|
Du Temple Monoplane
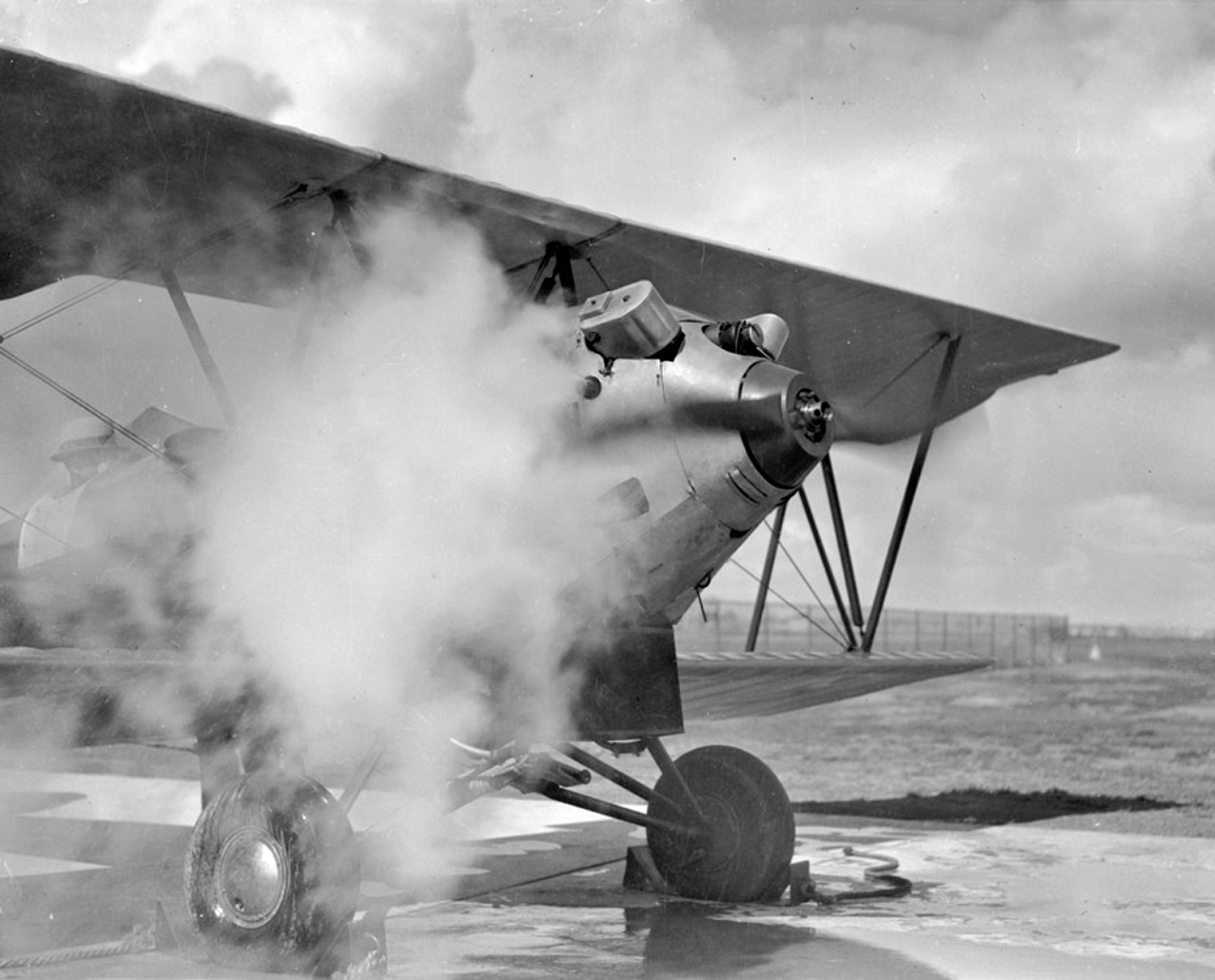
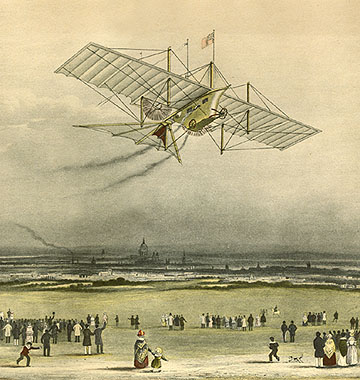
The du Temple Monoplane was a steam-powered aircraft made of aluminium, built in Brest, France, by naval officer Félix du Temple in 1874. It had a wingspan of 13 m (43 ft) and weighed 80 kg (180 lb) without the pilot. Several trials were made with the aircraft, and it is generally recognized that it achieved lift-off – described by Dollfus as "short hop or leap" and in ''Flight International'' as "staggered briefly into the air" – (from a combination of its own power and running down an inclined ramp), glided for a short time and returned safely to the ground, making it the first successful powered flight in history though not the first self-powered one. It was displayed at the 1878 ''Exposition Universelle'' ("World Fair") in Paris. Steam engine The aircraft used a very compact, high-speed circulation steam engine for which Félix du Temple applied for a patent on 28 April 1876. The engine used very small pipes packed together "to obtain the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Aircraft
A steam-powered aircraft is an aircraft propelled by a steam engine. Steam power was used during the 19th century, but fell into disuse with the arrival of the more practical internal combustion engine at the beginning of the pioneer era. Steam power is distinct from its use as a lifting gas in thermal airships and early balloons. History * 1842: The Aerial Steam Carriage of William Samuel Henson and John Stringfellow was patented, but was never successful, although a steam-powered model was flown in 1848. * 1852: Henri Giffard flew a 3-horsepower (2 kW) steam-powered dirigible over Paris; it was the first powered aircraft. * 1861 Gustave Ponton d'Amécourt made a small steam-powered craft, coining the name helicopter. * 1874: Félix du Temple flew a steam-powered aluminium monoplane off a downhill run. While it did not achieve level flight, it was the first manned heavier-than-air powered flight. * 1877: Enrico Forlanini built and flew a model steam-powered helicop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Boiler
A flash boiler is a type of water-tube boiler. The tubes are close together and water is pumped through them. A flash boiler differs from the type of monotube steam generator in which the tube is permanently filled with water. In a flash boiler, the tube is kept so hot that the water feed is quickly flashed into steam and superheated. Flash boilers had some use in automobiles in the 19th century and this use continued into the early 20th century. History There is disagreement about the exact definition of a flash boiler. Some writers use the term interchangeably with monotube boiler and there is even use of the term ''semi-flash boiler''. However, the flash boiler is generally attributed to Léon Serpollet who used a flash boiler in the Gardner-Serpollet steam-powered car from 1896. Serpollet's boiler was a low-water-content type with thick-walled tubes to provide a store of heat. Serpollet patented a steam generator in 1888, US Patent 379,421, but this is an early version which d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam-powered Aircraft
A steam-powered aircraft is an aircraft propelled by a steam engine. Steam power was used during the 19th century, but fell into disuse with the arrival of the more practical internal combustion engine at the beginning of the pioneer era. Steam power is distinct from its use as a lifting gas in thermal airships and early balloons. History * 1842: The Aerial Steam Carriage of William Samuel Henson and John Stringfellow was patented, but was never successful, although a steam-powered model was flown in 1848. * 1852: Henri Giffard flew a 3-horsepower (2 kW) steam-powered dirigible over Paris; it was the first powered aircraft. * 1861 Gustave Ponton d'Amécourt made a small steam-powered craft, coining the name helicopter. * 1874: Félix du Temple flew a steam-powered aluminium monoplane off a downhill run. While it did not achieve level flight, it was the first manned heavier-than-air powered flight. * 1877: Enrico Forlanini built and flew a model steam-powered helicopter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Experimental Aircraft
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Aviation – 19th Century
This is a list of aviation-related events during the 19th century (1 January 1801 – 31 December 1900): 1800s - 1850s * 1802 ** 5 July – André-Jacques Garnerin and Edward Hawke Locker make a balloon flight from Lord's Cricket Ground in St John's Wood, London, England, to Chingford in just over 15 minutes. ** 2 December – A manned illuminated balloon is launched from the front of Notre Dame de Paris during the Coronation of Napoleon I. * 1803 ** British Rear Admiral Charles Knowles proposes to the Admiralty that the Royal Navy loft an observation balloon from a ship in order to reconnoitre French preparations for the invasion of Britain in Brest. The proposal is ignored.Layman 1989, p. 31. ** 18 July – Etienne Gaspar Robertson and his copilot Lhoest ascend from Hamburg, Germany, to an altitude of around in a balloon. ** 3–4 October – André-Jacques Garnerin covers a distance of from Paris, France, to Clausen, Germany. ** 7–8 October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Aviation
The history of aviation extends for more than two thousand years, from the earliest forms of aviation such as kites and attempts at tower jumping to supersonic and hypersonic flight by powered, heavier-than-air jets. Kite flying in China dates back to several hundred years BC and slowly spread around the world. It is thought to be the earliest example of man-made flight. Leonardo da Vinci's 15th-century dream of flight found expression in several rational designs, but which relied on poor science. The discovery of hydrogen gas in the 18th century led to the invention of the hydrogen balloon, at almost exactly the same time that the Montgolfier brothers rediscovered the hot-air balloon and began manned flights. Various theories in mechanics by physicists during the same period of time, notably fluid dynamics and Newton's laws of motion, led to the foundation of modern aerodynamics, most notably by Sir George Cayley. Balloons, both free-flying and tethered, began to be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Flying Machines
Early flying machines include all forms of aircraft studied or constructed before the development of the modern aeroplane by 1910. The story of modern flight begins more than a century before the first successful manned aeroplane, and the earliest aircraft thousands of years before. Primitive beginnings Legends Some ancient mythologies feature legends of men using flying devices. One of the earliest known is the Greek legend of Daedalus; in Ovid's version, Daedalus fastens feathers together with thread and wax to mimic the wings of a bird. Other ancient legends include the Indian Vimana flying palace or chariot, the biblical Ezekiel's Chariot, the Irish ''roth rámach'' built by blind druid Mug Ruith and Simon Magus, various stories about magic carpets, and the mythical British King Bladud, who conjured up flying wings. The Flying Throne of Kay Kāvus was a legendary eagle-propelled craft built by the mythical Shah of Persia, Kay Kāvus, used for flying him all the way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. These were inshore craft created to counter both the threat of battleships and other slow and heavily armed ships by using speed, agility, and powerful torpedoes, and the overwhelming expense of building a like number of capital ships to counter an enemy's. A swarm of expendable torpedo boats attacking en masse could overwhelm a larger ship's ability to fight them off using its large but cumbersome guns. A fleet of torpedo boats could pose a similar threat to an adversary's capital ships, albeit only in the coastal areas to which their small size and limited fuel load restricted them. The introduction of fast torpedo boats in the late 19th century was a serious concern to the era's naval strategists, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in the world, ranking seventh in combined fleet tonnage and fifth in number of naval vessels. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the U.S., U.K., China, Russia, Italy, India and Spain with its flagship being the only nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the 17th century, the French Navy is one of the oldest navies still in continual service, with precursors dating back to the Middle Ages. It has taken part in key events in French history, including the Napoleonic Wars and both world wars, and played a critical role in establishing and securing the French colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
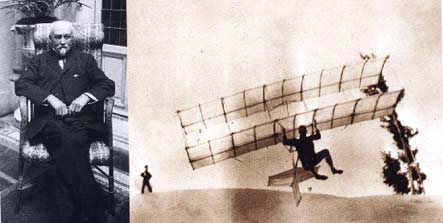
Octave Chanute
Octave Chanute (February 18, 1832 – November 23, 1910) was a French-American civil engineer and aviation pioneer. He provided many budding enthusiasts, including the Wright brothers, with help and advice, and helped to publicize their flying experiments. At his death he was hailed as the father of aviation and the initial concepts of the heavier-than-air flying machine. Biography Born in Paris, Chanute was the son of Elise and Joseph Chanut, professor at the Collège de France. He emigrated with his father to the United States of America in 1838, when the former was named Vice-President at Jefferson College in Louisiana. Octave attended private schools in New York. Civil engineer (railroads) Octave Chanute began his training as a budding civil engineer in 1848. He was widely considered brilliant and innovative in the engineering profession. During his career he designed and constructed the United States two biggest stockyards, Chicago Stock Yards (1865) and Kansas City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |