|
Dselect
dselect is a computer program used to manage software packages in the Debian operating system. dselect is one of the oldest front-ends to dpkg, and the bulk of its development happened when it was originally written by Ian Jackson, who wrote it alongside dpkg. The work on dselect started in dpkg version 0.93.12, and the first alpha release of dselect was made on March 27, 1995 in version 0.93.32. dselect was distributed in the dpkg package until June 21, 2002; even after it was split out into its own package, it was kept as a pre-dependency of dpkg in order to assist upgrades. It has been a standalone package since March 3, 2005. dselect has a text-mode user interface, a set of key bindings that is generally considered to be fairly non-intuitive, and its dependency resolution mechanism is suboptimal. dselect can now use apt as the back-end 'method' for installing packages. Today, dselect is largely superseded by Advanced Packaging Tool Advanced package tool, or APT, is a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Packaging Tool
Advanced package tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian, and Debian-based Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code. Usage APT is a collection of tools distributed in a package named ''apt''. A significant part of APT is defined in a C++ library of functions; APT also includes command-line programs for dealing with packages, which use the library. Three such programs are apt, apt-get and apt-cache. They are commonly used in examples because they are simple and ubiquitous. The ''apt'' package is of "''important''" priority in all current Debian releases, and is therefore included in a default Debian installation. APT can be considered a front-end to dpkg, friendlier than the older dse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
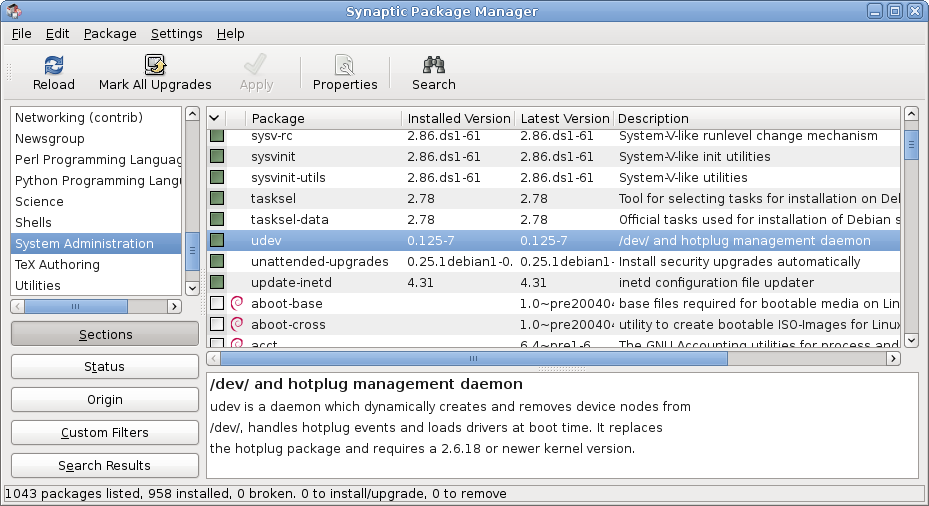
Software Package (installation)
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components. A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using the language's compiler. ( Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within the language's interpreter. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. If the source code is requested for execution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debian
Debian (), also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software, developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of Debian (0.01) was released on September 15, 1993, and its first stable version (1.1) was released on June 17, 1996. The Debian Stable branch is the most popular edition for personal computers and servers. Debian is also the basis for many other distributions, most notably Ubuntu. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kernel. The project is coordinated over the Internet by a team of volunteers guided by the Debian Project Leader and three foundational documents: the Debian Social Contract, the Debian Constitution, and the Debian Free Software Guidelines. New distributions are updated continually, and the next candidate is released after a time-based freeze. Since its founding, Debian has been developed openly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dpkg
dpkg is the software at the base of the package management system in the free operating system Debian and its numerous derivatives. dpkg is used to install, remove, and provide information about .deb packages. dpkg (Debian Package) itself is a low-level tool. APT (Advanced Package Tool), a higher-level tool, is more commonly used than dpkg as it can fetch packages from remote locations and deal with complex package relations, such as dependency resolution. Frontends for APT, like aptitude (ncurses) and synaptic (GTK), are used for their friendlier interfaces. The Debian package "dpkg" provides the dpkg program, as well as several other programs necessary for run-time functioning of the packaging system, including dpkg-deb, dpkg-split, dpkg-query, dpkg-statoverride, dpkg-divert and dpkg-trigger. It also includes the programs such as update-alternatives and start-stop-daemon. The install-info program used to be included as well, but was later removed as it is now developed and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Jackson
Ian Jackson is a longtime free software author and Debian developer. Jackson wrote dpkg (replacing a more primitive Perl tool with the same name), SAUCE (Software Against Unsolicited Commercial Email), userv and debbugs. He used to maintain the Linux FAQ. He runchiark.greenend.org.uk a Linux system which is home to PuTTY among other things. Jackson has a PhD in Computer Science from Cambridge University. As of October 2021, he works for the Tor Project. He has previously worked for Citrix for Canonical Ltd. and nCipher Corporation. Jackson became Debian Project Leader in January 1998, before Wichert Akkerman took his place in 1999. Debian GNU/Linux 2.0 (hamm) was released during his term. During that time he was also a vice-president and then president of Software in the Public Interest in 1998 and 1999. Jackson was a member of the Debian Technical Committee until November 2014 when he resigned as a result of controversies around the proposed use of systemd in Debian. Additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |