|
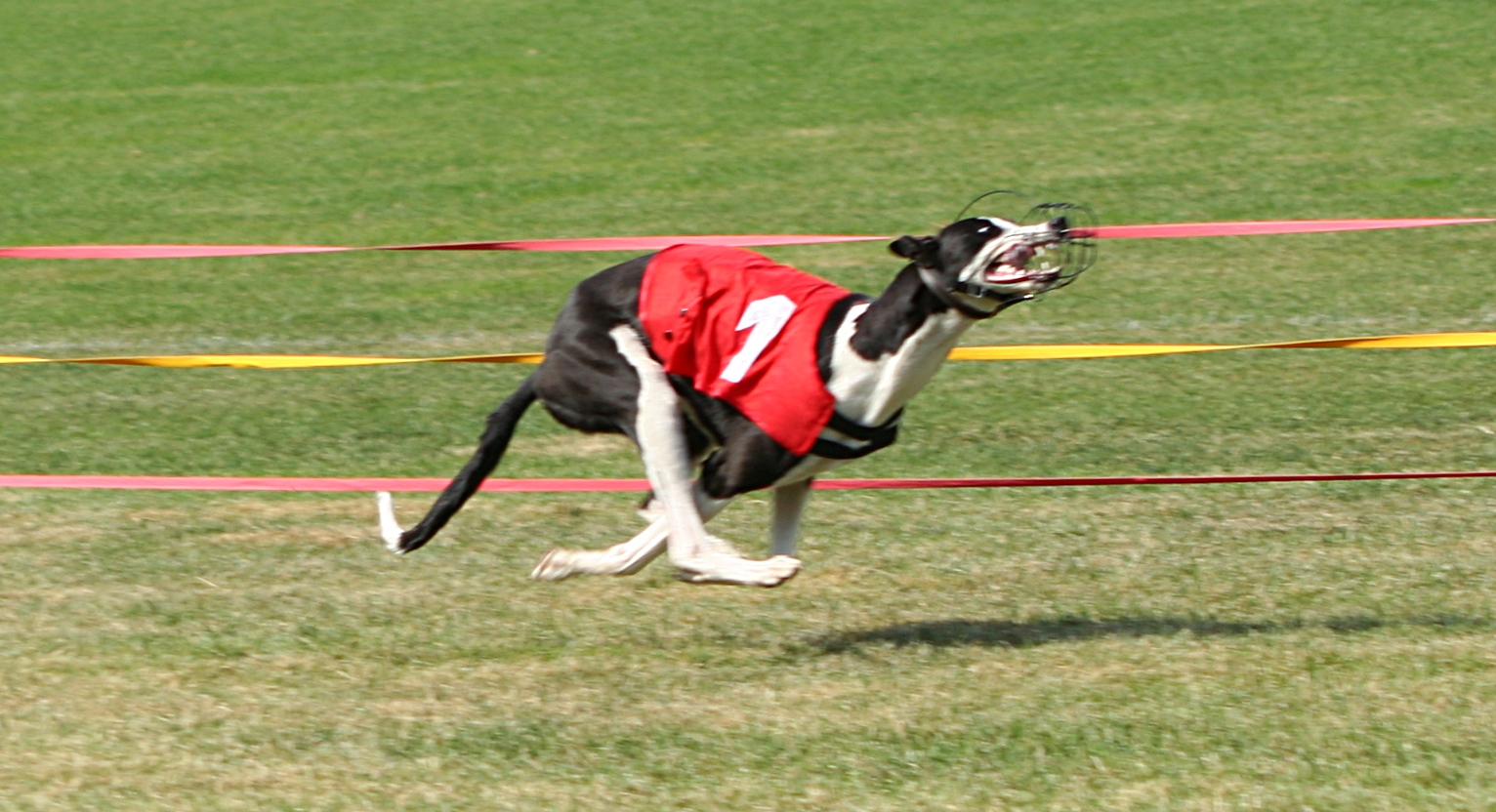
Double Suspension Gallop
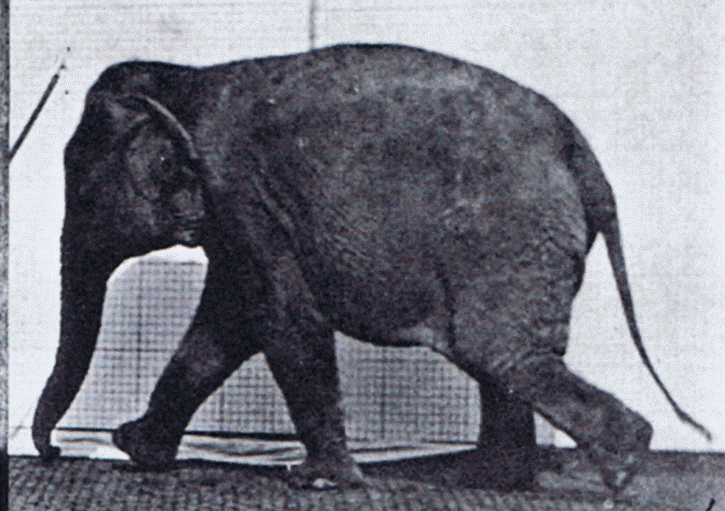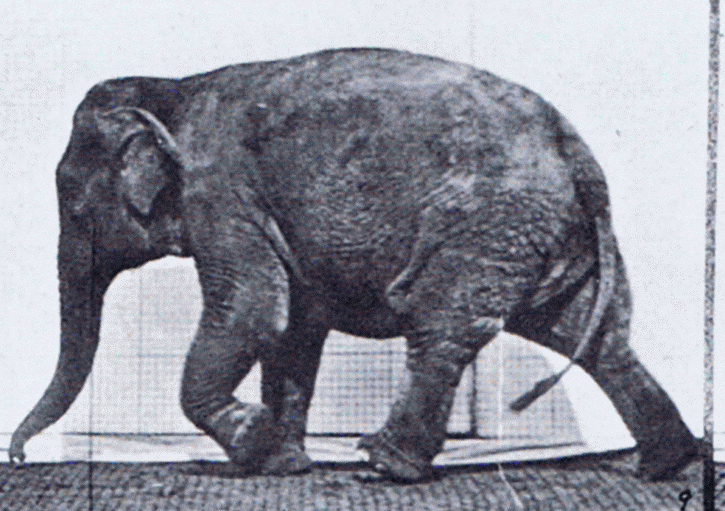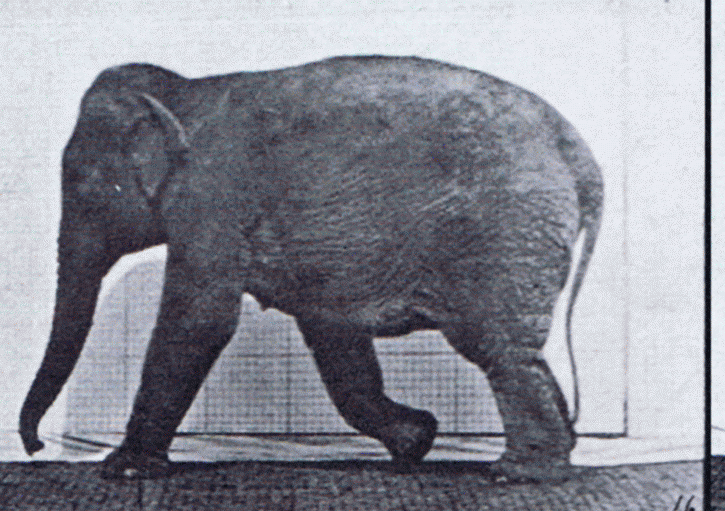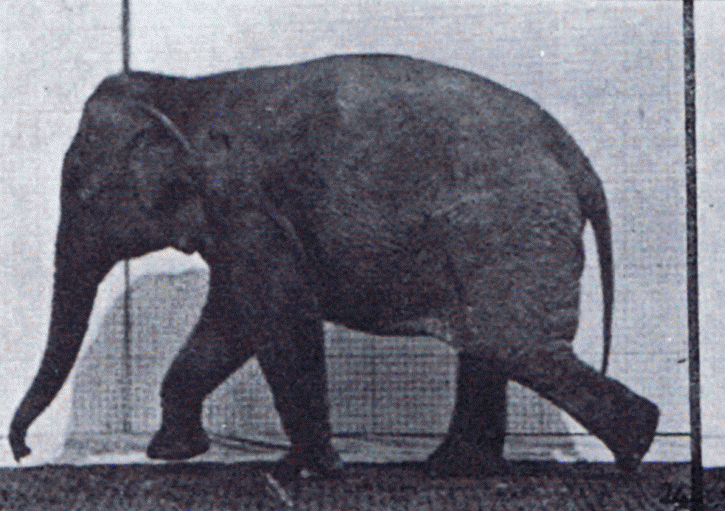
The gait of a dog is its quality of movement. It is given a great deal of importance in the breed standard of some breeds, of lesser importance in other standards, and in some breeds gait is not described in the standard at all. A dog's gait is similar to a horse's. A dog judge must know the gait requirements in the Standard of the breed they are judging. The Miniature Pinscher, for example, ''must'' have what is called a ''hackney gait'', reminiscent of the gait of a horse. In working small breeds such as the Miniature Fox Terrier, a hackney gait is a serious or disqualifying fault. Types of gait ;Walk: Gaiting pattern in which three legs are in support of the body at all times, each foot lifting from the ground one at a time in regular sequence.AKC Glossary. Retrieved from https://www.akc.org/about/glossary.cfm. ;Amble: A relaxed, easy gait in which the legs on either side move almost, but not quite, as a pair. Often seen as the transition movement between the walk and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against it (which can apply to walking while underwater as well as on land). Due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyhound Racing 2 Amk
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Since the rise in large-scale adoption of retired racing Greyhounds, the breed has seen a resurgence in popularity as a family pet. Greyhounds are defined as a tall, muscular, smooth-coated, "S-shaped" type of sighthound with a long tail and tough feet. Greyhounds are a separate breed from other related sighthounds, such as the Italian greyhound. The Greyhound is a gentle and intelligent breed whose combination of long, powerful legs, deep chest, flexible spine, and slim build allows it to reach average race speeds exceeding . The Greyhound can reach a full speed of within , or six strides from the boxes, traveling at almost for the first of a race. Appearance Males are usually tall at the withers, and weigh on average . Females tend to be smaller, with shoulder heights ranging from and weights from , although weights can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Health
The health of dogs is a well studied area in veterinary medicine. Dog health is viewed holistically; it encompasses many different aspects, including disease processes, genetics, and nutritional health, for example. Infectious diseases that affect dogs are important not only from a veterinary standpoint, but also because of the risk to public health; an example of this is rabies. Genetic disorders also affect dogs, often due to selective breeding to produce individual dog breeds. Due to the popularity of both commercial and homemade dog foods, nutrition is also a heavily studied subject. Diseases Some diseases and other health problems are common to both humans and dogs; others are unique to dogs and other animals. Dogs are susceptible to various diseases; similarly to humans, they can have diabetes, epilepsy, cancer, or arthritis. Timely vaccination can reduce the risk and severity of an infection. The most commonly recommended viruses to vaccinate dogs against are: * Rabie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sighthound
Sighthounds, also called gazehounds, are a Dog type, type of dog, hounds that hunt primarily by sight and speed, rather than by scent and endurance as scent hounds do. Appearance These dogs specialize in pursuing prey, keeping it in sight, and overpowering it by their great speed and agility. They must be able to detect motion quickly, so they have keen vision. Sighthounds must be able to capture fast, agile prey such as deer, and hares, so they have a very flexible back and long legs for a long stride, a deep chest to support an unusually (compared to other dogs) large heart, very efficient lungs for both Anaerobic exercise, anaerobic and Aerobic exercise, aerobic sprints, and a lean, wiry body to keep their weight at a minimum. Sighthounds have unique anatomical and physiological features likely due to intentional selection for hunting by speed and sight; laboratory studies have established reference intervals for hematology and serum biochemical profiles in sighthounds, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamstring
In human anatomy, a hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in between the hip and the knee (from medial to lateral: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris). The hamstrings are susceptible to injury. In quadrupeds, the hamstring is the single large tendon found behind the knee or comparable area. Criteria The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are: # Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity. # Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint, in the tibia or in the fibula. # Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve. # Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint. Those muscles which fulfill all of the four criteria are called true hamstrings. The adductor magnus reaches only up to the adductor tubercle of the femur, but it is included amongst the hamstrings because the tibial collateral ligament of the knee joint morphologically is the degenerated tendon of this muscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
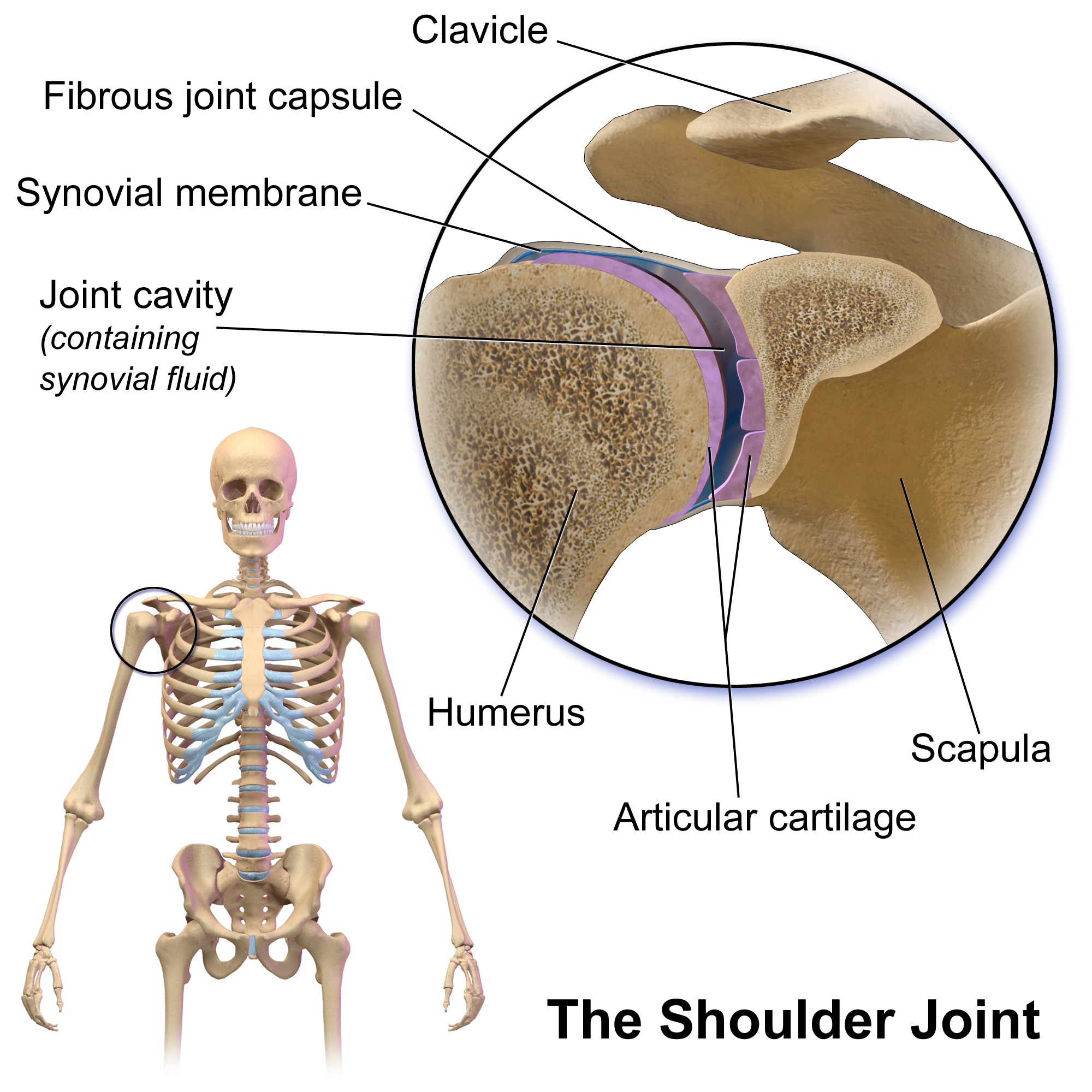
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a thin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent collapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loin
The loins, or lumbus, are the sides between the lower ribs and pelvis, and the lower part of the back. The term is used to describe the anatomy of humans and quadrupeds, such as horses, pigs, or cattle. The anatomical reference also applies to particular cuts of meat, including tenderloin or sirloin steak. Human anatomy In human anatomy the term "loin" or "loins" refers to the side of the human body below the rib cage to just above the pelvis. It is frequently used to reference the general area below the ribs. While the term "loin" is generally not used in medical science, some disorders do include the term. The lumbar region of the spinal column is located in the loin area of the body. Society and culture In contemporary usage the term appears primarily in two contexts: where loins are "girded" in preparation for a challenge, or else euphemistically referring to human genitals. In literature or poetry, to feel a "stirring" in one's loins may suggest sexual excitement. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szombierki Greyhound 18
Szombierki (german: Schomberg) is a district of Bytom, Poland, located in the southern part of the city. Szombierki Heat Power Station and Szombierki Coal Mine (KWK Szombierki), both recognized as important historical and industrial monuments, are located here. In 2004 the winding tower "Krystyna" of the former coal mine KWK Szombierki and its surroundings was listed as a National Heritage Site. In 2009 the tower and the Power Station were voted as two of the "Seven Architectural Wonders of the Silesian Voivodeship." In 2013 the Power Station was also recognized as a national heritage site. The village of Szombierki was first mentioned in documents in 1369. In 1768, the first coal mine was established in Szombierki. However, it was closed around 1820. During World War II, Nazi Germany held prisoners of war in the settlement. POWs worked as forced labourers in the local coal mine, which formed the E72 subcamp of the Stalag VIII-B/344 prisoner of war camp. Szombierki is home t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breed Standard
In animal husbandry or animal fancy, a breed standard is a description of the characteristics of a hypothetical or ideal example of a breed. The description may include physical or morphological detail, genetic criteria, or criteria of athletic or productive performance. It may also describe faults or deficiencies that would disqualify an animal from registration or from reproduction. The hypothetical ideal example may be called a "breed type". Breed standards are devised by breed associations or breed clubs, not by individuals, and are written to reflect the use or purpose of the species and breed of the animal. Breed standards help define the ideal animal of a breed and provide goals for breeders in improving stock. In essence a breed standard is a blueprint for an animal fit for the function it was bred - i.e. herding, tracking etc. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (conformation Point)
In animal breed standards, a fault is an aspect of appearance or temperament that is considered detrimental to the breed type of the animal's breed. In dogs, faults have to do with the externally observable qualities of the dog such as appearance, movement, and temperament. Qualities separately tested such as tests for ability in specific work or sports, tests for genetic health, tests for general health or specific inherited disease, or any other specific tests for characteristics that cannot be directly observed are not referred to as ''faults''. Minor faults may or may not have anything to do with the individual dog's ability to work or suitability as a pet. Defining specific faults Faults are formally defined in reference to the breed standard of the specific dog breed, and, due to the extreme variability of the dog ("Phenotypic variation among dog breeds, whether it be in size, shape, or behavior, is greater than for any other animal"), a single set of faults cannot be generic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature Fox Terrier
The Miniature Fox Terrier is a small, fine, lightweight working terrier developed as a hunting dog and vermin router. It is known colloquially in its native Australia as the “Mini Foxie”. Appearance A balanced, smoothly-muscled dog breed, the Miniature Fox Terrier has a small sized, distinctive head with erectile ears that can stand straight up or fold at the tips. Another distinguishing feature is its articulate, oval-shaped foot - a feature found in very few small breeds of dog. The breed standard has always allowed for the dog's tail to be Docking (dog), docked or undocked, however owners need to be aware of and obey local laws in this regard. Natural bobtails are known to occur. There are only three permitted colour combinations: black & white, tan & white, and black, tan & white. The coat of the Miniature Fox Terrier is always short and fine. Weight is 3.5 to 5.5 kilograms (8 to 12 lbs) and height at the withers is 9.5 to 12.0 inches (24 cm to 30.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |