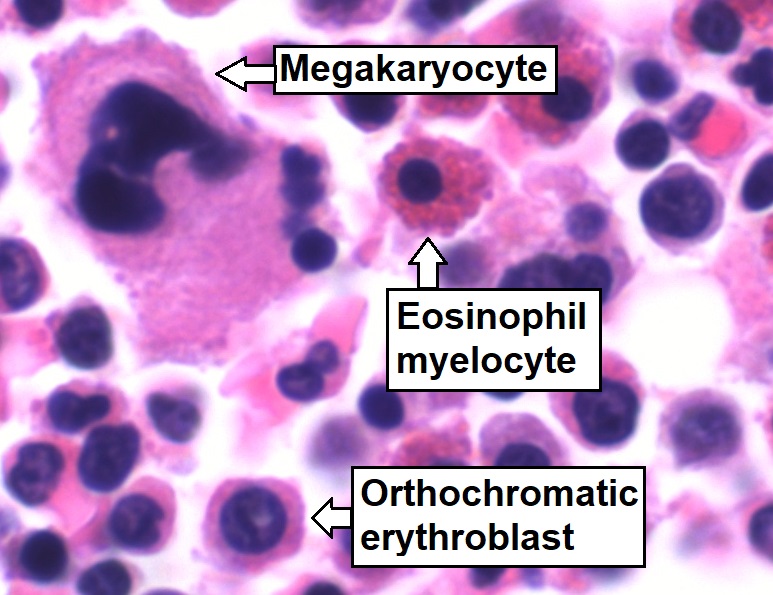
Megakaryocyte
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In humans, megakaryocytes usually account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells, but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases. Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte. Structure In general, megakaryocytes are 10 to 15 times larger than a typical red blood cell, averaging 50–100 μm in diameter. During its maturation, the megakaryocyte grows in size and replicates its DNA without cytokinesis in a process called endomitosis. As a result, the nucleus of the megakaryocyte can become very large and lobulated, which, under a light microscope, can give the false impression that there are several nuclei. In some cases, the nucleus may contain up t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Chédiak–Higashi Syndrome
Chédiak–Higashi syndrome (CHS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that arises from a mutation of a lysosomal trafficking regulator protein, which leads to a decrease in phagocytosis. The decrease in phagocytosis results in recurrent pyogenic infections, albinism, and peripheral neuropathy. In Chédiak–Higashi syndrome, the lysosomal trafficking regulator ( LYST) gene is mutated, leading to disruption of protein synthesis as well as the storage and secretory function of lysosomal granules in white blood cells. This results in defective white blood cell function with enlarged vesicles. This syndrome also leads to neutropenia and phagocyte bactericidal dysfunction due to impaired chemotaxis. Deficiency in serotonin and adenosine-phosphate-containing granules in platelets causes impaired platelet aggregation, leading to prolonged bleeding time. Thus, patients are susceptible to infections and often present with oculo-cutaneous albinism and coagulation defects. Patients oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino. Varied use and interpretation of the terms mean that written reports of albinistic animals can be difficult to verify. Albinism can reduce the survivability of an animal; for example, it has been suggested that albino alligators have an average survival span of only 24 hours due to the lack of protection from UV radiation and their lack of camouflage to avoid predators. It is a common misconception that all albino animals have characteristic pink or red eyes (resulting from the lack of pigment in the iris allowing the blood vessels of the retina to be visible), however this is not the case for some forms of albinism. Familiar albino animals include in-bred strains of laboratory animals (rats, mice and rabbits), but populations of naturally occurring albino animals exist in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Melanosome
A melanosome is an organelle found in animal cells and is the site for synthesis, storage and transport of melanin, the most common light-absorbing pigment found in the animal kingdom. Melanosomes are responsible for color and photoprotection in animal cells and tissues. Melanosomes are synthesised in the skin in melanocyte cells, as well as the eye in choroidal melanocytes and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. In lower vertebrates, they are found in melanophores or chromatophores. Structure Melanosomes are relatively large organelles, measuring up to 500 nm in diameter. They are bound by a bilipid membrane and are, in general, rounded, sausage-like, or cigar-like in shape. The shape is constant for a given species and cell type. They have a characteristic ultrastructure on electron microscopy, which varies according to the maturity of the melanosome, and for research purposes a numeric staging system is sometimes used. Synthesis of melanin Melanosomes are dependent f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Hermansky–Pudlak Syndrome
Heřmanský–Pudlák syndrome (often written Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome or abbreviated HPS) is an extremely rare autosomal recessive disorder which results in oculocutaneous albinism (decreased pigmentation), bleeding problems due to a platelet abnormality (platelet storage pool defect), and storage of an abnormal fat-protein compound ( lysosomal accumulation of ceroid lipofuscin). It is considered to affect around 1 in 500,000 people worldwide, with a significantly higher occurrence in Puerto Ricans, with a prevalence of 1 in 1800. Many of the clinical research studies on the disease have been conducted in Puerto Rico. There are eight classic forms of the disorder, based on the genetic mutation from which the disorder stems. Signs and symptoms There are three main disorders caused by Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome, which result in these symptoms: * Albinism and eye problems: Individuals will have varying amounts of skin pigment (melanin). Because of the albinism there are eye pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |