|
Dourine
Covering sickness, or dourine (French, from the Arabic ''darina'', meaning mangy (said of a female camel), feminine of ''darin'', meaning dirty), is a disease of horses and other members of the family Equidae. The disease is caused by '' Trypanosoma equiperdum'', which belongs to an important genus of parasitic protozoa. The occurrence of dourine is notifiable in the European Union under legislation from the OIE. There currently is no vaccine and although clinical signs can be treated, there is no cure. Parasite Out of the ''Trypanosoma'' genus, ''Trypanosoma equiperdum'' has been discovered to be most closely linked to ''Trypanosoma evansi'', so much so that even observation under microscope is not sufficient to differentiate between the two as their structure is very similar. Dourine has no known vectors or fomites existing in the natural world, being known only as a sexually transmitted disease of members of the equine family, including donkeys, mules, and horses. In a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dourine Of Horses - Its Cause And Suppression (1911) (14597773950)
Covering sickness, or dourine (French, from the Arabic ''darina'', meaning mangy (said of a female camel), feminine of ''darin'', meaning dirty), is a disease of horses and other members of the family Equidae. The disease is caused by ''Trypanosoma equiperdum'', which belongs to an important genus of parasitic protozoa. The occurrence of dourine is notifiable in the European Union under legislation from the OIE. There currently is no vaccine and although clinical signs can be treated, there is no cure. Parasite Out of the ''Trypanosoma'' genus, ''Trypanosoma equiperdum'' has been discovered to be most closely linked to ''Trypanosoma evansi'', so much so that even observation under microscope is not sufficient to differentiate between the two as their structure is very similar. Dourine has no known vector (epidemiology), vectors or fomites existing in the natural world, being known only as a sexually transmitted disease of members of the equine family, including donkeys, mules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
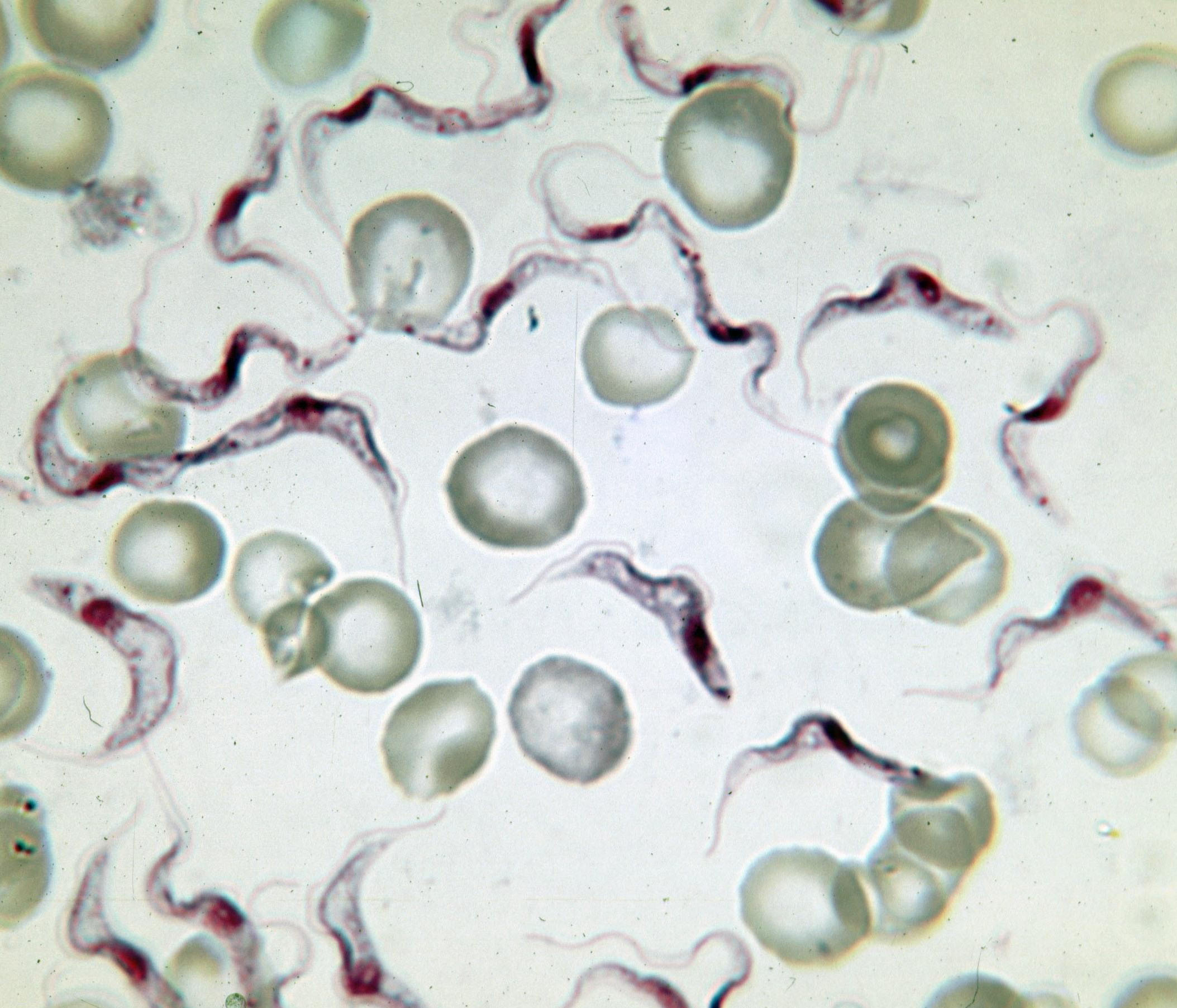
Trypanosoma (248 09) Trypanosoma Equiperdum
''Trypanosoma'' is a genus of kinetoplastids (class Trypanosomatidae), a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. Trypanosoma is part of the phylum Sarcomastigophora. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano-'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of their corkscrew-like motion. Most trypanosomes are heteroxenous (requiring more than one obligatory host to complete life cycle) and most are transmitted via a vector. The majority of species are transmitted by blood-feeding invertebrates, but there are different mechanisms among the varying species. Some, such as '' Trypanosoma equiperdum'', are spread by direct contact. In an invertebrate host they are generally found in the intestine, but normally occupy the bloodstream or an intracellular environment in the vertebrate host. Trypanosomes infect a variety of hosts and cause various diseases, including the fatal human diseases sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'', and Chagas disease, caused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraplegia
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Breeding And Studs
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Diseases
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seropositive
Serostatus refers to the presence or absence of a serological marker in the blood. The presence of detectable levels of a specific marker within the serum is considered seropositivity, while the absence of such levels is considered seronegativity. HIV/AIDS The term serostatus is commonly used in HIV/AIDS prevention efforts. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, social advocacy has emphasized the importance of learning one's HIV/AIDS serostatus in an effort to curtail the spread of the disease. Autoimmune disease Researchers have investigated the effects of autoantibody serostatus on autoimmune disease presentation. Study of seronegative patient populations has led to the identification of additional autoantibodies that could potentially help with diagnosis. See also * Seroconversion * Correlates of immunity Correlates of immunity or correlates of protection to a virus or other infectious pathogen are measurable signs that a person (or other potential host) is immune, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminazen
Diminazene (INN; also known as diminazen) is an anti-infective medication for animals that is sold under a variety of brand names. It is effective against certain protozoa such as ''Babesia'', ''Trypanosoma'', and '' Cytauxzoon''. The drug may also be effective against certain bacteria including ''Brucella'' and ''Streptococcus''. Chemically it is a di-amidine and it is formulated as its aceturate salt, diminazene aceturate. The mechanism is not well understood; it probably inhibits DNA replication, but also has affinity to RNA. __TOC__ Side effects Acute side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, and hypotension (low blood pressure). Diminazen can harm the liver, kidneys and brain, which is potentially life-threatening; camels are especially susceptible to these effects. Resistance The Gibe River Valley in southwest Ethiopia showed universal resistance between July 1989 and February 1993. This likely indicates a permanent loss of function in this area against the tested target, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suramin
Suramin is a medication used to treat African sleeping sickness and river blindness. It is the treatment of choice for sleeping sickness without central nervous system involvement. It is given by injection into a vein. Suramin causes a fair number of side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, skin tingling, and weakness. Sore palms of the hands and soles of the feet, trouble seeing, fever, and abdominal pain may also occur. Severe side effects may include low blood pressure, decreased level of consciousness, kidney problems, and low blood cell levels. It is unclear if it is safe when breastfeeding. Suramin was made at least as early as 1916. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States it can be acquired from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In regions of the world where the disease is common suramin is provided for free by the World Health Organization (WHO). Medical uses Suramin is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Surface Glycoprotein
Variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) is a ~60kDa protein which densely packs the cell surface of protozoan parasites belonging to the genus ''Trypanosoma''. This genus is notable for their cell surface proteins. They were first isolated from ''Trypanosoma brucei'' in 1975 by George Cross. VSG allows the trypanosomatid parasites to evade the mammalian host's immune system by extensive antigenic variation. They form a 12–15 nm surface coat. VSG dimers, ~90% of all cell surface protein. It also makes up ~10% of total cell protein. For this reason, these proteins are highly immunogenic and an immune response raised against a specific VSG coat will rapidly kill trypanosomes expressing this variant. However, with each cell division there is a possibility that the progeny will switch expression to change the VSG that is being expressed. VSG has no prescribed biochemical activity. The parasite has a large cellular repertoire of antigenically distinct VSGs (~1500/2000 complete and partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, ''Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, as this term is used to describe horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Trypanosoma_equiperdum.jpg)