|
Downy Hair
Lanugo is very thin, soft, usually unpigmented, downy hair that is sometimes found on the body of a fetus or newborn. It is the first hair to be produced by the fetal hair follicles, and it usually appears around sixteen weeks of gestation and is abundant by week twenty. It is normally shed before birth, around seven or eight months of gestation, but is sometimes present at birth. It disappears on its own within a few weeks. It is replaced by hair covering the same surfaces, which is called vellus hair. This hair is thinner and more difficult to see. The more visible hair that persists into adulthood is called terminal hair. It forms in specific areas and is hormone-dependent. The term is from the Latin ''lana'', meaning "wool." Humans Fetal development During human development, the lanugo grows on fetuses as a normal part of gestation, but it is usually shed and replaced by vellus hair at about thirty-three to thirty-six weeks of gestational age. As the lanugo is shed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary'' is a large American dictionary, first published in 1966 as ''The Random House Dictionary of the English Language: The Unabridged Edition''. Edited by Editor-in-chief Jess Stein, it contained 315,000 entries in 2256 pages, as well as 2400 illustrations. The CD-ROM version in 1994 also included 120,000 spoken pronunciations. History The Random House publishing company entered the reference book market after World War II. They acquired rights to the ''Century Dictionary'' and the ''Dictionary of American English'', both out of print. Their first dictionary was Clarence Barnhart's ''American College Dictionary'', published in 1947, and based primarily on ''The New Century Dictionary'', an abridgment of the ''Century''. In the late 1950s, it was decided to publish an expansion of the ''American College Dictionary'', which had been modestly updated with each reprinting since its publication. Under editors Jess Stein and Laurence Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus. For humans, the amniotic fluid is commonly called water or waters (Latin liquor amnii). Development Amniotic fluid is present from the formation of the gestational sac. Amniotic fluid is in the amniotic sac. It is generated from maternal plasma, and passes through the fetal membranes by osmotic and hydrostatic forces. When fetal kidneys begin to function around week 16, fetal urine also contributes to the fluid. In earlier times, it was believed that the amniotic fluid was composed entirely of fetal urine. The fluid is absorbed through the fetal tissue and skin. After 22 to 25 week of pregnancy, keratinization of an embryo's skin occurs. When this process completes around the 25th week, the fluid is primarily absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratoma
A teratoma is a tumor made up of several different types of tissue, such as hair, muscle, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the ovary, testicle, or coccyx. Symptoms Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular teratoma may present as a painless lump. Complications may include ovarian torsion, testicular torsion, or hydrops fetalis. They are a type of germ cell tumor (a tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or eggs). They are divided into two types: mature and immature. Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous. Most ovarian teratomas are mature. In adults, testicular teratomas are generally cancerous. Definitive diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Treatment of coccyx, testicular, and ovarian teratomas is generally by surgery. Testicular and immature ovarian teratomas are also frequently treated with chemotherapy. Teratomas occur in the coccyx in about one in 30,000 n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
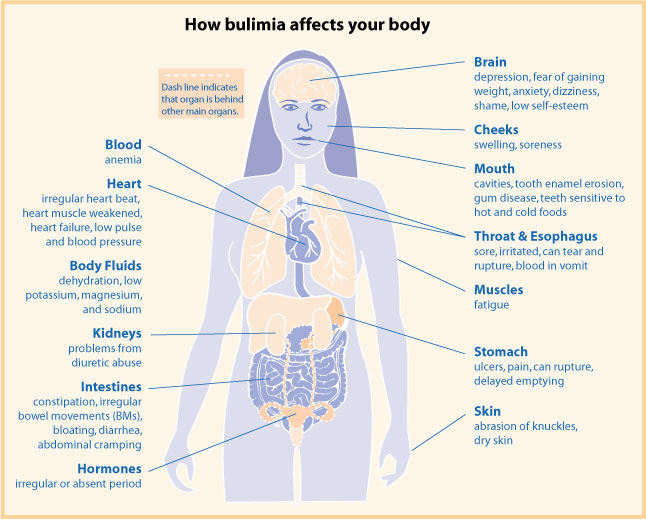
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten from the binging phase of the process. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in thickened skin on the knuckles, breakdown of the teeth and effects on metabolic rate and caloric intake which cause thyroid dysfunction. Bulimia is frequently associated with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder and problems with drugs or alcohol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Greek origin: ''an-'' (ἀν-, prefix denoting negation) and ''orexis'' (ὄρεξις, "appetite"), translating literally to "a loss of appetite"; the adjective ''nervosa'' indicating the functional and non-organic nature of the disorder. ''Anorexia nervosa'' was coined by Gull in 1873 but, despite literal translation, the feeling of hunger is frequently present and the pathological control of this instinct is a source of satisfaction for the patients. Individuals with anorexia nervosa have a fear of being overweight or being seen as such, although they are in fact underweight. The DSM-5 describes this perceptual symptom as "disturbance in the way in which one's body weight or shape is experienced". In research and clinical settings, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e., the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials. Heat flow is an inevitable consequence of contact between objects of different temperature. Thermal insulation provides a region of insulation in which thermal conduction is reduced, creating a thermal break or thermal barrier, or thermal radiation is reflected rather than absorbed by the lower-temperature body. The insulating capability of a material is measured as the inverse of thermal conductivity (k). Low thermal conductivity is equivalent to high insulating capability ( resistance value). In thermal engineering, other important properties of insulating materials are product density (ρ) and specific heat capacity (c). Definition T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernix Caseosa
Vernix caseosa, also known as vernix or birthing custard, is the waxy white substance found coating the skin of newborn human babies. It is produced by dedicated cells and is thought to have some protective roles during fetal development and for a few hours after birth. Etymology In Latin, ''vernix'' means ''varnish'' and ''caseosa'' means ''cheesy''. The term was first published in 1846 in the ''Dunglison Dictionary of Medical Sciences''. In-utero development Vernix is produced during a distinct phase of the epidermal development. Around the 21st week of gestation, periderm cells are being shed and replaced with stratum corneum; these shedding mix with secretions of sebum by the sebaceous glands to form vernix, which gradually covers the body in an anteroposterior and dorsoventral pattern. Vernix, in itself, is also believed to aid in the formation of stratum corneum. By early third trimester, the process is complete. Soon enough, part of the vernix is emulsified by increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 36 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, multiple gestation (being pregna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meconium
Meconium is the earliest stool of a mammalian infant resulting from defecation. Unlike later feces, meconium is composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus: intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, amniotic fluid, bile, and water. Meconium, unlike later feces, is viscous and sticky like tar – its color usually being a very dark olive green and it is almost odorless. When diluted in amniotic fluid, it may appear in various shades of green, brown, or yellow. It should be completely passed by the end of the first few days after birth, with the stools progressing toward yellow (digested milk). Clinical significance Meconium in amniotic fluid Meconium is normally retained in the infant's bowel until after birth, but sometimes it is expelled into the amniotic fluid (also called "amniotic liquor") prior to birth or during labor and delivery. The stained amniotic fluid (called "meconium liquor" or "meconium-stained liquor") is recognized by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Age (obstetrics)
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization (as is possible in in vitro fertilization), or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this definition of gestational age is that menstrual periods are essentially always noticed, while there is usually a lack of a convenient way to discern when fertilization occurred. Gestational age is contrasted with fertilization age which takes the date of fertilization as the start date of gestation. The initiation of pregnancy for the calculation of gestational age can differ from definitions of initiation of pregnancy in context of the abortion debate or beginning of human personhood. Methods According to American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
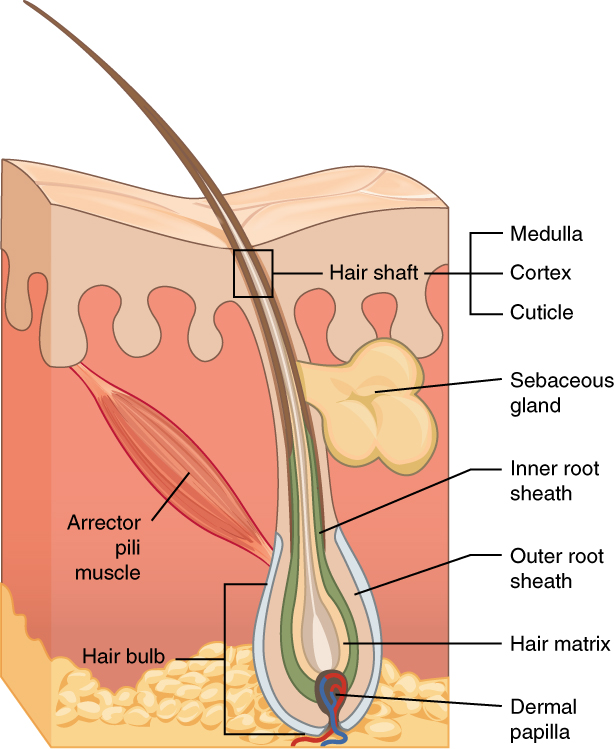
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)