|
Dally (gene)
Dally (division abnormally delayed) is the name of a gene that encodes a HS-modified-protein found in the fruit fly ('' Drosophila melanogaster''). The protein has to be processed after being codified, and in its mature form it is composed by 626 amino acids,Uniprot KB forming a proteoglycan rich in heparin sulfate which is anchored to the cell surface via covalent linkage to glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI), so we can define it as a glypican. For its normal biosynthesis it requires sugarless (''sgl''), a gene that encodes an enzyme which plays a critical role in the process of modification of dally. Dally’s function [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycophosphatidylinositol
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (), or glycophosphatidylinositol, or GPI in short, is a phosphoglyceride that can be attached to the C-terminus of a protein during posttranslational modification. The resulting GPI-anchored proteins play key roles in a wide variety of biological processes. GPI is composed of a phosphatidylinositol group linked through a carbohydrate-containing linker (glucosamine and mannose glycosidically bound to the inositol residue) and via an ethanolamine phosphate (EtNP) bridge to the C-terminal amino acid of a mature protein. The two fatty acids within the hydrophobic phosphatidyl-inositol group anchor the protein to the cell membrane. Synthesis Glycosylated (GPI-anchored) proteins contain a signal sequence, thus directing them to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The protein is co-translationally inserted in the ER membrane via a translocon and is attached to the ER membrane by its hydrophobic C terminus; the majority of the protein extends into the ER lumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glypican
Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypicans have been identified, and these are referred to as dally (division abnormally delayed) and dally-like. One glypican has been identified in ''C. elegans''. Glypicans seem to play a vital role in developmental morphogenesis, and have been suggested as regulators for the Wnt and Hedgehog cell signaling pathways. They have additionally been suggested as regulators for fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenic protein signaling. Structure While six glypicans have been identified in mammals, several characteristics remain consistent between these different proteins. First, the core protein of all glypicans is similar in size, approximately ranging between 60 and 70 kDa. Additionally, in terms of amino acid sequence, the location of fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glypican
Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypicans have been identified, and these are referred to as dally (division abnormally delayed) and dally-like. One glypican has been identified in ''C. elegans''. Glypicans seem to play a vital role in developmental morphogenesis, and have been suggested as regulators for the Wnt and Hedgehog cell signaling pathways. They have additionally been suggested as regulators for fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenic protein signaling. Structure While six glypicans have been identified in mammals, several characteristics remain consistent between these different proteins. First, the core protein of all glypicans is similar in size, approximately ranging between 60 and 70 kDa. Additionally, in terms of amino acid sequence, the location of fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part by the SPATS1 gene. The noncanonical plana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of atypical G protein-coupled receptors that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol. Species distribution Frizzled proteins and the genes that encode them have been identified in an array of animals, from sponges to humans. Function Frizzled proteins also play key roles in governing cell polarity, embryonic development, formation of neural synapses, cell proliferation, and many other processes in developing and adult organisms. These processes occur as a result of one of three signaling pathways. These include the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway, Wnt/calcium pathway, and planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway. Mutations in the human frizzled-4 receptor have been linked to familial exudative vitreoretinopathy, a rare disease affecting the retina at the back of the eye, and the vitreous, the clear fluid inside the eye. The frizzled (fz) locu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
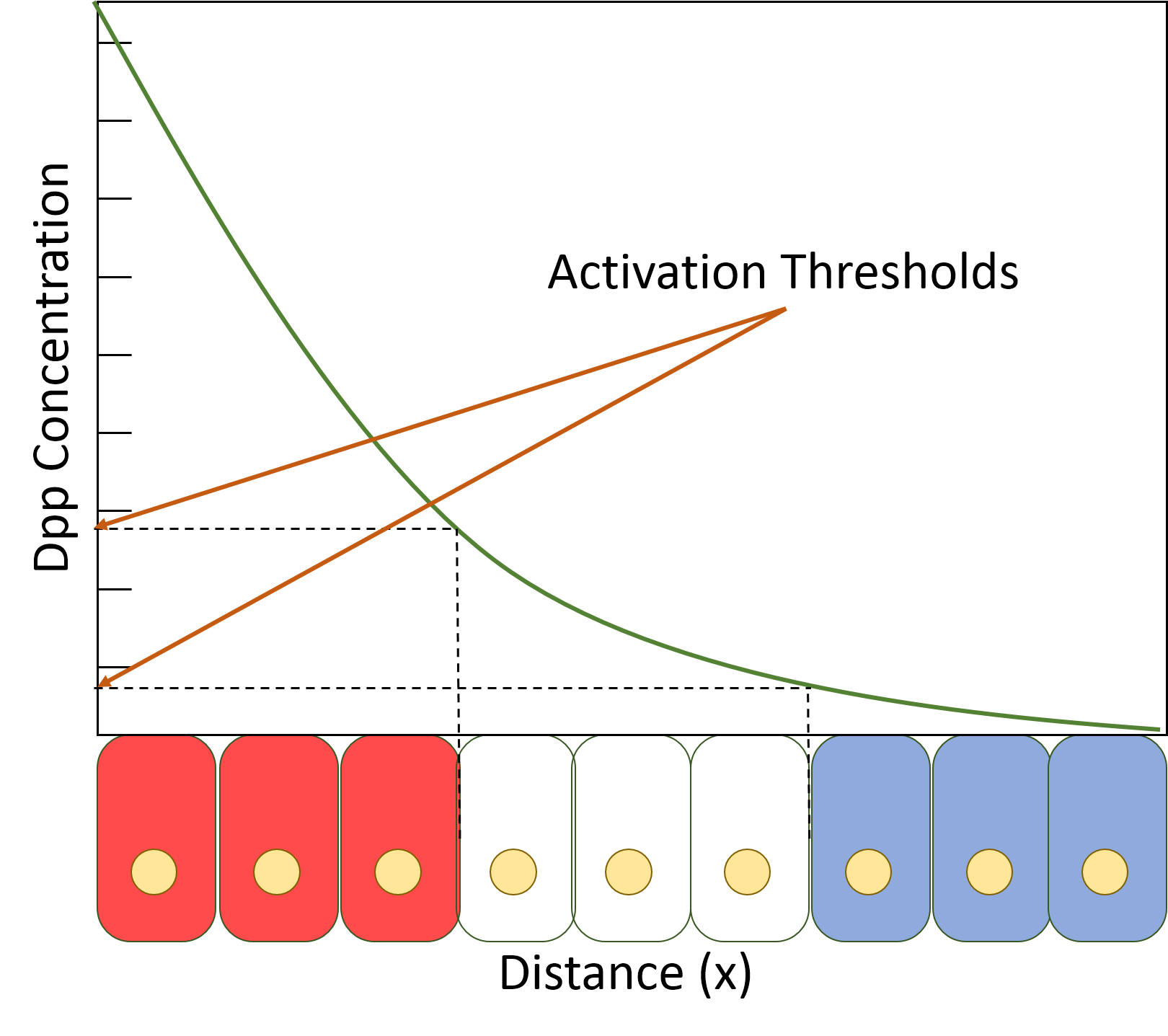
Decapentaplegic
Decapentaplegic (Dpp) is a key morphogen involved in the development of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and is the first validated secreted morphogen. It is known to be necessary for the correct patterning and development of the early ''Drosophila'' embryo and the fifteen imaginal discs, which are tissues that will become limbs and other organs and structures in the adult fly. It has also been suggested that Dpp plays a role in regulating the growth and size of tissues. Flies with mutations in decapentaplegic fail to form these structures correctly, hence the name (''decapenta''-, fifteen, -''plegic'', paralysis). Dpp is the Drosophila homolog of the vertebrate bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are members of the TGF-β superfamily, a class of proteins that are often associated with their own specific signaling pathway. Studies of Dpp in Drosophila have led to greater understanding of the function and importance of their homologs in vertebrates like humans. Func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |