|
Deep Temporal Arteries
The deep temporal arteries are two arteries of the head. They ascend between the temporalis muscle and the pericranium. They anastomose with the middle temporal artery, among other vessels. They supply the temporalis muscle. Structure The deep temporal arteries consist of an anterior and a posterior artery. They are branches of the maxillary artery, a terminal branch of the external carotid artery. They ascend between the temporalis muscle and the pericranium. Connections The deep temporal arteries anastomose with the middle temporal artery. The anterior artery communicates with the lacrimal artery by means of small branches which perforate the zygomatic bone and greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It may also communicate with the ophthalmic artery, a branch of the internal carotid artery. Function The deep temporal arteries supply the temporalis muscle. Clinical significance The deep temporal arteries may be affected by giant cell arteritis. This may be diagnosed using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral ptery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Artery
The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva. Structure Origin The lacrimal artery is normally a branch of the ophthalmic artery and represents one of its largest branches. It's origin occurs near the optic canal. It usually branches off the ophthalmic artery just after the ophthalmic artery's entery into the orbit. It can rarely arise before the ophthalmic artery enters the optic canal. Course and relations The lacrimal artery accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle. It travels anterior-ward to supply the lacrimal gland. Branches and distribution The lacrimal artery supplies the lacrimal gland, the eyelids and conjunctiva, and the superior rectus muscle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
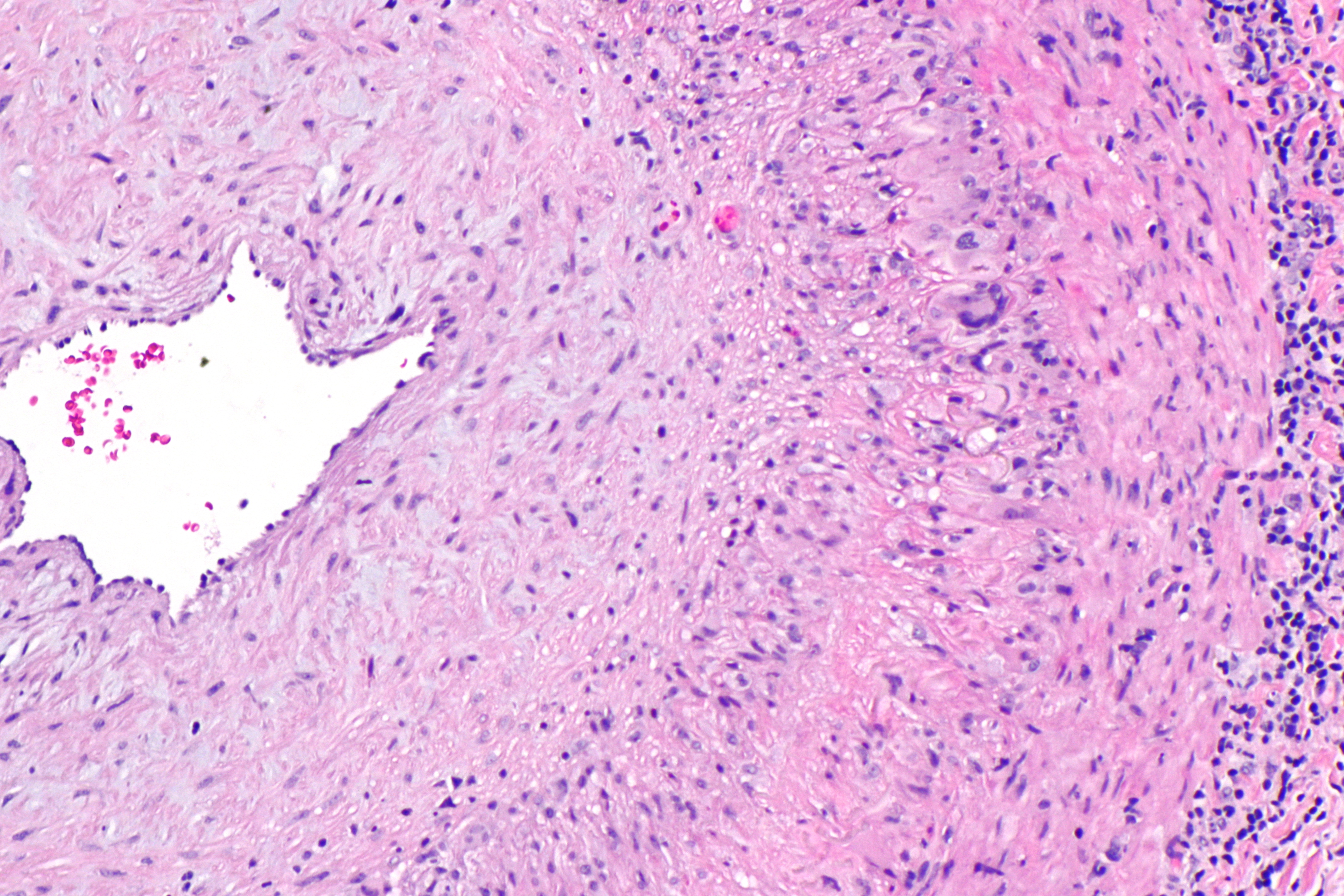
Giant Cell Arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of large blood vessels. Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth. Complication can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, as well as aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm. GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. The cause is unknown. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the small blood vessels that supply the walls of larger arteries. This mainly affects arteries around the head and neck, though some in the chest may also be affected. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, blood tests, and medical imaging, and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery. However, in about 10% of people the temporal artery is normal. Treatment is typical with high doses of steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone. Once symptoms have resolved, the dose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal conchae are situated at the anterior and inferior part of the body. Intrinsic ligaments of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Wing Of Sphenoid Bone
The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone; there is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward. Structure The greater wings of the sphenoid are two strong processes of bone, which arise from the sides of the body, and are curved upward, laterally, and backward; the posterior part of each projects as a triangular process that fits into the angle between the squamous and the petrous part of the temporal bone and presents at its apex a downward-directed process, the spine of sphenoid bone. Cerebral surface The superior or cerebral surface of each greater wing ig. 1forms part of the middle cranial fossa; it is deeply concave, and presents depressions for the convolutions of the temporal lobe of the brain. It has a number of foramina (holes) in it: * The foramen rotundum is a circular aperture at its anterior and medial part; it transmits the maxillary nerve. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from grc, ζῠγόν, zugón, yoke), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek, part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes (the frontosphenoidal, orbital, maxillary, and temporal), and four borders. Etymology The term ''zygomatic'' derives from the Ancient Greek , ''zygoma'', meaning "yoke". The zygomatic bone is occasionally referred to as the zygoma, but this term may also refer to the zygomatic arch. Structure Surfaces The ''malar surface'' is convex and perforated near its center by a small aperture, the zygomaticofacial foramen, for the passage of the zygomaticofacial nerve and vessels; below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Carotid Artery
The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. Structure The external carotid artery begins at the upper border of thyroid cartilage, and curves, passing forward and upward, and then inclining backward to the space behind the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches. At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle. Development In children, the external carotid artery is somewhat smaller than the internal carotid; but in the adult, the two vessels are of nearly equal size. Relations At the origin, external carotid artery is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Carotid Artery With Branches
{{disambig ...
External may refer to: * External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra * Externality, in economics, the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit * Externals, a fictional group of X-Men antagonists See also * *Internal (other) Internal may refer to: *Internality as a concept in behavioural economics *Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts *Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism *''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Temporal Artery
In anatomy, the middle temporal artery is a major artery which arises immediately above the zygomatic arch, and, perforating the temporal fascia, gives branches to the temporalis, anastomosing with the deep temporal branches of the internal maxillary. It occasionally gives off a zygomatico-orbital branch, which runs along the upper border of the zygomatic arch, between the two layers of the temporal fascia, to the lateral angle of the orbit In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ... (the eye socket). Additional images File:Gray137.png, Left temporal bone. Outer surface. References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |